Admission control
The admission control feature controls the number of concurrent queries running on the cluster, which avoids out-of-memory issues on busy clusters.
By: Manish Maheshwari, Data Architect and Data Scientist at Cloudera, Inc.
Once the limit that you set in admission control has been reached, subsequent queries are queued and wait for running queries to finish before they run. You can configure the amount of time that queries can wait. Using admission control, you can set the default memory that can be used by each query in a pool. If you do not set a default memory limit, Impala uses heuristics based on table and column statistics to determine the amount of memory that each query requires.
Cloudera recommends that you set the number of concurrently running queries between 40-60. This loosely corresponds to the number of threads on each of the Impala daemons.
Best practices for using admission control are:
- Ensure that admission control is enabled by checking the following
setting in Cloudera Manager:

-
Ensure that the Minimum Query Memory Limit and the Maximum Query Memory Limit, or the Default Query Memory Limit is set for all pools:
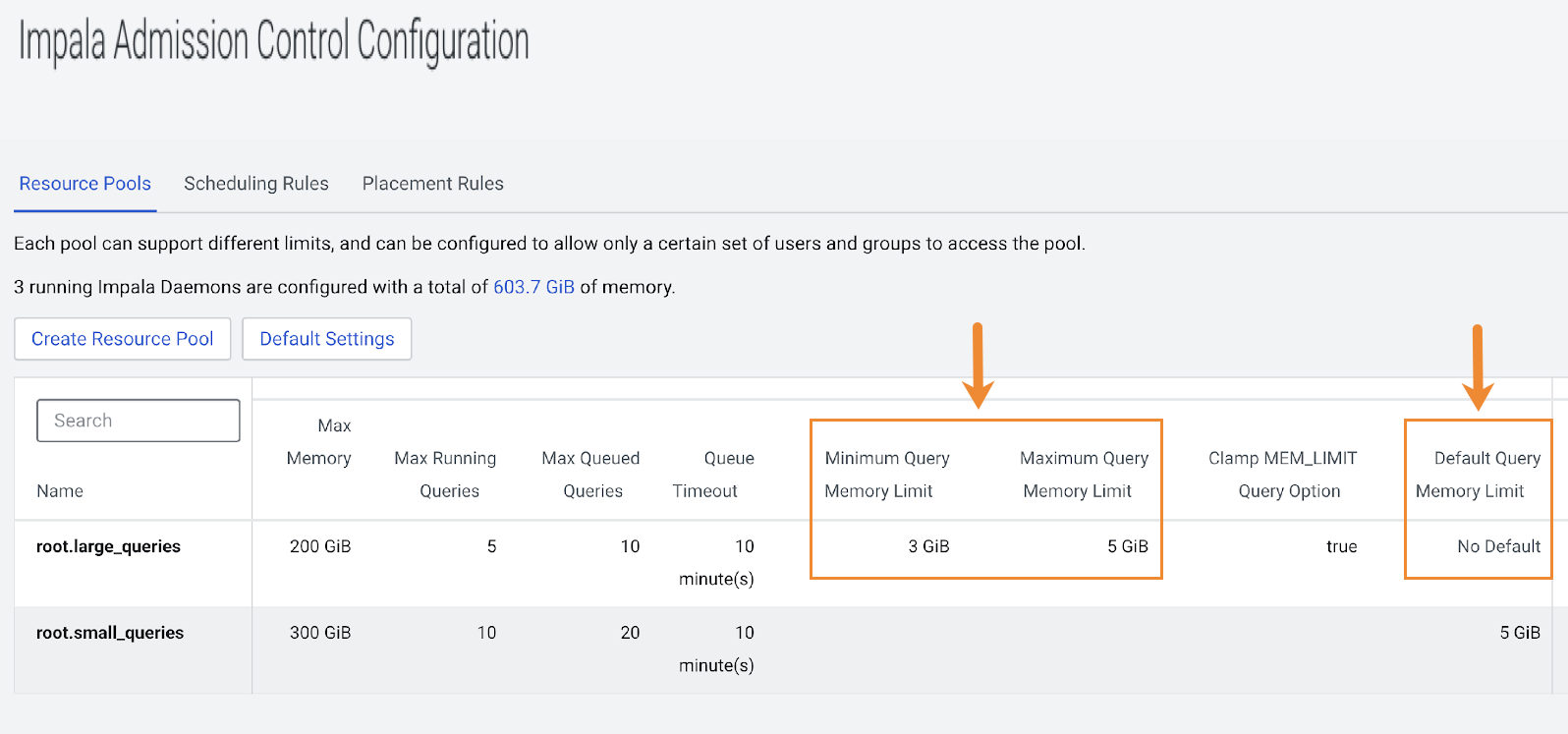
You can check these settings in Cloudera Manager. From the Cloudera Manager home page, click Clusters in the left navigation tree and select Impala Admission Control Configuration:
In CDH 6.2, admission control settings have also been added to the Impala Web UI. See Troubleshooting with the Impala Web UI in the product documentation for details.
- If the default memory limit is set, query profiles show the following message:

-
If the default memory limit is set too low and the query times out and you receive a “Memory limit exceeded” error message, rerun the query using the
SET MEM_LIMIToption. For example:SET MEM_LIMIT = 3gb;For details about this SET statement, see MEM_LIMIT Query Option.
- The total maximum memory set across all of the pools should be equal to the total memory that is allocated to the Impala service.
