Running SQL Stream jobs
Every time you run an SQL statement in the SQL Stream console, it becomes a job and runs on the deployment as a Flink job. You can manage the running jobs using the Jobs tab on the UI.
There are two logical phases to run a job:
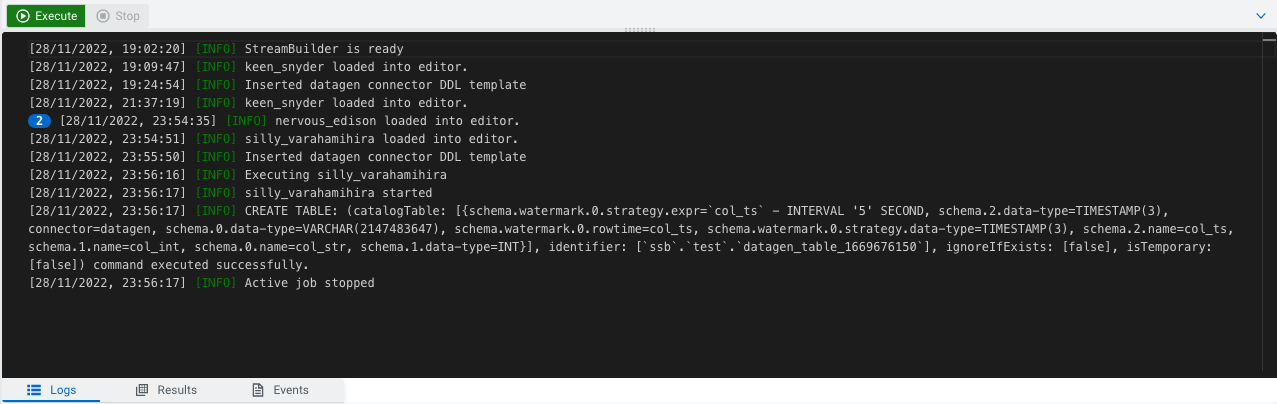
- Parse: The SQL is parsed and checked for validity and then compared against the virtual table schema(s) for correct typing and key/columns.
- Execution: If the parse phase is successful, a job is dynamically created, and runs on an open slot on your cluster. The job is a valid Flink job.
- Make sure that you have registered a Data Source if you use the Kafka service on your cluster.
- Make sure that you have added Kudu, Hive or Schema Registry as a catalog if you use them for your SQL job.