Migrating ACLs from Key Trustee KMS to Ranger KMS
Perform the procedures in this section to migrate ACLs from Key Trustee Key Management Server (KMS) to Ranger KMS.
Key Trustee ACL evaluation
Before going into the details of how Key Trustee ACLs are evaluated, it is critical that you understand the key rules that the Key Trustee Key Management Server uses in performing this evaluation.
KMS ACL Flow Rules:
- The whitelist class bypasses
key.aclanddefault.key.aclcontrols. - The
key.acldefinitions override all default definitions.
Encryption key access is evaluated as follows:
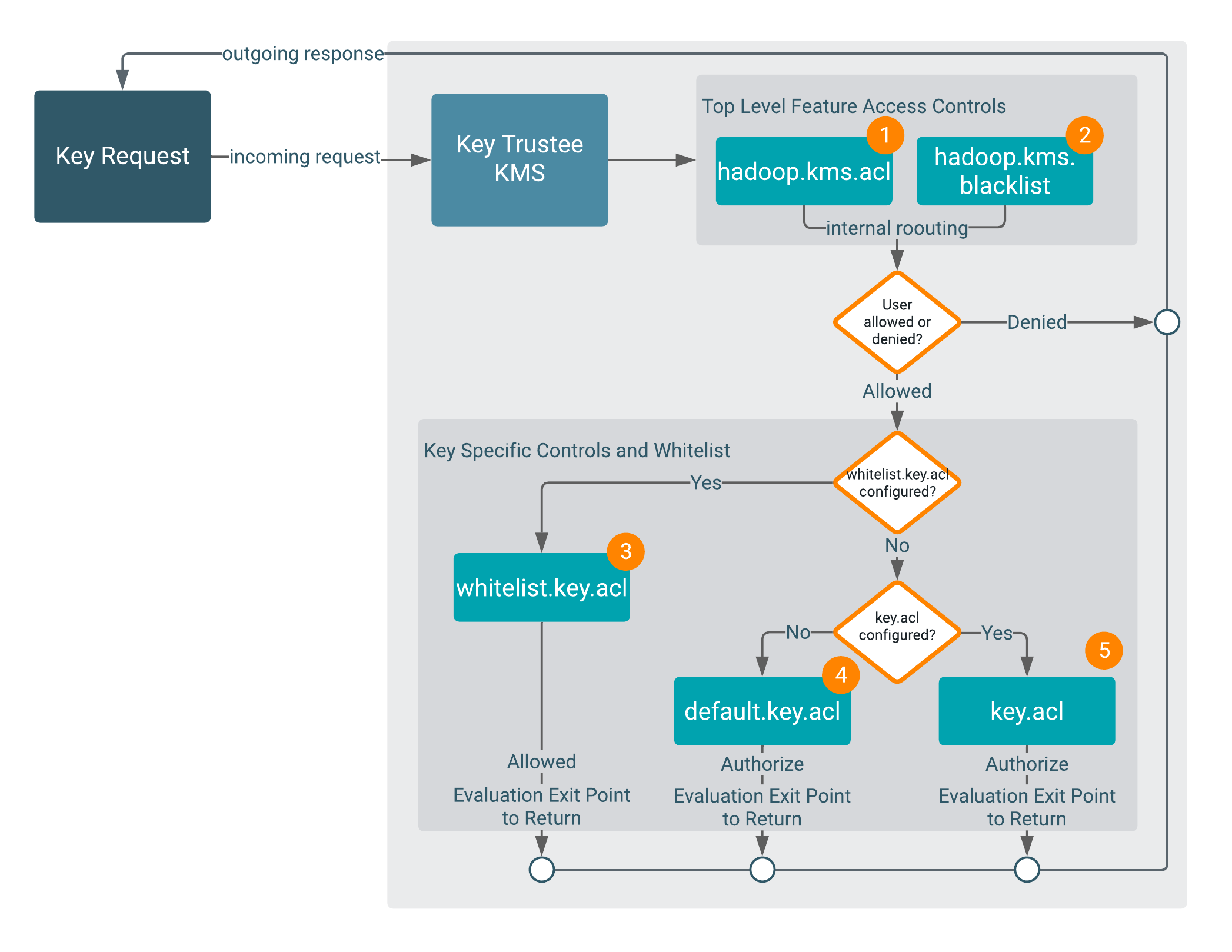
1 and 2
The KMS evaluates the hadoop.kms.acl.<OPERATION> and
hadoop.kms.blacklist.<OPERATION> classes to determine whether or not
access to a specific KMS feature or function is authorized.
In other words, a user must be allowed by
hadoop.kms.acl.<OPERATION>, and not be disallowed by
hadoop.kms.blacklist.<OPERATION>.
If a user is denied access to a KMS-wide operation, then the flow halts and
returns the result Denied.
If a user is allowed access to a KMS-wide operation, then the evaluation flow proceeds.
3
The KMS evaluates the whitelist.key.acl class.
The KMS ACL workflow evaluates the whitelist.key.acl.<OPERATION>, and
if the user is allowed access, then it is granted (Allowed) . If not, then
the flow continues with the evaluation.
4 and 5
The KMS evaluates the default.key.acl.<OPERATION> and
key.acl.<OPERATION> classes.
key.acl.KEY.<OPERATION>
class that matches the action the user is attempting to perform. If there is, it then
evaluates that value to determine whether or not the user can perform the requested
operation.Depending on the result of the Key Trustee ACL evaluation, controls are applied to the key
and results (Allowed or Denied).
Access evaluation with Ranger KMS policies
Access is evaluated with Ranger KMS policies as follows:
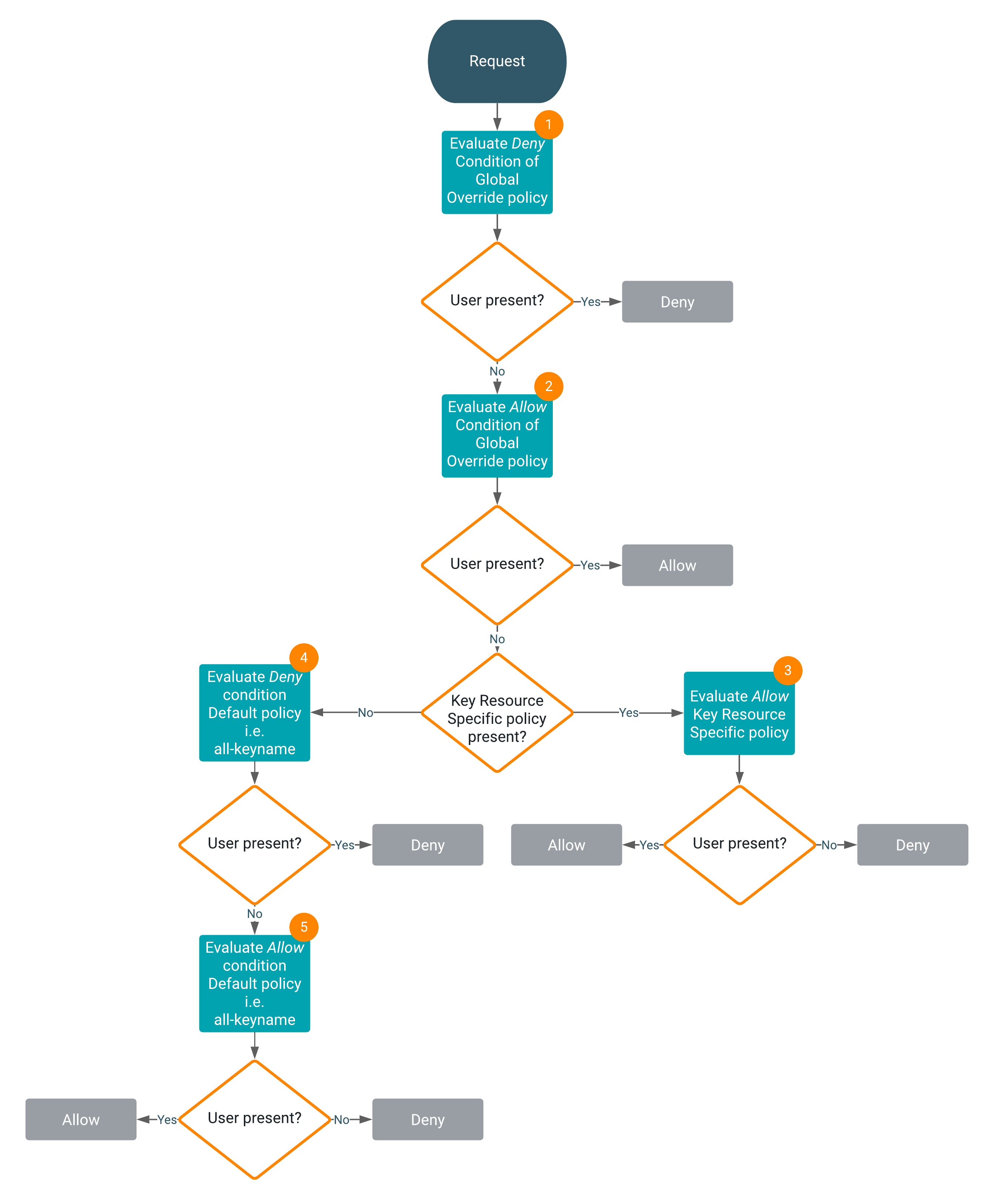
1
After the request is received, the Deny condition of the Global
Override policy is evaluated. If the user is present, the flow halts and returns the result
Deny. If the user is not present, the evaluation flow proceeds.
2
Now, the Allow condition of the Global Override policy is evaluated. If
the user is present, the flow halts and returns the result Allow. If the
user is not present, the evaluation flow proceeds.
3
If the Key Resource Specific policy is present, the Allow
condition of the Key Resource Specific policy is evaluated. If the user is not present, the
flow halts and returns the result Deny. If the user is present, the flow is
complete and returns the result Allow.
4
If the Key Resource Specific policy is not present, the Deny condition of
the Default policy, all-keyname, is evaluated. If the user is present, the flow halts and
returns the result Deny. If the user is not present, the evaluation flow
proceeds.
5
Now, the Allow condition of the Default policy, all-keyname, is evaluated.
If the user is not present, the flow halts and returns the result Deny. If
the user is present, the flow is complete and returns the result Allow.
