Using metadata for cluster governance
Concepts for collecting, creating, and using metadata.
What is Apache Atlas?
Atlas is a metadata management and governance system designed to help you find, organize, and manage data assets. Atlas creates “entities” or metadata representations of objects and operations in your data lake. You can add business metadata to these entities so you can use business vocabulary to make it easier to search for specific assets.

Apache Atlas uses metadata to create lineage relationships
Atlas reads the content of the metadata it collects to build relationships among data assets. When Atlas receives query information, it notes the input and output of the query and generates a lineage map that traces how data is used and transformed over time. This visualization of data transformations allows governance teams to quickly identify the source of data and to understand the impact of data and schema changes.
Adding to entity metadata makes searching easier
Atlas manages classifications and labels that you create and use to enhance the metadata for data assets. You can create and organize classifications and labels to use for anything from identifying data cleansing stages to recording user comments and insights on specific data assets. When you use classifications, the Atlas Dashboard makes it easy to search, group, report, and further annotate the entities you label. Classifications themselves can be organized into hierarchies to make them easier to manage.
Atlas also provides an infrastructure to create and maintain business ontologies to label your data assets. Atlas’ “glossaries” include “terms” so you can build agreed-upon lists for department- or organization-wide vocabulary to identify and manage data. Adding a term gives you a single-click report of entities identified by that term.
Apache Atlas architecture
Atlas runs as an independent service in a Hadoop environment. Many Hadoop data processing and storage services include Atlas add-ons that publish metadata for the services’ activities to a Kafka message topic. Atlas reads the messages and stores them in JanusGraph to model the relationships among entities. The datastore behind JanusGraph is HBase. Atlas stores a search index in Solr to take advantage of Solr’s search functionality.
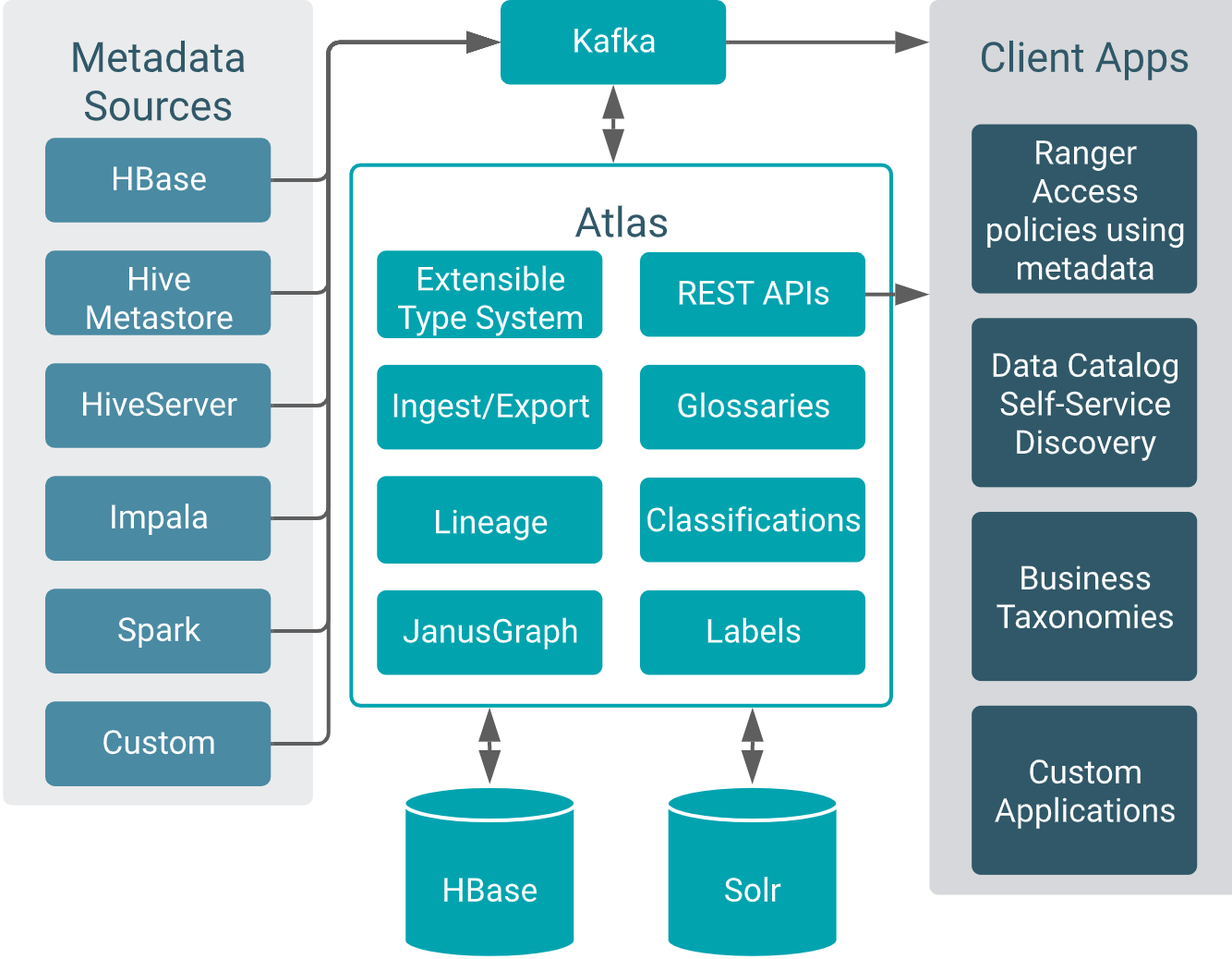
Pre-defined hooks exist for Hive, Impala, Kafka, NiFi, Spark, and Sqoop.
Atlas also provides “bridges” that import metadata for all of the existing data assets in a given source. For example, if you start Atlas after you’ve already created databases and tables in Hive, you can import metadata for the existing data assets using the Hive bridge. Bridges use the Atlas API to import the metadata rather than publishing messages to Kafka.
If you need a hook or bridge to automate collecting metadata from another source, use the Atlas Java API to create a custom Atlas addon.
