Discovering possible predicates
You can use Predicates (‘where’ clauses) to specify
filters on a wide range of aspects when querying metrics. In some cases, this large selection
makes it challenging to choose the right filters for the intended purpose. This topic describes a
way to find out more about applicable filters and values in the context of a specific
query.
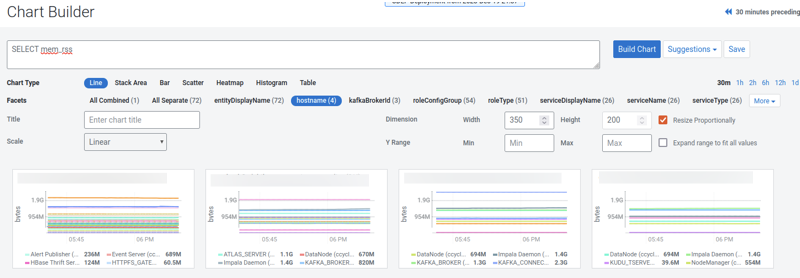
In a tsquery, the main way to filter results is by defining conditions on time series entity attributes. Like metrics, the set of applicable attributes are determined by the entity type(s) being queried. The Charting Time-Series Data topic describes this data model in more detail.
You can find more information in the following sections of the tsquery Language topic:
- Predicates: explains what can be used in
‘
where’ clauses, including and in addition to attributes. - Time Series Attributes: a subset of the attributes you can use, with a description for each.
- Time Series Entities and their Attributes: a subset of the time series entity types available, with the applicable attributes listed.
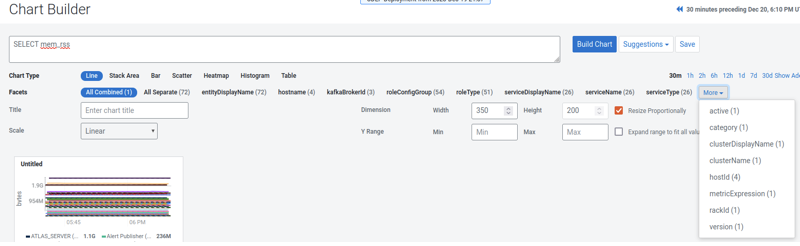
- Mapping of entity types to the metrics they have, as a JSON document:
GET /timeseries/schema(The response is large, approximately 50 MB.) This further clarifies the relationship between entity types, attributes, and metrics, while providing insight into the metrics applicable to each entity type. - A detailed explanation of attributes (similar to the Time Series Attributes table):
GET /timeseries/entityTypeAttributes. - Definitions of the entity types referred to in the schema document, along with applicable
attribute names (similar to the Time Series Entities and their Attributes table):
GET /timeseries/entityTypes
The results obtained from the API include all entity types and attributes tracked by the running cluster, including those added by service integrations.
