Security Levels
Securing a cluser requires a layered approach, applying the Pillars of Security to ensure data availability, integrity, and confidentiality. CDP Private Cloud offers four security levels, as security is no longer optional.
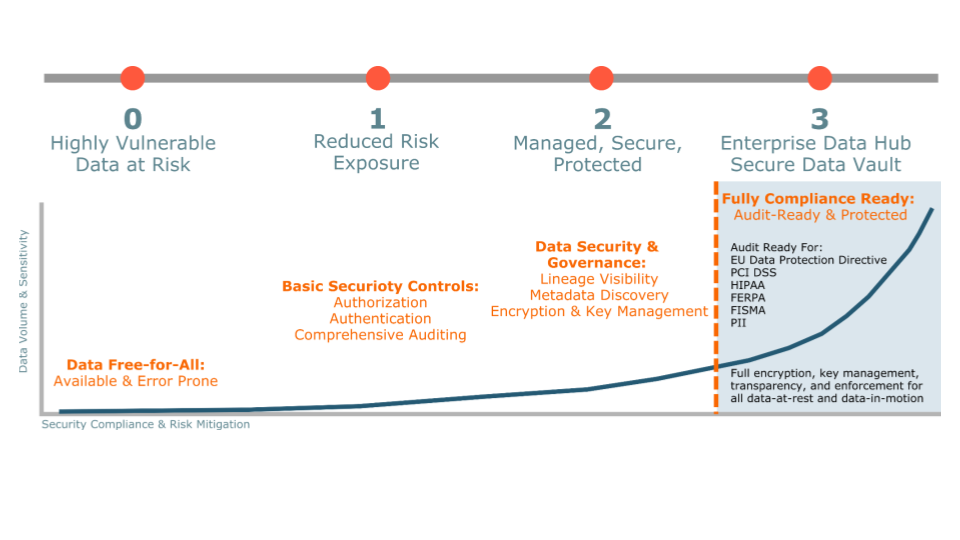
0 - Non-Secure
The cluster has no configured security. Clusters without security must not be used in production environments because they are highly vulnerable to all attacks and exploits. Cloudera does not support running an insecure environment.
1 - Minimally Secure
Minimally secure clusters are configured for authentication, authorization, and auditing. Authentication is first configured to ensure that users and services can only access the cluster after proving their identities. Authorization mechanisms are then applied to assign privileges to users and user groups. Auditing procedures keep track of who accesses the cluster.
2 - More Secure
Clusters that encrypt their sensitive data are more secure. These systems include a variety of steps, including key management, to ensure data is encrypted while in-transit.
Auditing has been set up for data governance to trace any data object’s lineage and verify its authenticity. It determines what people are doing with your data, and when they are doing it.
3 - Most Secure
The most secure clusters ensure that all data, both at-rest and in-transit, is encrypted and the key management system is fault-tolerant. Auditing mechanisms comply with industry, government, and regulatory standards such as PCI, HIPAA, GDPR, and NIST, and extend from the cluster to any integrated systems. Cluster administrators are well-trained, the security procedures are certified by an expert, and the cluster passes technical reviews.