Set up
You need to know how to use the Hive Warehouse Connector (HWC) with different programming languages and build systems. You find out where HWC binaries are located in CDP parcels and how a Spark application consumes the binaries.
Cloudera artifactory and HWC dependency
To pull the HWC dependency corresponding to a release, use the following artifactory:
https://repository.cloudera.com/artifactory/cloudera-repos
Use with Maven
To use HWC with maven, define the cloudera artifactory as a repository.
<repository>
<id>cloudera</id>
<name>cloudera</name>
<url>https://repository.cloudera.com/artifactory/cloudera-repos</url>
</repository>In the pom.xml of the project, add the dependency as shown in the following example:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.hortonworks.hive</groupId>
<artifactId>hive-warehouse-connector_2.11</artifactId>
<version>[***HWC VERSION***]</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>Use with Sbt
Add the Cloudera and Shibboleth repositories, and the HWC dependency to the build sbt as follows:
resolvers += "Cloudera repo" at "https://repository.cloudera.com/artifactory/cloudera-repos",
resolvers += "opensaml Repository" at "https://build.shibboleth.net/nexus/content/repositories/releases",
libraryDependencies += "com.hortonworks.hive" % "hive-warehouse-connector_2.11" % "[***HWC VERSION***]" % "provided",Dependency scope
Generally, you add HWC dependencies in provided scope unless there is a specific requirement to do otherwise. While running spark application, you can specify the HWC jar present in your distribution using the --jars option to spark-submit or spark-shell.
HWC binaries in CDP
HWC binaries are located within the appropriate directory in /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/. The directory contains the HWC jar, a python zip, and the R package. Use these binaries to launch Spark applications in Scala, Java, Python, or R.
For Spark 2, the files are available in /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hive_warehouse_connector/.
- hive-warehouse-connector-assembly-<version>.jar
- pyspark_hwc-<version>.zip
- SparklyrHWC-<version>
HWC binaries in Spark 3 parcel
HWC supports Spark 3 through CDS 3.3 Powered by Apache Spark, which is an add-on service for Cloudera Private Cloud Base and is distributed as a parcel.
The HWC binaries are located in /opt/cloudera/parcels/SPARK3/lib/spark3/hwc_for_spark3/. This directory contains HWC jar and a python zip. Use these binaries to launch Spark applications in Scala, Java, or Python.
The following files are in /opt/cloudera/parcels/SPARK3/lib/spark3/hwc_for_spark3/.
- hive-warehouse-connector-spark3-assembly-<version>.jar
- pyspark_hwc-spark3-<version>.zip
HWC configurations
Learn about the configurations that are required by Spark when using HWC. Setting HWC
configurations has been simplified. As a cluster administrator, you can specify the required
configurations in Cloudera Manager and then enable HWC by setting
spark.cloudera.useHWC=true. You can either add this property to
spark-defaults.conf to enable HWC for all Spark jobs or enable HWC
for a specific Spark job by using the --conf option in
spark-shell or spark-submit.
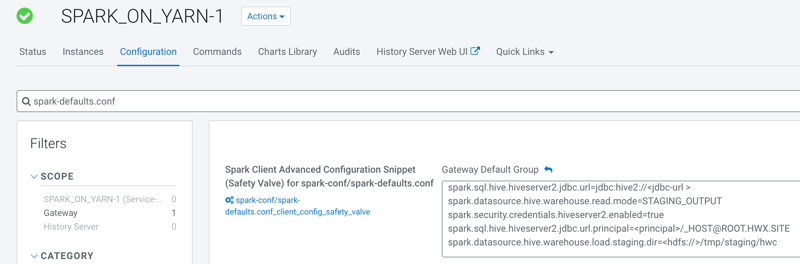
spark.sql.hive.hiveserver2.jdbc.url="jdbc:hive2://<jdbc-url>"spark.datasource.hive.warehouse.read.mode=<mode>spark.security.credentials.hiveserver2.enabled=truespark.sql.hive.hiveserver2.jdbc.url.principal=<principal>/_HOST@ROOT.HWX.SITEspark.datasource.hive.warehouse.load.staging.dir=<hdfs://>/tmp/staging/hwc
spark.cloudera.useHWC=true also adds all the jar files present in
/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hive_warehouse_connector/ to the Spark
classpath along with adding the following configurations to Spark configuration:spark.kryo.registrator=com.qubole.spark.hiveacid.util.HiveAcidKyroRegistratorspark.sql.extensions=com.hortonworks.spark.sql.rule.Extensions
[root@sim-hwc-1 hive_warehouse_connector]# spark-shell --conf spark.cloudera.useHWC=true --master yarn
Spark context Web UI available at http://sim-hwc-1.sim-hwc.root.hwx.site:4040
Spark context available as 'sc' (master = yarn, app id = application_1629916909355_0013).
Spark session available as 'spark'.
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/___/ .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 2.4.8.7.2.12.0-195
/_/
Using Scala version 2.11.12 (OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM, Java 1.8.0_232)
Type in expressions to have them evaluated.
Type :help for more information.
scala> val hive = com.hortonworks.hwc.HiveWarehouseSession.session(spark).build()
hive: com.hortonworks.spark.sql.hive.llap.HiveWarehouseSessionImpl = com.hortonworks.spark.sql.hive.llap.HiveWarehouseSessionImpl@5995ba6c
scala> hive.sql("select * from acidtable").show
+---+-----+----+-----+----+-----+
| id| name|col3| col4|col5| col6|
+---+-----+----+-----+----+-----+
| 1|name1| 2|name2| 3|name3|
| 4|name4| 5|name5| 6|name6|
+---+-----+----+-----+----+-----+
Optional HWC configurations
Optionally, you can set the following properties:
spark.datasource.hive.warehouse.write.path.strictColumnNamesMapping— Validates the mapping of columns against those in Hive to alert the user to input errors. Default = true.spark.sql.hive.conf.list— Propagates one or more configuration properties from the HWC to Hive. Set properties on the command line using the --conf option. For example:--conf spark.sql.hive.conf.list="hive.vectorized.execution.filesink.arrow.native.enabled=true;hive.vectorized.execution.enabled=true"
Do not attempt to set spark.sql.hive.conf.list programmatically.
Working with different languages
You use HWC APIs to perform basic read and write operations. You need to understand how to use HWC APIs with different languages. The following examples show basic capabilities that are covered in detail later in this documentation.
Use with Scala
import com.hortonworks.hwc.HiveWarehouseSession
import org.apache.spark.sql.{SaveMode, SparkSession}
object HWCApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("HWCApp").enableHiveSupport.getOrCreate
val hwc = HiveWarehouseSession.session(spark).build
// create sample data
val tvSeries = createSampleDataDf(spark)
val tableName = "tv_series"
hwc.dropTable(tableName, true, true)
println(s"=======Writing to hive table - $tableName via HWC=======")
// write to hive table via HWC
tvSeries.write.format(HiveWarehouseSession.HIVE_WAREHOUSE_CONNECTOR)
.option("table", tableName)
.mode(SaveMode.Append).save
println(s"=======Reading hive table $tableName via HWC=======")
// Read via HWC
hwc.sql(s"select * from $tableName").show(truncate = false)
hwc.close()
spark.stop
}
private def createSampleDataDf(spark: SparkSession) = {
spark.sql("drop table if exists tv_series_dataset")
spark.sql("create table tv_series_dataset(id int, name string, genres string, rating double) using orc")
spark.sql("insert into tv_series_dataset values " +
"(1, 'Chernobyl', 'Drama|History|Tragedy|Science', 9.4), " +
"(2, 'Westworld', 'Sci-fi', 8.6), (3, 'Sense8', 'Sci-fi', 8.3), " +
"(4, 'Person of Interest', 'Drama|Sci-fi', 8.4), " +
"(5, 'Its okay to not be okay', 'Drama', 8.7), " +
"(6, 'Daredevil', 'Action|Sci-fi', 8.6), " +
"(7, 'Money Heist', 'Drama|Thriller', 8.3), " +
"(8, 'Breaking Bad', 'Crime|Drama', 9.5)")
spark.sql("select * from tv_series_dataset")
}
Use with Java
The following Java code is equivalent to the scala code above.
import com.hortonworks.hwc.HiveWarehouseSession
import org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset;
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SaveMode;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession;
public class HWCApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("HWCApp").enableHiveSupport().getOrCreate();
// HiveWarehouseSession creation
HiveWarehouseSession hwc = HiveWarehouseBuilder.session(spark).build();
// create sample data
Dataset<Row> tvSeries = createSampleDataDf(spark);
String tableName = "tv_series";
hwc.dropTable(tableName, true, true);
System.out.println("=======Writing to hive table - " + tableName + " via HWC=======");
// write data to hive table via HWC
tvSeries.write().format(HiveWarehouseSession.HIVE_WAREHOUSE_CONNECTOR)
.option("table", tableName)
.mode(SaveMode.Append).save();
System.out.println("=======Reading hive table - " + tableName + " via HWC=======");
// read hive table as dataframe using HWC
hwc.sql("select * from " + tableName).show(false);
hwc.close();
spark.stop();
}
private static Dataset<Row> createSampleDataDf(SparkSession spark) {
spark.sql("drop table if exists tv_series_dataset");
spark.sql("create table tv_series_dataset(id int, name string, genres string, rating double) using orc");
spark.sql("insert into tv_series_dataset values " +
"(1, 'Chernobyl', 'Drama|History|Tragedy|Science', 9.4), " +
"(2, 'Westworld', 'Sci-fi', 8.6), (3, 'Sense8', 'Sci-fi', 8.3), " +
"(4, 'Person of Interest', 'Drama|Sci-fi', 8.4), " +
"(5, 'Its okay to not be okay', 'Drama', 8.7), " +
"(6, 'Daredevil', 'Action|Sci-fi', 8.6), " +
"(7, 'Money Heist', 'Drama|Thriller', 8.3), " +
"(8, 'Breaking Bad', 'Crime|Drama', 9.5)");
return spark.sql("select * from tv_series_dataset");
}
}Launching a Java or Scala app
After packaging the app in a jar, launch the app using standard Spark syntax for launching applications. Provide HWC jar from the distribution. The Spark application can be launched as follows:
spark-submit --jars /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hive_warehouse_connector/hive-warehouse-connector-assembly-<version>.jar \
--class com.cloudera.HWCApp \
...More spark/HWC confs...
...More spark/HWC confs...
/path-to-jar/hwc-app.jar Use with Python
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark_llap import HiveWarehouseSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.enableHiveSupport().appName("hwc-app").getOrCreate()
hwc = HiveWarehouseSession.session(spark).build()
tableName = "tv_series"
hwc.dropTable(tableName, True, True)
tvSeries = spark.createDataFrame([
(1, "Chernobyl", "Drama|History|Tragedy|Science", 9.4),
(2, "Westworld", "Sci-fi", 8.6),
(3, "Sense8", "Sci-fi", 8.3),
(4, "Person of Interest", "Drama|Sci-fi", 8.4),
(5, "It's okay to not be okay", "Drama", 8.7),
(6, "Daredevil", "Action|Sci-fi", 8.6),
(7, "Money Heist", "Drama|Thriller", 8.3),
(8, "Breaking Bad", "Crime|Drama", 9.5)
], ["id", "name", "genres", "rating"])
print("=======Writing to hive table - " + tableName + " via HWC=======")
# write to hive table via HWC
tvSeries.write.format(HiveWarehouseSession.HIVE_WAREHOUSE_CONNECTOR).option("table", tableName).mode("append").save()
print("=======Reading hive table - " + tableName + " via HWC=======")
# Read via HWC
hwc.sql("select * from " + tableName).show()
hwc.close()
spark.stop()Launching a Python app
After getting the python code ready, launch it using spark-submit. Provide the HWC jar and HWC python zip as follows:
spark-submit --jars /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hive_warehouse_connector/hive-warehouse-connector-assembly-<version>.jar \
--py-files /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hive_warehouse_connector/pyspark_hwc-<version>.zip \
...More spark/HWC confs...
...More spark/HWC confs...
/path-to-python-app/hwc-app.pyUse with Sparklyr
You can access Hive tables through R by loading the sparklyr library along with the SparklyrHWC package available in /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hive_warehouse_connector/, which can be used to trigger HWC APIs from R.
library(sparklyr)
library(SparklyrHWC, lib.loc = c(file.path(“<path to SparklyrHWC>")))
#Set env variables
Sys.setenv(SPARK_HOME = "/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/spark/")
Sys.setenv(HADOOP_HOME = "/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hadoop")
#Configurations needed to use spark-acid and related configurations.
config <- spark_config()
config$spark.sql.hive.hiveserver2.jdbc.url="jdbc:hive2://<url>:10000/default"
config$spark.datasource.hive.warehouse.user.name="hive"
config$spark.hadoop.hive.metastore.uris="thrift://<url>:9083"
config$spark.sql.extensions="com.hortonworks.spark.sql.rule.Extensions"
config$spark.kryo.registrator="com.qubole.spark.hiveacid.util.HiveAcidKyroRegistrator"
config$spark.datasource.hive.warehouse.read.mode="DIRECT_READER_V2"
#Build HWC session
hs <- build(HiveWarehouseBuilder.session(sc))
#Use database
sparklyr::sdf_sql(sc,"use test")
#Reading a managed table using spark acid direct-reader
intDf <- sparklyr::spark_read_table(sc, 'emp_hwc')
#Converts SparkDataframe to R dataframe
sparklyr::sdf_collect(intDf1)
#Writing into a managed table
#Read first table
intDf <- sparklyr::spark_read_table(sc, 'emp_hwc')
#read second table
intDf1 <- sparklyr::spark_read_table(sc, 'emp_overwrite')
#Commit transaction if read using spark-acid
commitTxn(hs)
#Append the second table, to the first.
SparklyrHWC::spark_write_table('emp_hwc',intDf1,'append')
#Overwrite the first table with the second table.
SparklyrHWC::spark_write_table('emp_hwc',intDf1,'overwrite')
#Using HWC Api’s
#create a table from existing table
SparklyrHWC::executeUpdate(hs,"create table hwc1 as select * from 'emp_hwc'")
#Execute query
hwcDf <- SparklyrHWC::executeQuery(hs, "select * from hwc1")
#convert into R dataframe.
hwcSdf <- sparklyr::sdf_copy_to(sc, hwcDf)