Learn how to configure a custom CREATE TABLE statement that Sqoop uses during the
Hive table creation process. For example, if you have configured Sqoop to use the CREATE
EXTERNAL TABLE statement, then external tables are created by default during the table
creation
process.
You can configure the required property either through
Cloudera Manager or by using the --hive-create-table-statement argument
in your Sqoop import command.
- Order of precedence
- The configuration set through the Sqoop argument in the command line takes
precedence over the configuration specified through Cloudera Manager.
-
If you are specifying the custom
CREATE TABLE statement
through Cloudera Manager, perform the following steps:
-
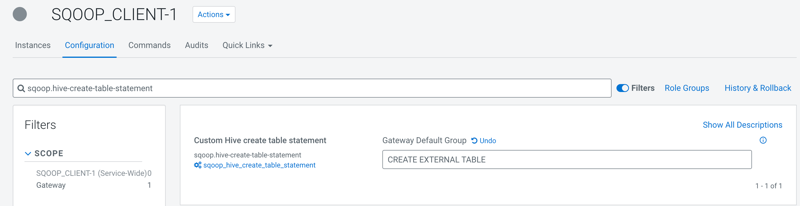
In Cloudera Manager, click Clusters and then
select the SQOOP_CLIENT-1 service.
-
From the Sqoop service, go to the Configuration
tab and search for
sqoop.hive-create-table-statement.
-
Enter the custom
CREATE TABLE statement.
-
Click Save Changes.
-
If you are specifying the custom
CREATE TABLE statement
through the Sqoop argument, specify the required statement using the
--hive-create-table-statement argument while constructing
the Sqoop import command.
/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/bin/sqoop import \
-Dsqoop.beeline.env.preserve=KRB5CCNAME \
--connection-manager org.apache.sqoop.manager.MySQLManager \
--connect jdbc:mysql://db.foo.com:3306/employees \
--username [***USERNAME***] \
--password [***PASSWORD***] \
--table employees \
--warehouse-dir /user/hrt_qa/test-sqoop \
--hive-import \
--delete-target-dir \
--hive-overwrite \
--hive-create-table-statement "CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE"