Configuring audit filters in Ranger Admin Web UI
You can configure audit filter conditions for each service, using the Create/Edit Service option.
You can stop certain audit logs from being sent to destinations like SOLR and HDFS by setting up audit filters for a service using the Ranger Admin Web UI.
- In the , click Add New Service or Edit (existing service).
-
On Create/Edit Service, scroll down to Audit
Filters.
- For a service, the following audit filter is used to capture all ALLOWED
audits for user
systest: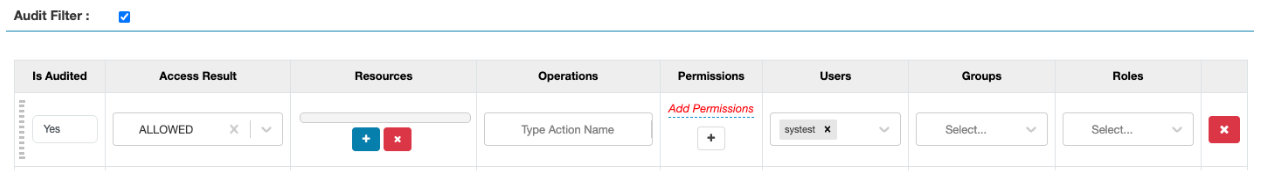
- The following filter specifies all DENIED audits to be audited:
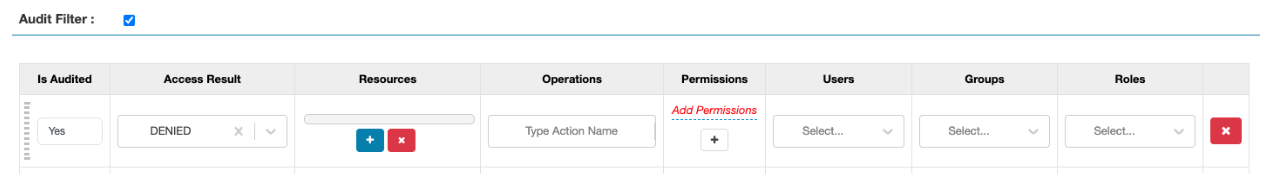
- The following is an example where all operations for users
kafkaandrangertagsyncare NOT audited, configured for a Kafka service: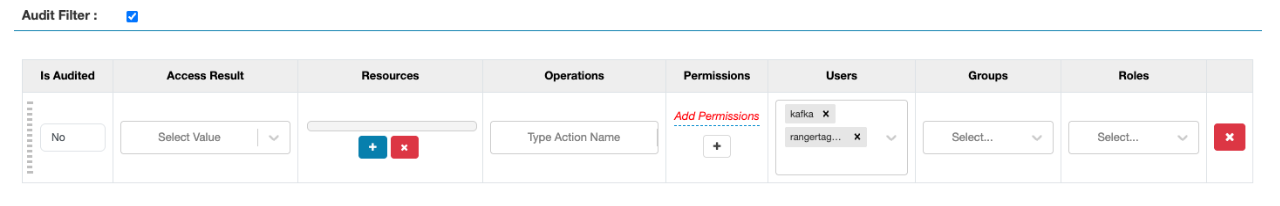
- Audit filter evaluation order
- Audit Filters, implemented as Ranger Policies, determine whether to audit an authorization request after it is processed by Tag/Resource-based Ranger policies. After an Audit Filter condition is fulfilled and executed for a request, no other audit filters are evaluated. If the evaluation dictates that the authorization request should be audited, an audit record is then added to the designated audit destination(s).
- Audit filters with REST APIs
- Audit filters can be configured through REST when creating or updating a
service as well. The following are examples where you can use JSON to
configure audit filters:
- Audit all denied accessesThe following audit filter specifies that any access with
accessResult = DENIEDwill be audited:{ "accessResult": "DENIED", "isAudited": true } - Do not audit access to path
/unauditedThe following audit filter specifies that access to the resource path/unaudited(recursively) will not be audited:{ "resources": { "path": { "values": ["/unaudited"], "isRecursive": true } }, "isAudited": false } - Do not audit access to database
sys, tabledump, by useruser2The following audit filter specifies that access to resource database=> sys table=> dump by user “user2” will not be audited:{ "resources": { "database": { "values": ["sys"] }, "table": { "values": ["dump"] } }, "users": ["user2"], "isAudited": false } - Do not audit actions
listStatusandgetfileinfowith access typeexecuteThe following audit filter specifies that access result in actions => listStatus, getfileInfo and accessType => execute will not be audited:{ "actions": ["listStatus", "getfileinfo"], "accessTypes": ["execute"], "isAudited": false } - Do not audit access by user
superuser1and groupsupergroup1The following audit filter specifies that access by user "superuser1" and group "supergroup1" will not be audited:{ "users": ["superuser1"], "groups": ["supergroup1"], "isAudited": false } - Do not audit access to any resource
tagged as
NO_AUDITThe following audit filter specifies that access to any resource tagged asNO_AUDITwill not be audited:{ "resources": { "tag": { "values": ["NO_AUDIT"] } }, "isAudited": false }
Above are examples of individual filters. You can apply them together in JSON when using REST to create/update a service as well.
- Audit all denied accesses
