How replication policies work
In Cloudera Replication Manager, you create replication policies to establish the rules you want applied to your replication jobs.
The policy rules you set can include which cluster is the source and which is the destination, what data is replicated, what day and time the replication job occurs, the frequency of job runs, and bandwidth restrictions.
The first time you run a job (an instance of a policy) with data that has not been previously replicated, the Cloudera Replication Manager creates a new folder or database and bootstraps the data. During a bootstrap operation, all data is replicated from the source cluster to the destination. As a result, the initial execution of a job can take a significant amount of time, depending on how much data is being replicated, network bandwidth, and so on. So you should plan the bootstrap operation accordingly.
After the bootstrap operation succeeds, an incremental data replication is automatically performed. This job synchronizes, between the source and destination clusters, any events that occurred during the bootstrap process. After the data is synchronized, the replicated data is ready for use on the destination. Data is in a consistent state only after incremental replication has captured any new changes that occurred during bootstrap.
Subsequent replication jobs from the same source location to the same target on the destination are incremental, so only the changed data is copied.
When a bootstrap operation is interrupted, such as due to a network failure or an unrecoverable error, the Cloudera Replication Manager does not retry the job instead it runs the job at the next scheduled interval, if available. Therefore, if the bootstrap operation is interrupted, you must manually correct the issue and then run the policy.
When scheduling how often you want a replication job to run, you should consider the recovery point objective (RPO) of the data being replicated; that is, what is the acceptable lag time between the active site and the replicated data on the destination.
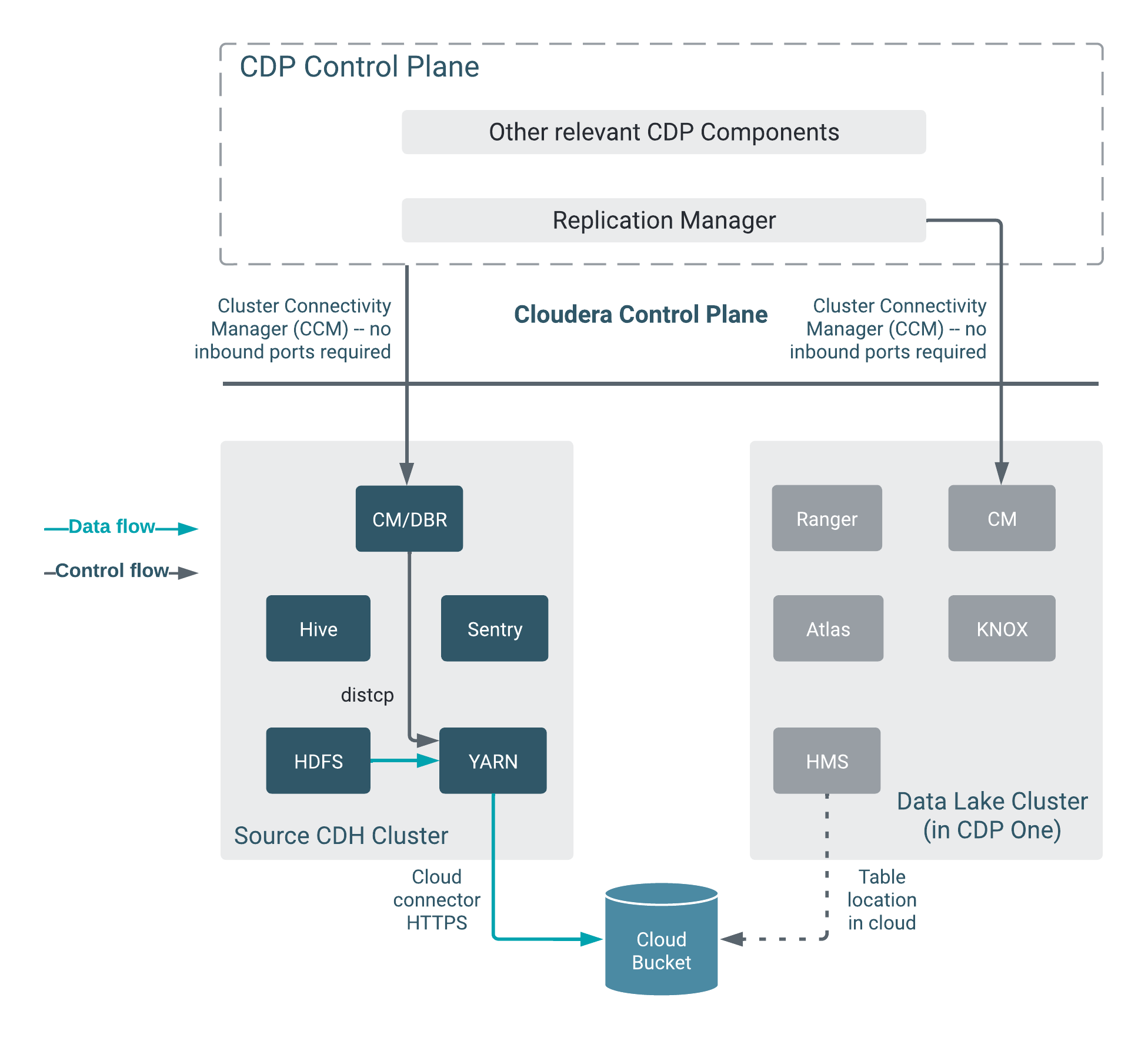
The following diagram shows the HDFS replication architecture:
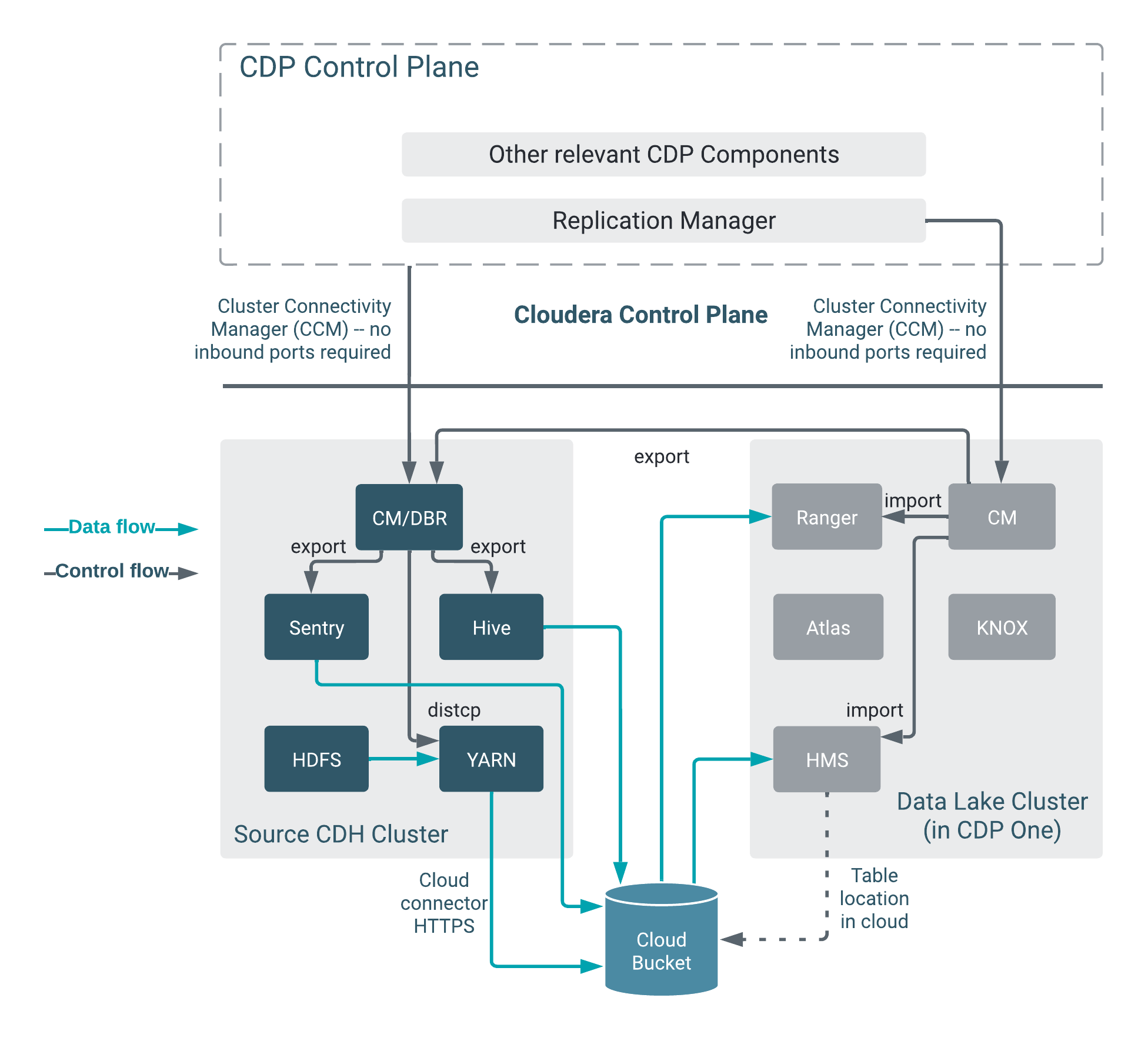
The following diagram shows the Hive replication architecture: