Examples of AI functions and UDFs
Learn to use the ai_generate_text_default function for tasks like analyzing Amazon book reviews. Also, see how to create custom UDFs to make AI text analysis easier and more efficient, enhancing your data workflows and insights.
Examples of using the built-in AI function
ai_generate_text_default(), the
following configuration parameters are set in the flagfile. Below are the required settings
for different AI models:- For Open
AI:
ai_endpoint: https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions ai_model: gpt-4 ai_api_key_jceks_secret: <your_jceks_key> - For llama model in Cloudera AI
Platform:
ai_endpoint: https://prod-long-running.ml-test.cloudera.site/serving-default/endpoints/llama-31-70b-instruct-8xl40s/v1/chat/completions ai_model: meta/llama-3.1-70b-instruct ai_api_key_jceks_secret: <your_jceks_key> ai_api_additional_platforms: cloudera.site
hadoop-core-site-default-warehouse, see Configuring the JCEKS
keystore location for Impala AI integration:- hadoop.security.credential.provider.path: jceks://s3a@test-bucket/jceks/keystore.jceks
ai_generate_text_default() to transform a prompt into a custom SQL
function.
> select ai_generate_text_default('hello');
Response:
Hello! How can I assist you today?
> select customer_id, star_rating, ai_generate_text_default(CONCAT(‘Classify the following review as positive, neutral, or negative’, and only include the uncapitalized category in the response: ‘, review_body)) AS review_analysis, review_body from amazon_book_reviews where product_title=’Artificial Superintelligence’ order by customer_id LIMIT 1;
Response:
+--+------------+------------+----------------+------------------+
| |customer_id |star_rating |review_analysis |review_body |
+--+------------+------------+----------------+------------------+
|1 |4343565 | 5 |positive |What is this book |
| | | | |all about ………… |
+--+------------+------------+----------------+------------------+
Examples of creating and using custom UDFs along with the built-in AI function
Instead of writing the prompts in a SQL query, you can build an UDF with your intended
prompt. Once you build your custom UDF with the prompt, you can pass that prompt into the
ai_generate_text_default built-in Impala function.
Example: Classify input customer reviews
The following UDF uses the Amazon book reviews database as the input and requests the LLM to classify the sentiment.
Classify input customer reviews:
IMPALA_UDF_EXPORT
StringVal ClassifyReviewsDefault(FunctionContext* context, const StringVal& input) {
std::string request =
std::string('Classify the following review as positive, neutral, or negative')
+ std::string(' and only include the uncapitalized category in the response: ')
+ std::string(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(input.ptr), input.len);
StringVal prompt(request.c_str());
return context->Functions()->ai_generate_text_default(context, prompt);
}
Now you can define these prompt building UDF and build them in Impala. Once you have them running, you can query your data sets using them.
Creating analyze_reviews function:
> CREATE FUNCTION analyze_reviews(STRING)
RETURNS STRING
LOCATION 's3a://dw-...............'
SYMBOL='ClassifyReviews'
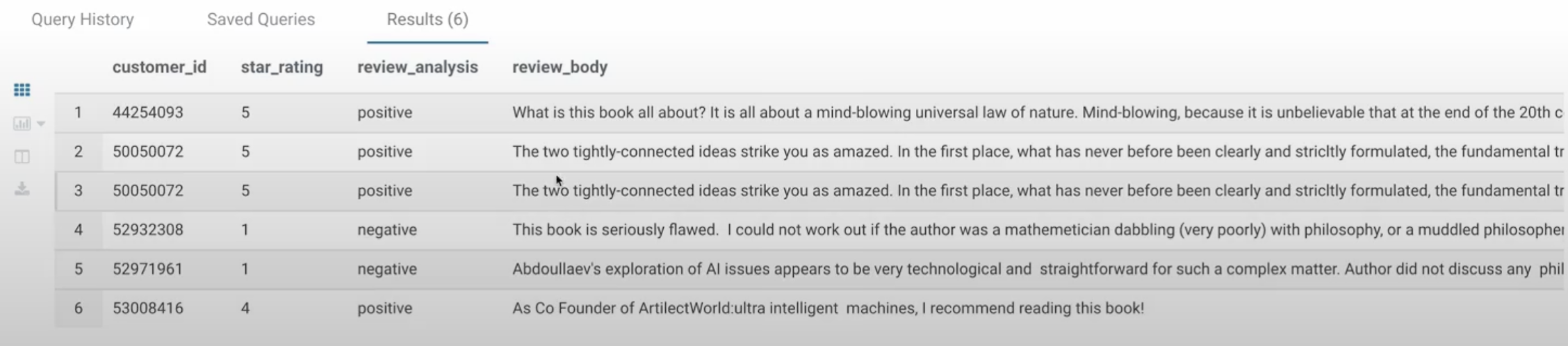
Using SELECT query for Sentiment analysis to classify Amazon book reviews
> SELECT customer_id, star_rating, analyze_reviews(review_body) AS review_analysis, review_body from amazon_book_reviews where product_title='Artificial Superintelligence' order by customer_id;