Migrating components using flow definition JSON as input
Learn how to use the Cloudera Flow Management Migration Tool to migrate components from flow definition JSON files.
Example flow for migrating components
The following NiFi flow demonstrates both variable and component migration.
Flow definition file:
- TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json
This file contains the TCP Listener process group (ID: b41940d7-0194-1000-42fc-458834630567)
TCP Listener Process Group
This process group contains the following simple flow:
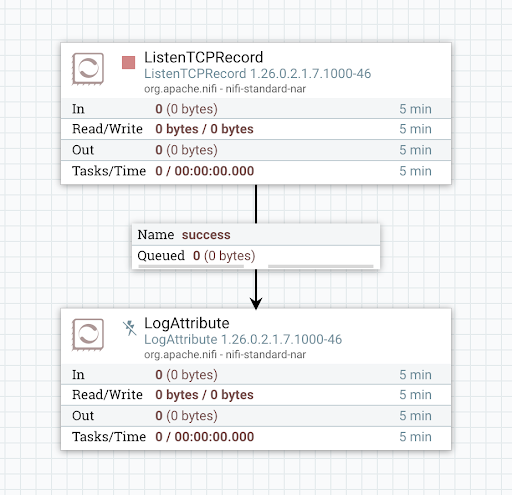
The process group defines a variable called TCP Listener Port, which is referenced by the ListenTCPRecord processor.
The example guides you through the variable migration process and shows how to maintain a clear activity log. Although the example uses a simple flow, the step-by-step approach can be applied to more complex scenarios. In real-world scenarios, Cloudera recommends defining a migration strategy based on the structure of each flow.
-
Use the flow definition files in the
/etc/migration-tool-input from step 3.
This is a NiFi-1 compatible flow that no longer contains variables.
-
Run Stage 1 component migration on
TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json using the following
command.
bin/migration.sh nifi migrate-components \ -i /etc/migration-tool-input/TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json \ -od /etc/migration-tool-output/components \ --sourceCompatibleOutputThis generates a sourceVersion folder that contains the output files of the Stage 1 migration.
components └── sourceVersion ├── activity_log.json └── migrated_output └── migrated_TCP_Listener.json- activity_log.json
-
-
The log describes all the actions that were performed for this stage of the process group migration.
-
Log of all actions performed during this stage of the process group migration.
-
- migrated_TCP_Listener.json
-
-
A modified NiFi 1 flow, which is not compatible with NiFi 2 yet.
-
It contains everything the original flow did, except the TCP Listener process group was modified as described in the activity log.
-
-
Validate the Stage 1 component migration output for
TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json.
- Load the migrated_TCP_Listener.json into a NiFi 1 instance and check the flow.
-
Review the activity_log.json file and check for
any
manual-change-requestsormanual-validation-requests. If none are present, proceed to the next step.In this example, you can see the following information in the activity log:{ "sequence" : 2, "type" : "change-info", "subject" : "b41966ad-0194-1000-a08d-a92489457356", "message" : "Component [org.apache.nifi.processors.standard.ListenTCPRecord] has been deprecated (NIFI-13509)", "context" : { "rule" : "36227b60-75f0-40dc-8caf-a2ec577aa54c" }-
Open the targetVersion/migrated_TCP_Listener.json file and search for the "subject" ID, b41966ad-0194-1000-a08d-a92489457356. This ID refers to the ListenTCPRecord processor.
-
Search for the value of the identifier as “subject” element in NiFi’s search box.
You are directed to the ListenTCPRecord processor. No manual modifications are needed at this stage. However, it is important to note that the ListenTCPRecord processor is deprecated and is not available in NiFi 2. Once the full component migration (Stage 1 and Stage 2) is complete, instructions will be provided on how to handle this deprecation.
-
- If manual changes are necessary, update the migrated_TCP_Listener.json on the NiFi canvas after loading it. Once the flow is validated and meets expectations, continue with the next step.
At this stage, you have completed Stage 1 of both variable and component migration for your flow definition file. After reviewing the logs, you confirmed that no manual changes were needed. You can proceed with a full component migration using the /etc/migration-tool-input from Step 3.
-
Run full component migration (Stage 1 and 2) for
TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json.
-
Make a backup of the output folder
(/etc/migration-tool-output/components) before
running the next migration step.
-
Run the full component migration using the following command.
bin/migration.sh nifi migrate-components \ -i /etc/migration-tool-input/TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json \ -od /etc/migration-tool-output/componentsThis generates the following output:
components ├── sourceVersion │ ├── activity_log.json │ └── migrated_output │ └── migrated_TCP_Listener.json └── targetVersion ├── activity_log.json └── migrated_output └── migrated_TCP_Listener.jsonThe contents of the previously generated sourceVersion folder will be overwritten. The contents represent the NiFi 1 compatible version of the migrated flow definition. Since you already performed Stage 1 component migration, the activity log will only include the same entries as those in Steps 2 and 4.
Additionally, a targetVersion directory is created, containing the output files of the Stage 2 part of the migration:
- migrated_TCP_Listener.json
-
-
NiFi 2-compatible flow definition
-
You can load it into NiFi 2 and validate it
-
- activity_log.json
-
-
List of all actions performed during this stage of the migration, and any manual steps that you need to perform.
-
-
Make a backup of the output folder
(/etc/migration-tool-output/components) before
running the next migration step.
-
Validate the Stage 2 component migration output for
TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json.
- Load the targetVersion/migrated_output/migrated_TCP_Listener.json into a NiFi 2 instance and check the flow.
-
Review the targetVersion/activity_log.json
file.
In this example, you can see the following manual-change-request entry.
{ "sequence" : 6, "type" : "manual-change-request", "subject" : "b41966ad-0194-1000-a08d-a92489457356", "message" : "The component has been deprecated. It is suggested to replace it with a combination of [org.apache.nifi.processors.standard.ListenTCP] and [org.apache.nifi.processors.standard.ConvertRecord] processors", "context" : { "rule" : "36227b60-75f0-40dc-8caf-a2ec577aa54c" }-
Open the targetVersion/migrated_TCP_Listener.json file and search for the "subject" ID, b41966ad-0194-1000-a08d-a92489457356. This ID refers to the ListenTCPRecord processor.
-
To identify the processor affected by these changes, search for the identifier value of the “subject” element in NiFi’s search box. It refers to the ListenTCPRecord processor. Open the TCP Listener process group. You can see that the processor is marked with dashed borders and its version number still shows that of the NiFi 1 instance. It means that it is a "ghost processor", not available in NiFi 2. The log message suggests replacing it with a combination of ListenTCP and ConvertRecord processors.
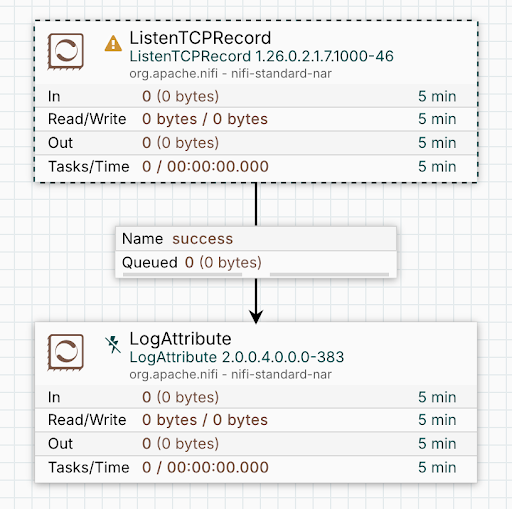
Instantiate and configure the ListenTCP and ConvertRecord processors, connect them appropriately, and then remove the ghost processor.
Besides these changes there are no further
manual-change-requestsormanual-validation-requestsin the activity log. - Download the flow definition and you have the fully NiFi 2 compatible TCP_Listener_flow_definition.json.
-
