Enabling Knox authentication
You can use Knox authentication for SQL Stream Builder (SSB) to provide integration with customer Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions. Knox uses Kerberos (SPNEGO) to strongly authenticate itself towards the services.
Apache Knox Gateway is used to help ensure perimeter security for SSB. With Knox, enterprises can confidently extend the SSB UI and API endpoints to new users without Kerberos complexities. Knox provides a central gateway and has varying degrees of authorization, authentication, SSL, and SSO capabilities to enable a single access point for SSB.
- Install and configure Knox on your cluster. For more information, see the Installing Apache Knox documentation.
- Enable Kerberos authentication for SSB. For more information, see Enabling Kerberos authentication section.
Enabling Knox Auto Discovery for MVE without Load Balancer
When using SQL Stream Builder (SSB), the Auto Discovery feature of Knox is supported for the Materialized View Engine (MVE). This means that you need to enable the Knox Auto Discovery feature for the MVE if you plan to use SSB without Load Balancer, and Cloudera Manager provides and manages all the required service definition files. In case the Load Balancer is enabled, you need to manually add the service definition to Knox.
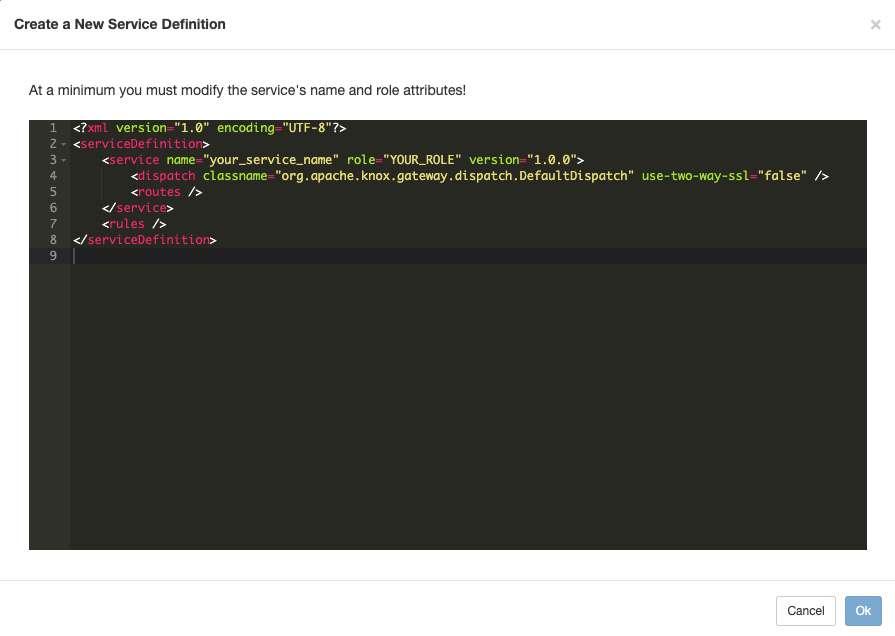
Extending Knox with the SSB service definitions in CDP Private Cloud Base 7.1.7
When using CDP Private Cloud Base 7.1.7, you must create service definitions for the SSB engines and APIs in the Knox Admin UI.
Adding SSB services to the default topologies
You must add the SSB services to the Knox default topologies in Cloudera Manager.
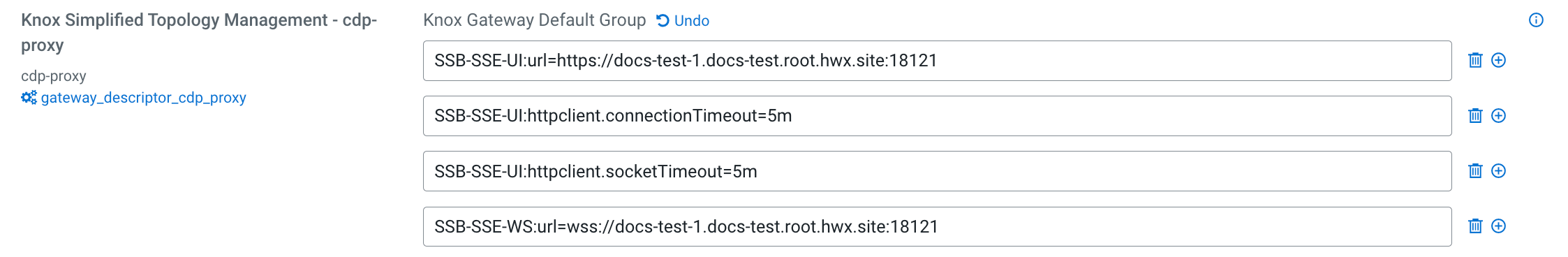
Defining Knox proxy paths for SSB
You must provide the Knox proxy paths for YARN and the Materialized View API in Cloudera Manager to authenticate the user when accessing the Materialized Views and the Resource Manager through the Streaming SQL Console.
Accessing the Streaming SQL Console through Knox
After manually configuring Knox and SSB, you should check if the SSO authentication works for the Streaming SQL Console.