Managing SQL jobs
You can configure your SQL jobs with Flink features in the Streaming SQL Console or through REST API using the API Explorer.
Configuring SQL job settings
If you need to further customize your SQL Stream job, you can add more advanced features to configure the job restarting method and time, threads for parallelism, sample behavior, exactly once processing and restoring from savepoint.
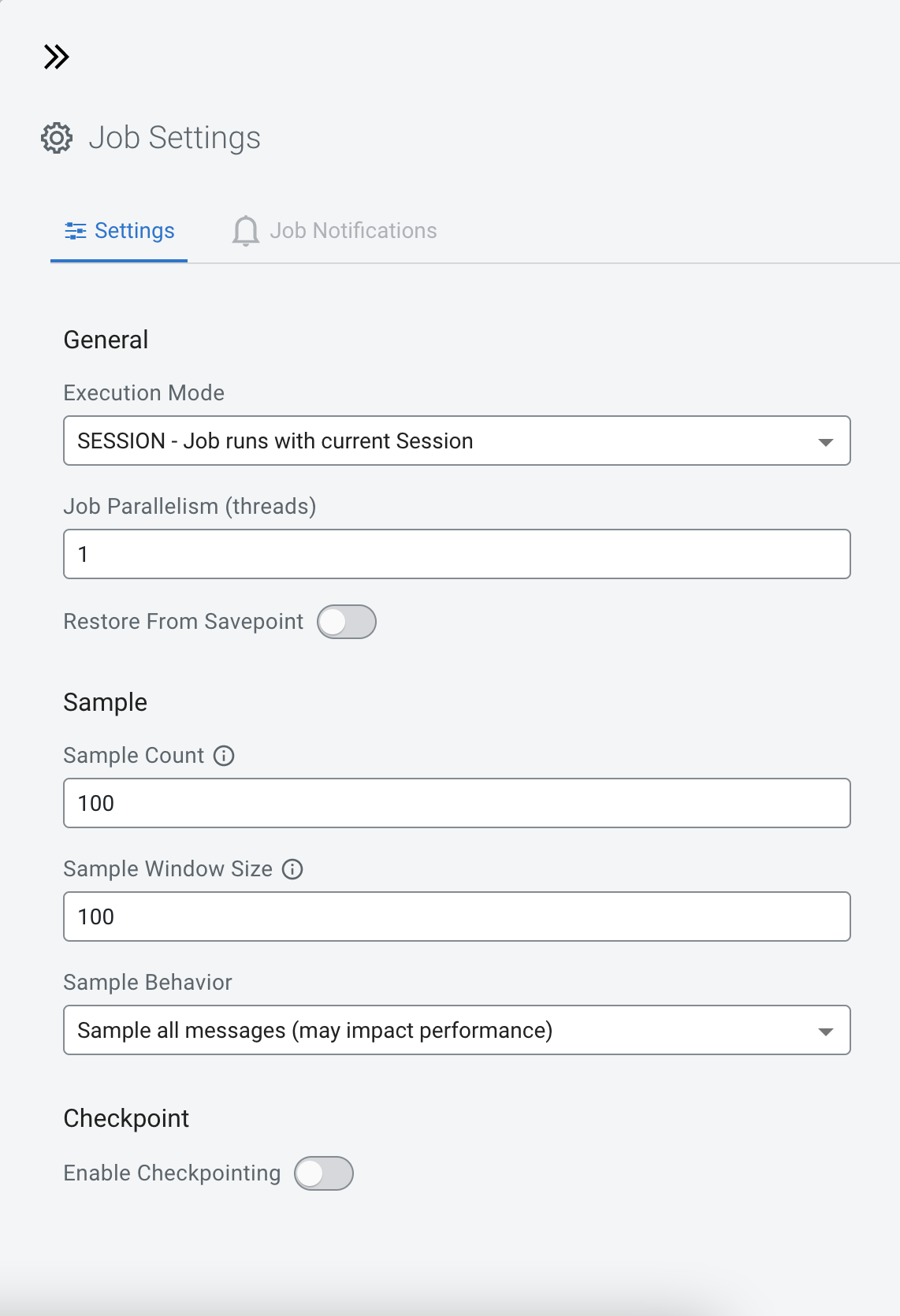
- Job parallelism (threads)
- The number of threads to start to process the job. Each thread consumes a slot on the cluster. When the Job Parallelism is set to 1, the job consumes the least resources. If the data source supports parallel reads, increasing the parallelism can raise the maximum throughput. For example, when using Kafka as a data source, setting the parallelism to the equal number as the partitions of the topic can be a starting point for performance tuning.
- Sample Count
- The number of sample entries shown under the Results tab. To have an unlimited number of sample entries, add 0 to the Sample Count value.
- Sample Window Size
- The number of sample entries to keep in under the Results tab. To have an unlimited number of sample entries, add 0 to the Sample Window Size value.
- Sample Behavior
- You have the following options to choose the behavior of the sampled data under the
Results tab:
- Sample all messages
- Sample one message every second
- Sample one message every five seconds
- Restore From Savepoint
- You can enable or disable restoring a SQL job from a Flink savepoint after stopping it.
- Enable Checkpointing
- You can enable and disable checkpointing for a SQL job. By default the checkpointing is enabled.
- Checkpoint Mode
- Switching between checkpointing modes. You can choose between At Least Once or Exactly Once.
- Checkpoint Interval
- The time in milliseconds between checkpointing attempts.
- Checkpoint Timeout
- The maximum time in milliseconds until a checkpointing attempt is timed out.
- Tolerable Checkpoint Failures
- The number of checkpointing attempts until the job is aborted.
- Failure Restart Strategy
- Switching between restarting strategies when checkpointing is failed. You can choose between enabling and disabling auto recovery. By default auto recovery is enabled for checkpointing.
Managing SQL jobs
You can manage your SQL jobs and reload them regardless of success to the SQL Editor to make further and additional changes, and execute them again.
You can manage the SQL Jobs on the Jobs tab if you need to stop them, restart them, delete them, duplicate them, review their events and also reload them to the SQL Editor in case any change is needed to their configuration. To reload a SQL job to the SQL Editor, you can simply click on it from the list of jobs or use . The details of the job are reloaded to the SQL Editor with the latest saved configuration and Materialized Views.
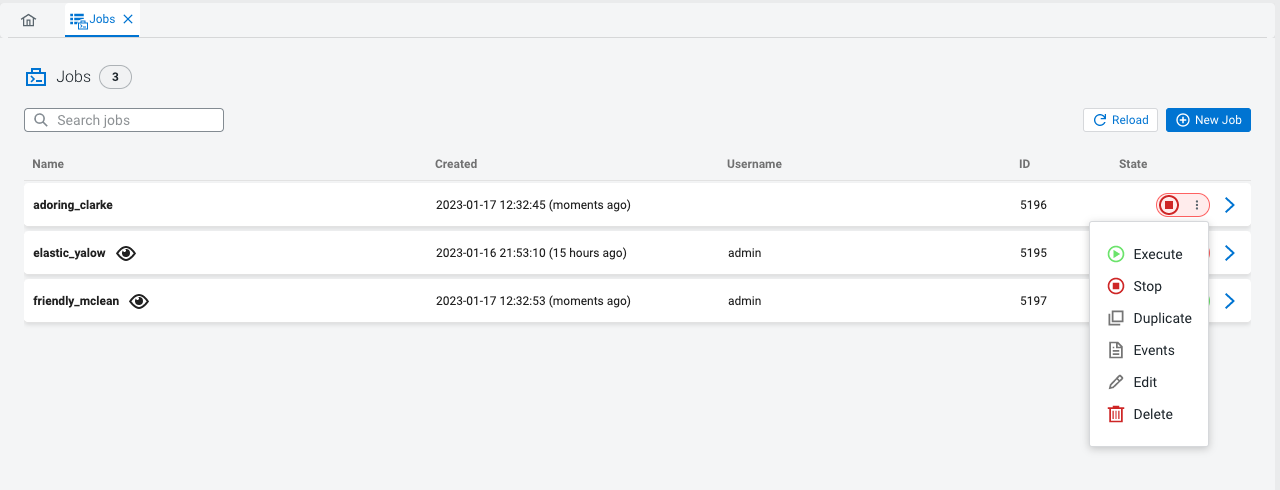
Loading SQL queries to SQL Editor
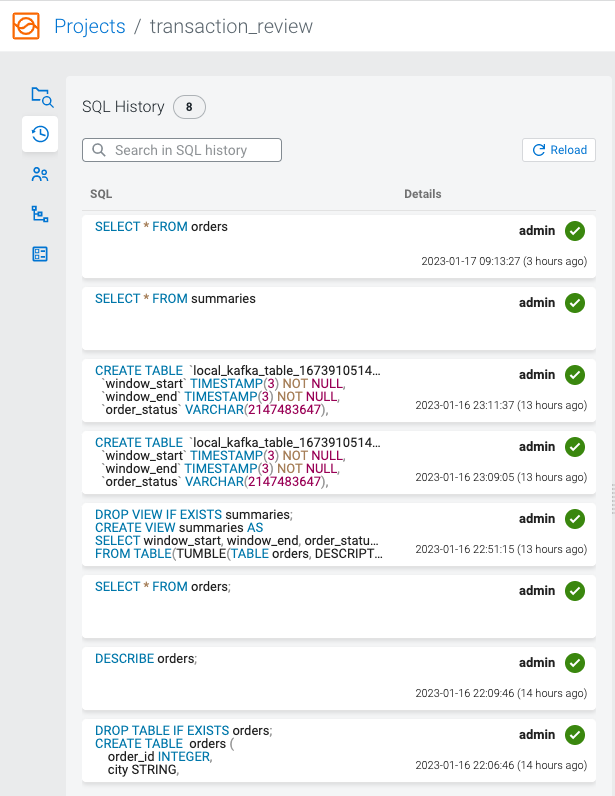
You can reuse an already submitted SQL query from SQL History view of Streaming SQL Console.
Using Cloudera SQL Stream Builder REST API
You can use the REST API to monitor, manage and configure the SQL Stream jobs with GET, POST and DELETE HTTP methods. You can use the Cloudera SQL Stream Builder REST API in command line, import them to REST API Tools or by accessing the Swagger UI.
- GET to query information about the specified endpoint
- POST to create resources for the specified endpoint
- PUT to update existing resources for the specified endpoint as a whole
- PATCH to partially update existing resources for the specified endpoint
- DELETE to remove objects from the specified endpoint
The REST API Reference document contains the available endpoints for Cloudera SQL Stream Builder.
You can also reach the SSB REST API reference document from the main menu of Streaming SQL Console using the API Explorer.
- Heartbeat
- Admin Operations
- User Operations
- User Keytab Operations
- Data Source Operations
- Table Operations
- Project Operations
- Project Environment Operations
- Project Sync Operations
- Project Invitation Operations
- Project Permission Operations
- SQL Operations
- SSB Session Operations
- Job Operations
- Sampling Operations
- Flink Job Operations
- Flink Session Cluster Operations
- Artifact Operations
- UDF Artifact Operations
- UDF Operations
- API Key Operations
- Connector Operations
- Data Format Operations
- Diagnostic Operations
Materialized View Pagination
You can set a limit and order the results of a Materialized View query by adding values to the limit and offset configurations.
localhost:18131/api/v1/query/5275/summary_query?key=6ef33a7a-c82a-4a72-946b-5fe0b33e033c&limit=20&offset=3When you edit the Materialized View, the set limit and offset change based on the new filters set for the Materialized View query. If you set an invalid number for the limit and offset, an error message is displayed.
