Materialized view recommendations introduction
Materialized views can improve query performance greatly, but deciding which query results to materialize is difficult. You can use the materialized view recommender command-line interface to help you decide which query results to materialize.
The recommender design is based on Agrawal et al. - Automated Selection of Materialized Views and Indexes for SQL Databases (VLDB 2000). The recommender takes a set of Hive queries as input and creates materialized views as output by exploring many table subsets and syntactical variants for each view candidate.
Typically, instead of considering a single, or just a few queries for materializing, you are considering an entire workload. Even the most experienced database experts have difficulty. There are many factors to consider, such as view maintenance and effectiveness. Making a bad decision about what to materialize can make performance worse.
You provide a set of queries or explain plans to the recommender, and then run the Workload Insights (wi) script to get recommendations. You can get recommendations online or offline, depending on the type of input you have:
- Online: input = queries only
- Offline: input = explain plans
If you have explain plans to provide as input to the Workload Insights (wi)
script, you can run the script offline; otherwise, you have to provide the HiveServer
endpoint for example, jdbc:hive2://myhost:10000, to the script. In lieu
of explain plans, the recommender needs to gather information about the query, such as
the number of rows of each query, how long the query ran, and other statistics, from
HiveServer.
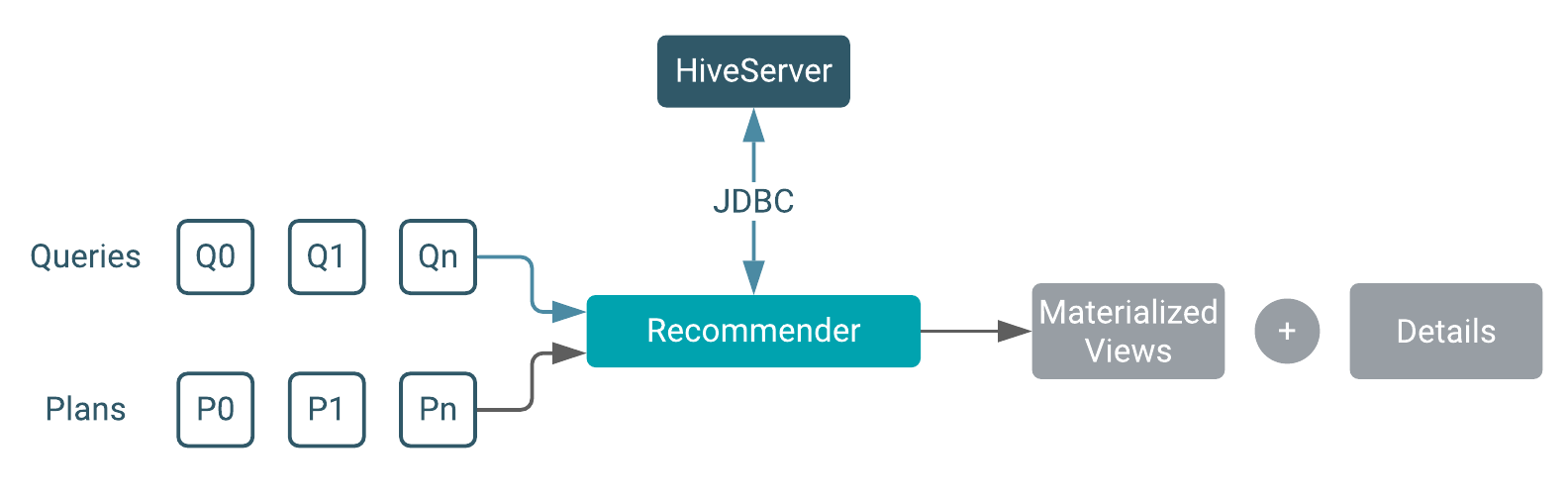
How much detail you receive in a recommendation depends on your configuration. Details include the number of recommendations and other information, such as why a particular view is recommended and how to exploit the view.
Workload Insights input requirements
- One or more directories containing one or more select and aggregation
queries in .sql files and multiple queries in files, separated by a
semicolon (;).
A .sql file name suffix is required.
- One or more directories containing an explain plan in .json files. A .json file name suffix is required.
