Use your own VPC
If you choose to use your own VPC, verify that it meets the minimum requirements and review Cloudera's recommended setup.
VPCs can be created and managed from the VPC console on AWS. For instructions on how to create a new VPC on AWS, refer to Create and configure your VPC in the AWS documentation.
Verify that your VPC meets the following requirements and recommendations:
Minimum requirements
- Cloudera Data Flow requires at least two subnets, each in a different Availability Zone (AZ). If you require a public endpoint for Cloudera Data Flow, provision at least one public subnet.
-
Ensure that the CIDR block for the subnets is sized appropriately for each Cloudera Data Flow environment. You must have enough IPs to accommodate:
- The maximum number of autoscaling compute instances.
- A fixed overhead of 48 IP addresses for three instances for core Cloudera Data Flow services.
- You must enable DNS for the VPC.
Cloudera's recommended setup
- Provision two subnets, each in a different Availability Zone (AZ).
- If you do not require a public endpoint, use two private subnets.
- If you require a public endpoint, use one private subnet and one public subnet.
- Private subnets should have routable IPs over your internal VPN. If IPs are not routable, private Cloudera Data Flow endpoints must be accessed via a SOCKS. This is not recommended.
- Tag the VPC and the subnets as shared so that Kubernetes can find them. Also, for load
balancers to be able to choose the subnets correctly, you must tag either the private or public
subnets.
A tag in AWS consists of a key and a value.
- To tag private subnets, enter
kubernetes.io/role/internal-elbfor the key and1for the value.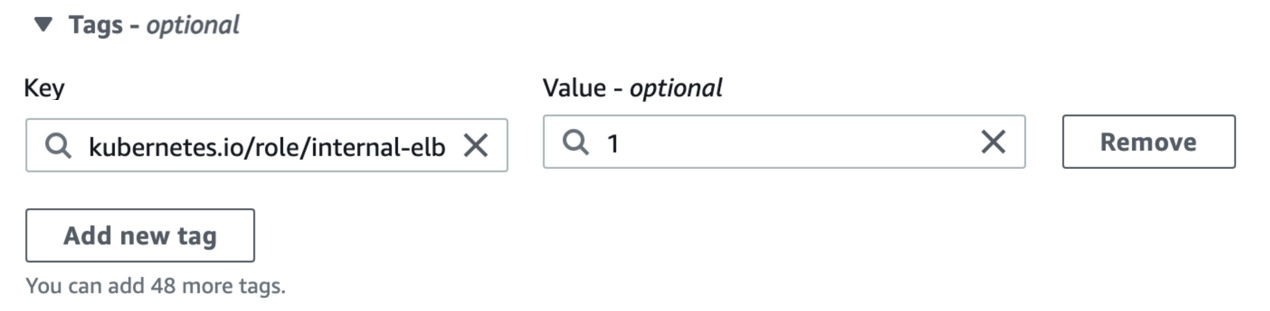
- To tag public subnets, enter
kubernetes.io/role/elbfor the key and1for the value.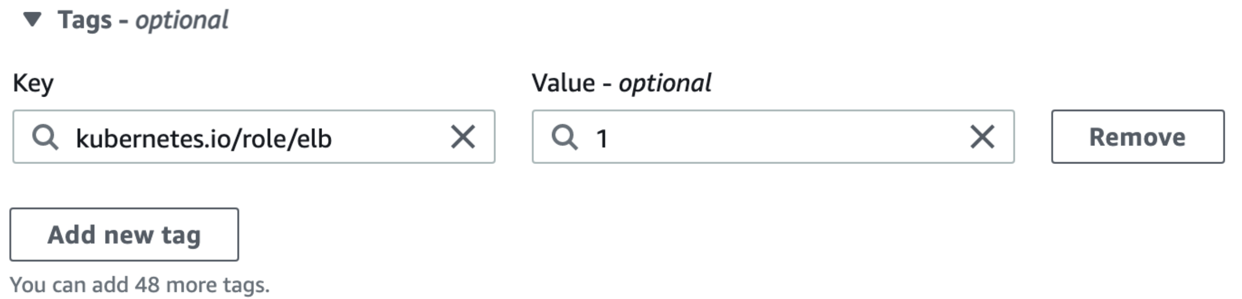
- To tag private subnets, enter
