Ephemeral storage
Ephemeral storage space is scratch space that a Cloudera AI session, job, application or model can use. This feature helps in better scheduling of Cloudera AI pods, and provides a safety valve to ensure runaway computations do not consume all available scratch space on the node.
By default, each user pod in Cloudera AI is allocated 0 GB of scratch space, and it is allowed to use up to 10 GB. These settings can be applied to an entire site, or on a per-project basis.
How Spark uses ephemeral storage in Cloudera AI
Spark drivers and executors write shuffle files, spilled RDD/DataFrame blocks, broadcast
variables, and task logs under directories referenced by SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS.
On Kubernetes these paths are mounted as one emptyDir volume per pod;
emptyDir is wiped as soon as the pod terminates, so the data is ephemeral.
kubelet evicts the pod and Spark surfaces errors
such as:- java.io.IOException: No space left on device
- org.apache.spark.shuffle.MetadataFetchFailedException
This is followed by a Kubernetes event similar to Evicted: The node was low on resource: ephemeral‑storage.
How does the CML UI map to Kubernetes resources
| CML field | Pod spec element | What it does |
|---|---|---|
| Ephemeral Storage (GB) – Request | resources.requests.ephemeral-storage |
Scheduler bin‑packing & cluster‑autoscaler logic |
| Ephemeral Storage (GB) – Max | resources.limits.ephemeral-storage |
Hard ceiling; usage ≥ limit → pod eviction |
Sizing guidelines for common Spark workloads
| Work‑load pattern | Rule of thumb (across all executors) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| SQL/ETL with light aggregations | ≈ 1 × largest input size | Minimal shuffle spill |
| Joins, `groupByKey`, heavy shuffle | 2 – 3 × largest input size | Shuffle writes often exceed input volume |
ML pipelines with .cache() / .persist() |
Cached dataset size × #replicas | Cached blocks are duplicated |
Tips to reduce Spark’s scratch‑disk footprint
| Goal | Knob | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fewer shuffle bytes | spark.sql.shuffle.partitions (closer to number of executors) and
spark.sql.adaptive.enabled=true |
Adaptive Query Execution coalesces partitions on the fly |
| Eliminate shuffle joins | Broadcast the small side: '/*+ BROADCAST(t) */' |
Keeps data in RAM when feasible |
| Compress spill data | Ensure spark.shuffle.compress=true (default) |
Small CPU cost, large disk savings |
| Use RAM‑backed volumes (SSD‑less nodes) | spark.kubernetes.local.dirs.tmpfs=true and raise
spark.kubernetes.{driver,executor}.memoryOverheadFactor |
Mounts emptyDir as tmpfs |
| Persist scratch across pod restarts | Mount a PVC at /spark-local with
spark.kubernetes.executor.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.<name>.mount.path |
Gives Spark a dedicated disk |
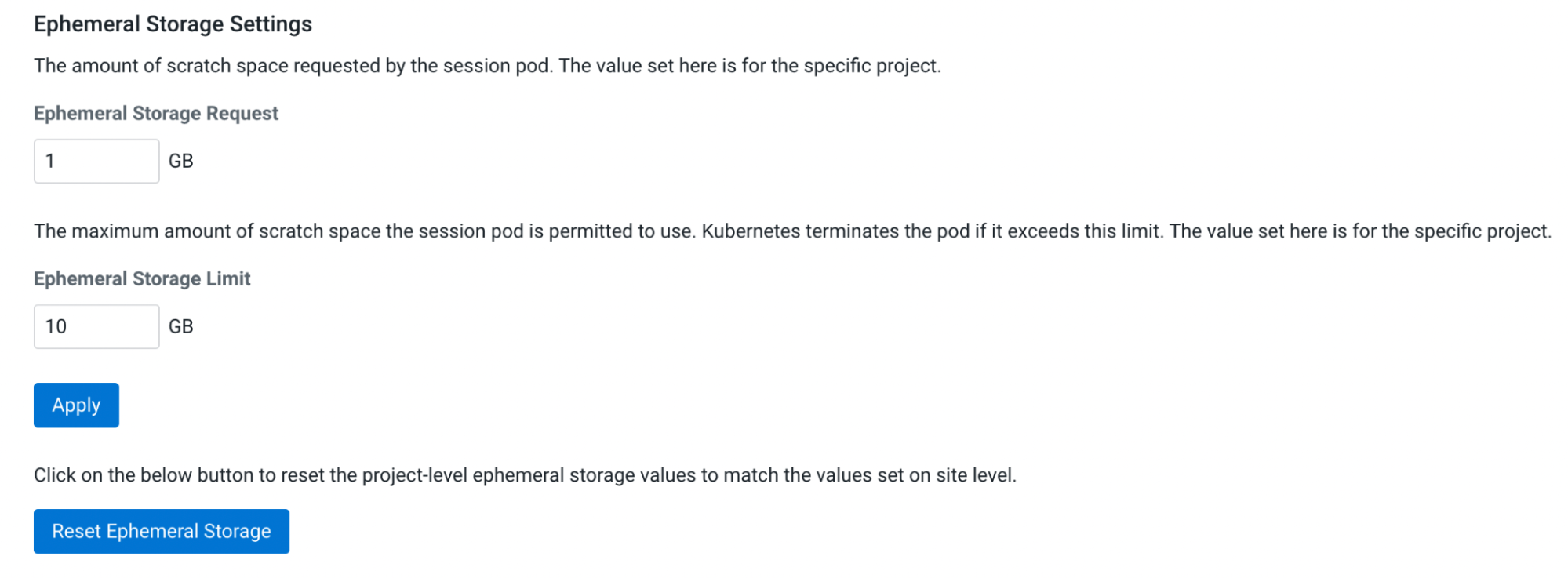
Change site-wide ephemeral storage configuration
In , you can see the fields to change the ephemeral storage request (minimum) and maximum limit.
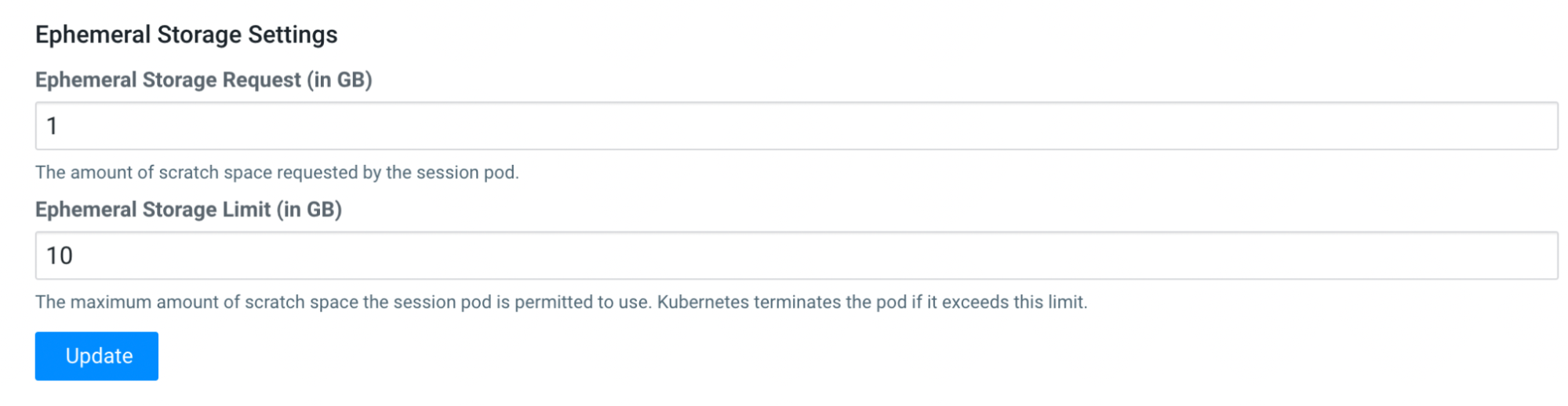
Override Site-wide ephemeral storage configuration
If you want to customize the ephemeral storage settings, you can do so on a per-project basis. Open your project, then click on and adjust the ephemeral storage parameters.