Example: Connect a Spark session to the Data Lake
After the Administrator sets up the correct permissions, you can access the Data Lake from your project, as this example shows.
Make sure you have access to a Data Lake containing your data.
The s3 or abfs path can be retrieved from the
environment’s cloud storage. To read from this location, in the Cloudera AI Workbenches UI, select the name of the environment, and in the Action menu, select
. Ensure that the user (or group) has been assigned an AWS IAM role
that can read this location. For Fine Grained Access Control (Raz) enabled
environments, go to Ranger to ensure that the user (or group) has access through an
appropriate s3 or adls policy.
Setting up the project looks like this:
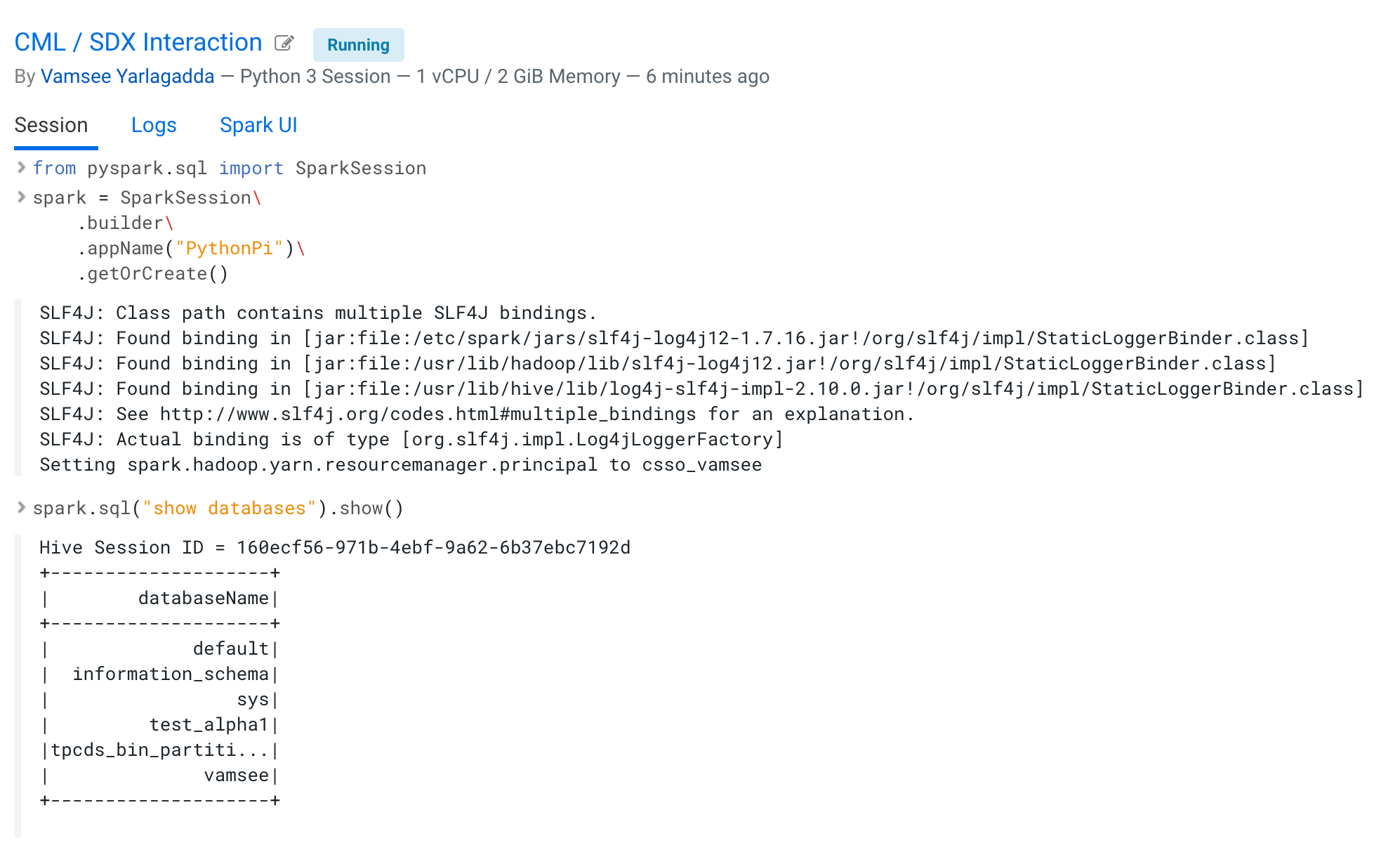
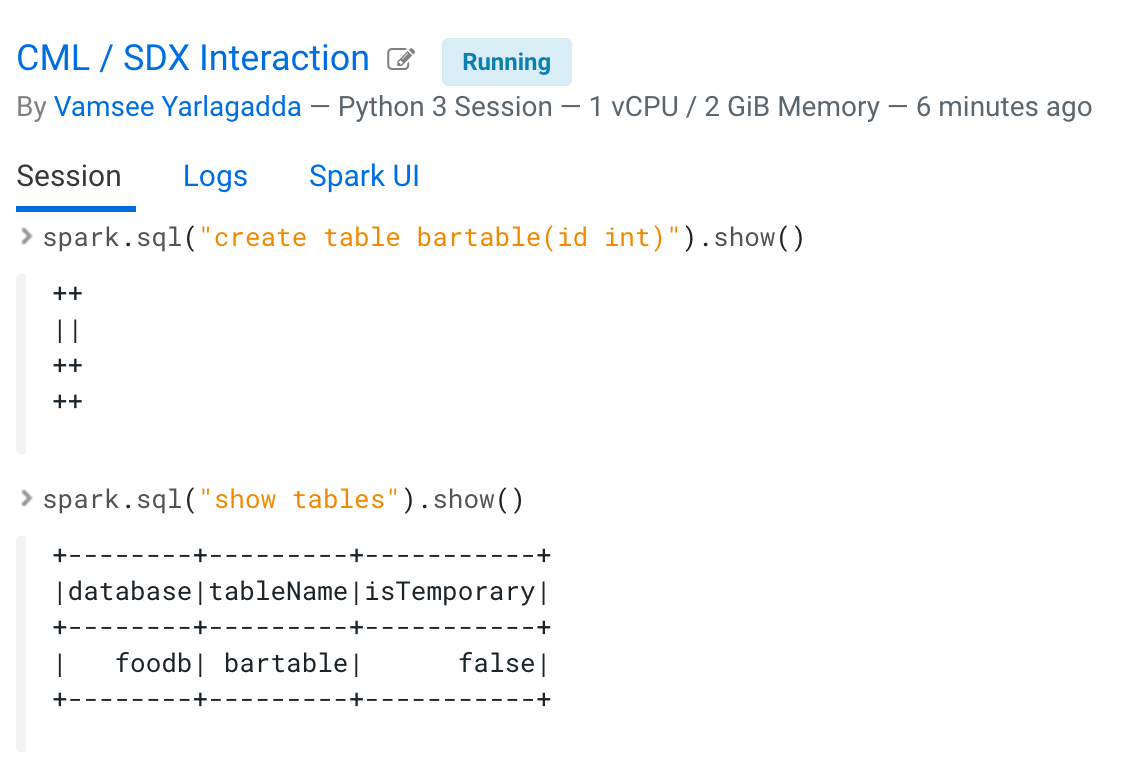
Now you can run Spark SQL commands. For example, you can:
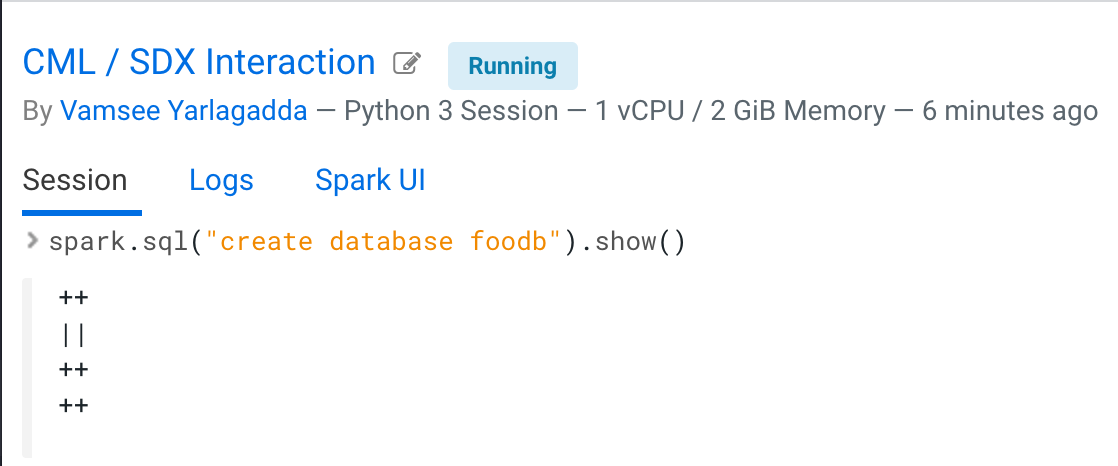
- Create a database foodb.
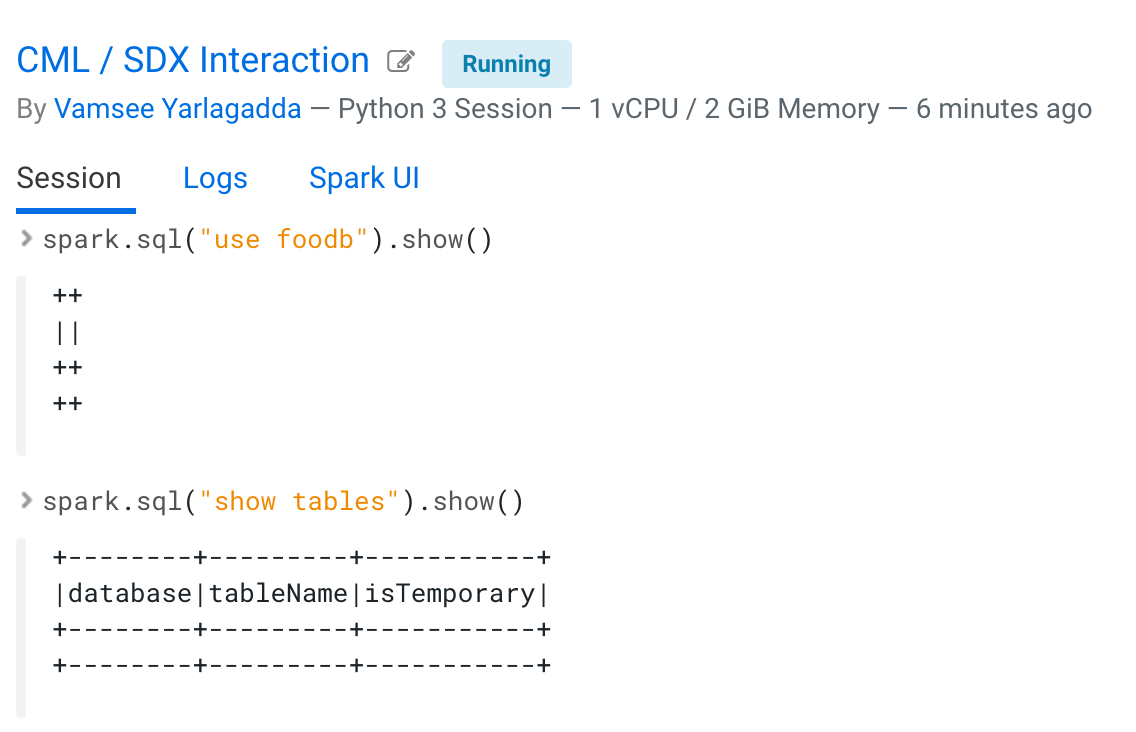
- List databases and tables.
- Create a table bartable.
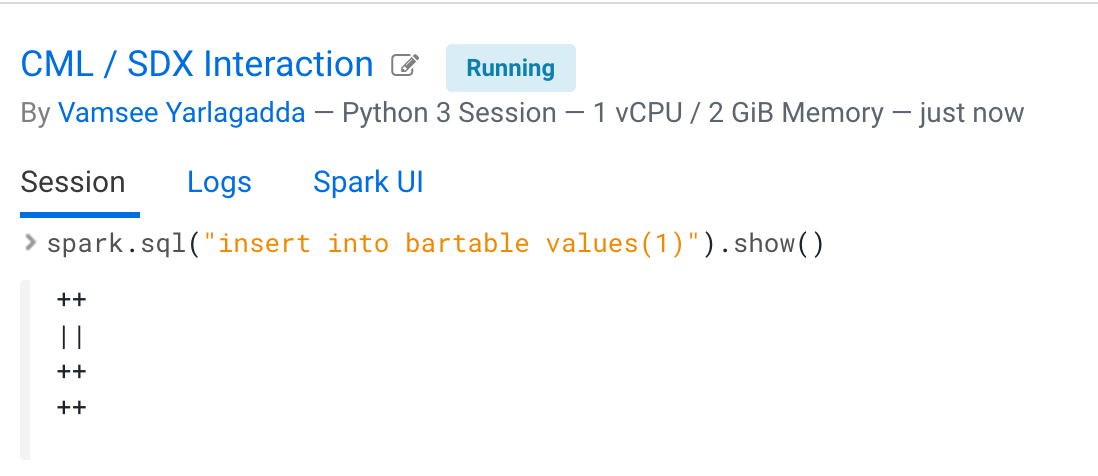
- Insert data into the table.
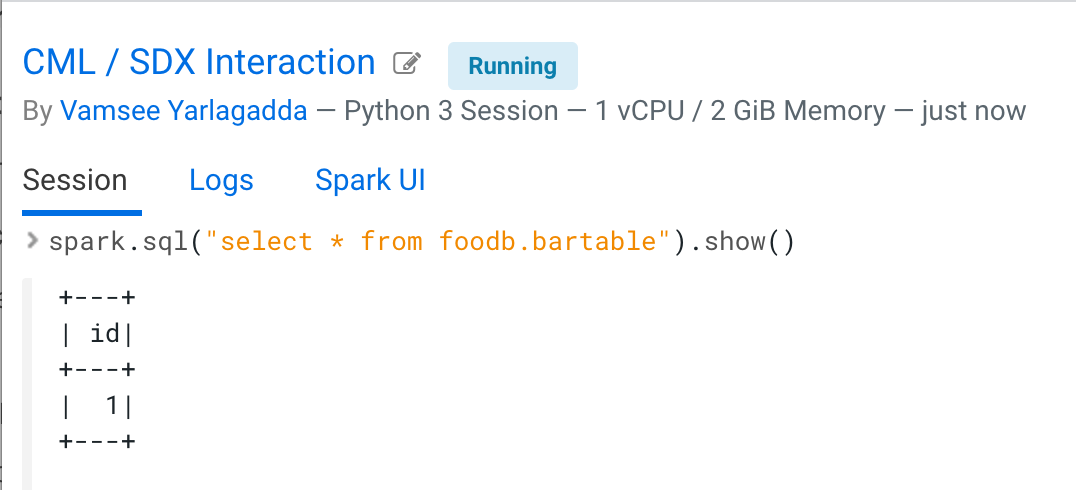
- Query the data from the table.