Deploying Cloudera in multiple AWS availability zones
By default, Cloudera provisions Data Lake, FreeIPA and Cloudera Data Hub clusters in a single AWS availability zone (AZ), but you can optionally choose to deploy them across multiple availability zones (multi-AZ). It is possible to enable it either for all or some of these components.
Single-AZ vs multi-AZ deployment
Each AWS region has multiple availability zones, which act as failure domains, preventing small outages from affecting entire regions. By default, a Cloudera environment (FreeIPA and Data Lake) and Cloudera Data Hub clusters running in it are deployed across one subnet, meaning that each of them has VMs spread across a single availability zone (as on AWS every subnet is related to a single availability zone). This is illustrated in the following diagram, where all of the resources run in the eu-central region, and each of them is in a different subnet and availability zone (eu-central-1a for the FreeIPA, eu-central-1b for the Data Lake, and eu-central-1c for the Cloudera Data Hub clusters):
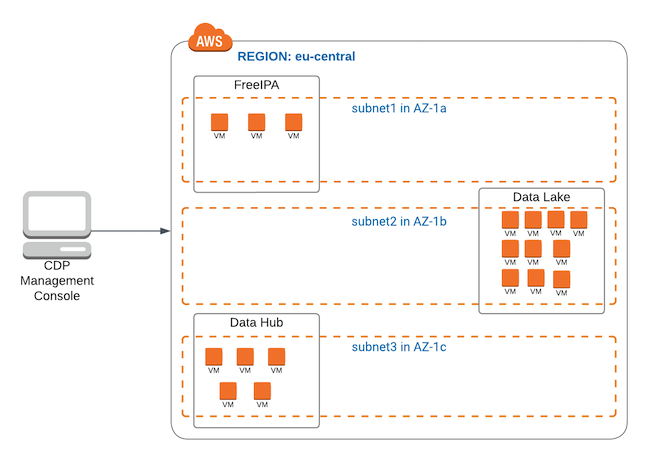
If you choose to deploy your Cloudera environment (FreeIPA and Data Lake) and Cloudera Data Hub clusters across multiple subnets and availability zones, each of these components is spread across three or more availability zones, providing high availability and fault tolerance. This is illustrated in the following diagram, where each of the components (FreeIPA, Data Lake, and Cloudera Data Hub clusters) is deployed across multiple subnets and multiple availability zones: eu-central-1a, eu-central-1b, and eu-central-1c:
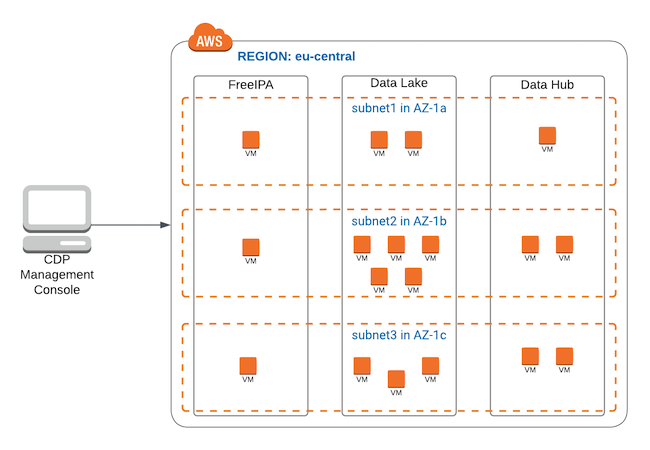
The Data Lake deployed in this setup is the enterprise Data Lake, which has enough nodes to utilize multiple availability zones for providing high availability and fault tolerance.
Multi-AZ can be enabled for Data Lake, FreeIPA, and Cloudera Data Hub clusters. It is possible to enable it either for all or some of these components.
Instances within a host group are distributed across availability zones equally, with the least used availability zone(s) preferred. For example, if there is a group of instances across three availability zones with 100 instances in AZ-1, 30 in AZ-2 and 30 in AZ-3, when an upscale of 10 nodes is requested, Cloudera provisions 5 instances in AZ-2 and 5 in AZ-3.
When a failure happens and a cluster needs to be repaired, the replacement VMs are always provisioned in the same subnet and availability zone as the old ones since the detached disks can only be reattached to a VM in the same availability zone. This means that if there is an availability zone outage, cluster repair is not possible.Use cases
A multi-AZ Data Lake and FreeIPA constitute a resilient environment that provides a solid basis for multi-AZ Data Hubs and Cloudera data services. Data Hubs and Cloudera data services depend on the FreeIPA instance in the Data Lake to provide DNS resolution. Deploying FreeIPA across multiple availability zones ensures that critical DNS resolution is available in the event of an availability zone outage. Furthermore, an enterprise Data Lake provides high availability, and additional compute and memory resources for key SDX services and is recommended for production workloads.
Deploying your Cloudera Data Hub clusters across multiple availability zones is key if your mission-critical applications depend on HBase and Kafka. Multiple availability zone deployment for operational workloads is considered best practice by the cloud vendors. It ensures that your applications can continue to run in the event of a single availability zone outage.
When an entire availability zone fails, HBase utilized in Cloudera Operational Database automatically rebalances regions among the remaining instances in the cluster to maintain availability. The write-ahead log (WAL), which is replicated across the three availability zones is automatically replayed by the newly assigned region servers in other availability zones to ensure writes to the database are not lost.
When using the multi availability zone feature, Cloudera ensures that Kafka replicates partitions across brokers in different availability zones. During an availability zone failure this ensures that no data is lost and applications can continue to access the data they need. Cruise Control, which is deployed alongside every Kafka cluster in Cloudera on cloud, detects that topics need to be rebalanced to the remaining brokers. Once the availability zone is back online, you can repair your Kafka cluster, restoring the initial broker distribution across availability zones. Afterwards Cruise Control kicks in and ensures that all topic partitions are balanced across the cluster.
Limitations
The following limitations apply when deploying a multi-AZ Cloudera:
-
When an AZ is down, you cannot create a new Cloudera Data Hub, and create or activate Cloudera data services within the environment. Existing workloads will continue to work.
-
When an AZ is down, you cannot resize, stop, or restart Cloudera Data Hub clusters.
-
When an AZ is down, existing running workloads will continue to run. Some Data Lake services will still be functioning (because they run across more than one AZ) but others may be down if the AZ where they are running is down.
The following diagram shows how Data Lake services are distributed across AZs (assuming that there are 3 AZs per region). The Data Lake services marked in red run in a single AZ only and will be down if that AZ is down:
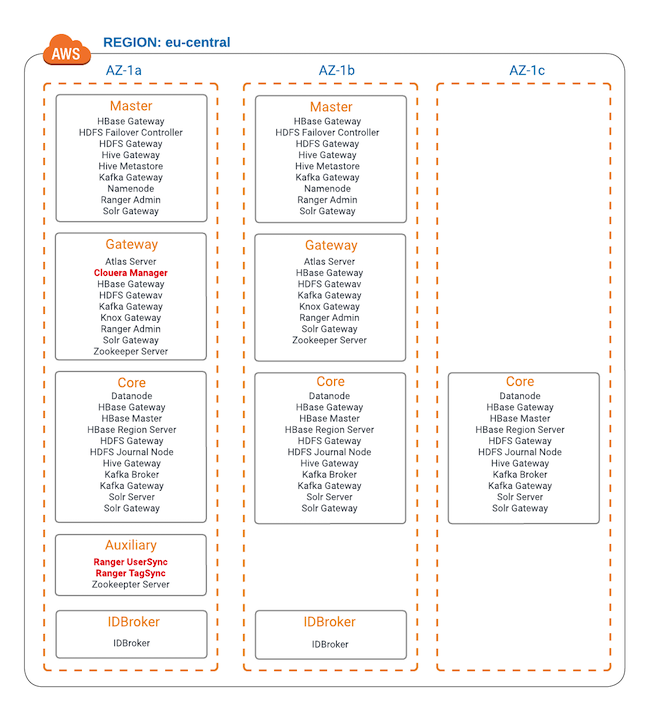
The following table shows which services aren’t affected by an AZ outage (column 1 and 2) and those that may potentially be affected (column 3):
Services running in all available AZs Services running in two AZs Services running in a single AZ Datanode HBase Gateway
HBase Master
HBase Region Server
HDFS Gateway
HDFS Journal Node
Hive Gateway
Kafka Broker
Kafka Gateway
Solr Server
Atlas Server HDFS Failover Controller
Hive Metastore
IDBroker
Knox Gateway
Namenode
Ranger Admin
Solr Gateway
Zookeeper Server
Cloudera Manager Ranger UserSync
Ranger TagSync
As shown in the diagram and the table, the following three services will be down if the AZ where they are running is down:
-
Cloudera Manager - When Cloudera Manager is down, you cannot perform administrative tasks that you would normally perform via Cloudera Manager.
-
Ranger UserSync - When Ranger UserSync is down, existing users are not impacted, but synchronizing new users to Ranger is disrupted. For example, if you add a new user and sync it to FreeIPA while Ranger UserSync is down, the newly added user will not be synced to Ranger and as a result the user will not be able to access workload data.
-
Ranger TagSync - When Ranger TagSync is down, existing tags and policies are not impacted, but synchronizing new, updated, or removed tags with an external metadata service such as Apache Atlas and creating Ranger policies with these tags is disrupted.
-
- Single AZ environments or clusters cannot be converted to multi-AZ.
- While CDP CLI allows you to specify multiple subnets per Cloudera Data Hub cluster’s host group, due to load balancer requirements only one subnet per AZ can be configured for the Cloudera Manager node group of the Cloudera Data Hub cluster.
- While by default Cloudera deploys Data Lake, FreeIPA, and Cloudera Data Hub clusters using CloudFormation, in case of the multi-AZ setup no CloudFormation is used. This affects vertical scaling: After vertical scaling (for example during cluster repair or upgrade) Cloudera always provisions the original instance types. For example, if you are using vertical scaling runbooks, repair and upgrade operations will use the previous instance type and root volume settings.
Enabling multi-AZ
Multi-AZ can be enabled for Data Lake, FreeIPA, and Cloudera Data Hub clusters running on AWS. It is possible to enable it either for all or some of these components.
To enable multi-AZ, you should register a multi-AZ Cloudera environment with an enterprise Data Lake. You can also create multi-AZ Cloudera Data Hub clusters within any existing environment. Detailed steps are provided below.
Register a multi-AZ environment
You can register a multi-AZ AWS environment via Cloudera UI or CDP CLI. You may choose to enable multi-AZ for Data Lake only or for FreeIPA only. There is no requirement to enable both.
Steps
Register your environment as usual, just make sure to do the following:
-
On the Data Access and Data Lake Scaling page, select the enterprise Data Lake.
-
On the same page, scroll down and in the bottom of the page enable the Advanced Options.
-
In the Network and Availability section enable the Enable Multiple Availability Zones for Data Lake toggle button in order to enable multi-AZ for Data Lake. The option is disabled by default. The option only appears when an enterprise Data Lake is selected.
- On the Region, Networking, and Security page, scroll down and in the bottom of the page enable the Advanced Options.
-
In the Network and Availability section enable the Enable Multiple Availability Zones for Data Lake toggle button in order to enable multi-AZ for FreeIPA. The option is disabled by default.
Register your AWS environment via CDP CLI as usual, but when creating a template for the environment registration commands, add the following to enable multi-AZ:
-
In the environment creation command, add the
multiAz=trueto the--free-ipaoption. -
In the Data Lake creation command, add the
--multi-azoption. -
In the Data Lake creation command, make sure to specify the enterprise Data Lake.
The following example illustrates these necessary additions, which are emphasized using bold typeface:
cdp environments create-aws-environment \
--environment-name tb-multiaz-env \
--credential-name tb-cldr-acc \
--region "eu-central-1" \
--security-access cidr=0.0.0.0/0 \
--no-enable-tunnel \
--authentication publicKeyId="test" \
--log-storage storageLocationBase=s3a://cb-group/test,instanceProfile=arn:aws:iam::152413716728:instance-profile/mock-idbroker-admin-role \
--vpc-id vpc-03e505817e3619238 \
--subnet-ids subnet-013855b2gc32c2cd8 subnet-02b9054ef829374fe subnet-085c9ff36b38c0b35 \
--free-ipa instanceCountByGroup=3,multiAz=truecdp environments set-id-broker-mappings \
--environment-name tb-multiaz-env \
--data-access-role arn:aws:iam::152413716728:role/mock-idbroker-admin-role \
--ranger-audit-role arn:aws:iam::152413716728:role/mock-idbroker-admin-role \
--set-empty-mappingscdp datalake create-aws-datalake \
--datalake-name tb-multiaz-dl \
--environment-name tb-multiaz-env \
--cloud-provider-configuration instanceProfile=arn:aws:iam::152413716728:instance-profile/mock-idbroker-assumer,storageBucketLocation=s3a://cb-group/test \
--scale ENTERPRISE_HA \
--runtime 7.2.12 \
--no-enable-ranger-raz \
--profile mowdev \
--multi-azCreate multi-AZ Cloudera Data Hub clusters
If you would like to create multi-AZ Cloudera Data Hub clusters, see Creating a multi-AZ Cloudera Data Hub on AWS.
