Troubleshooting an abnormal job duration
You can identify areas of risk from jobs running on your workload cluster that complete within an unusual time period, using Cloudera Observability.
Steps with examples from a Virtual Cluster's Spark engine are used to explain how to further investigate and troubleshoot the cause of an abnormal job duration.
-
Verify that you are logged in to the Cloudera Observability web UI.
-
Log in to Cloudera in a supported browser.
The Cloudera Cloud web interface landing page opens.
-
From the Your Enterprise Data Cloud landing
page, select the Observability tile.
The Cloudera Observability landing page opens.
-
Log in to Cloudera in a supported browser.
-
From the Environment Name column in the Environments
page, locate and click the name of the environment whose workload diagnostic
information requires analysis and troubleshooting.
For this example, select Virtual Cluster from the Environments list and then select a Virtual Cluster required for analysis.
The Environment navigation panel opens, which hierarchically lists the environment and its services hosted on the selected environment.
-
Verify that the Cluster Summary page is displayed.
The Cluster Summary page, displays performance trends and metrics about the cluster's processed jobs and queries.
- Optional: From the time-range list, select a time period that meets your requirements.
- If not already expanded, from the Environment navigation panel expand the Virtual Cluster and then select the Spark engine.
-
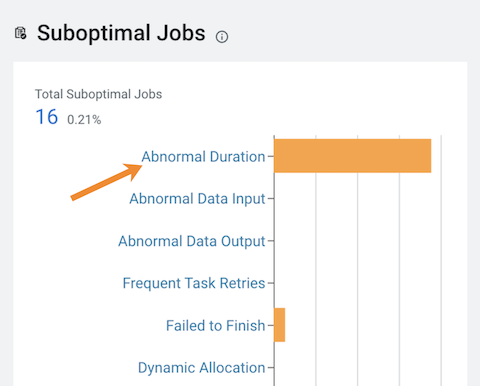
Scroll down to the Suboptimal Jobs chart widget and
click the Abnormal Duration health check bar.
The Jobs page opens, listing all the jobs that triggered the Abnormal Duration Health check during the time period, including their health status, the length of time the job took to run, the user who ran the job, the job identification number, and the amount of CPU used to run the job.
-
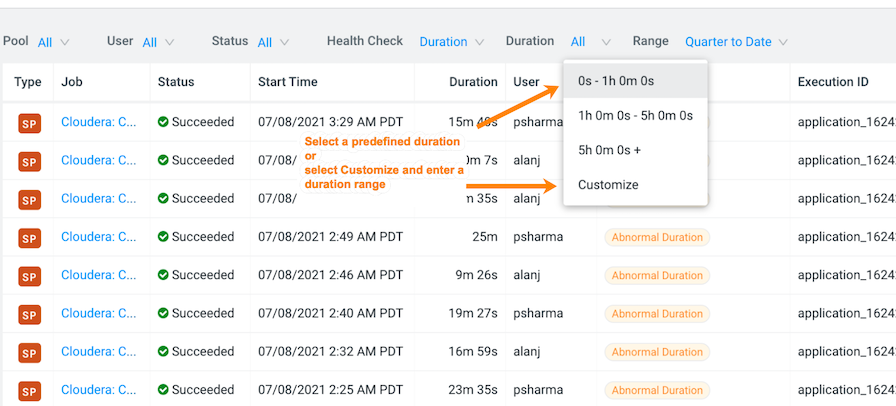
Specify a specific amount of time in which the job either ran less than or more
than the Health check rule by either selecting a predefined time duration or
selecting Customize and enter the minimum or maximum time
period from the Duration filter.
-
View more details about a job by selecting a job's name from the Job
column and then clicking the Health Checks
tab.
The Baseline and Skew Health checks are displayed.
-
Display more information about the job's duration by selecting
Duration from the Baseline
section. As shown in the image below.
In the following example, the job finished much slower than the baseline duration, which is the aggregate calculated over multiple jobs.
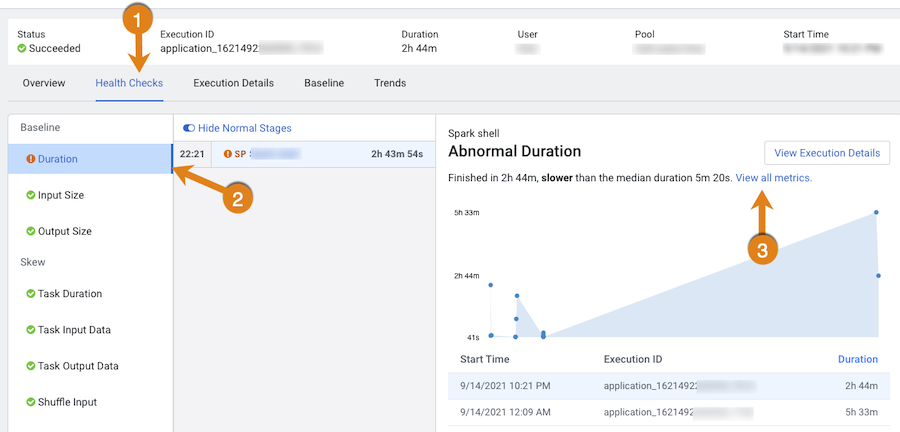
- Compare and analyze this job against other baseline metrics by clicking View all metrics.
-
Continue to analyze and search for probable causes by doing one or more of the
following:
- To display more information about the length of time the processing
tasks took within a job, select Task Duration, which
opens a panel that describes the health check, displays information about
the possible causes, and lists recommended solutions. In the following example, issues arose during Stage-9 of the job due to poor parallelization. The Recommendation section lists items for you to complete that may resolve the problem and the specific outlier tasks that produced the unusual results:
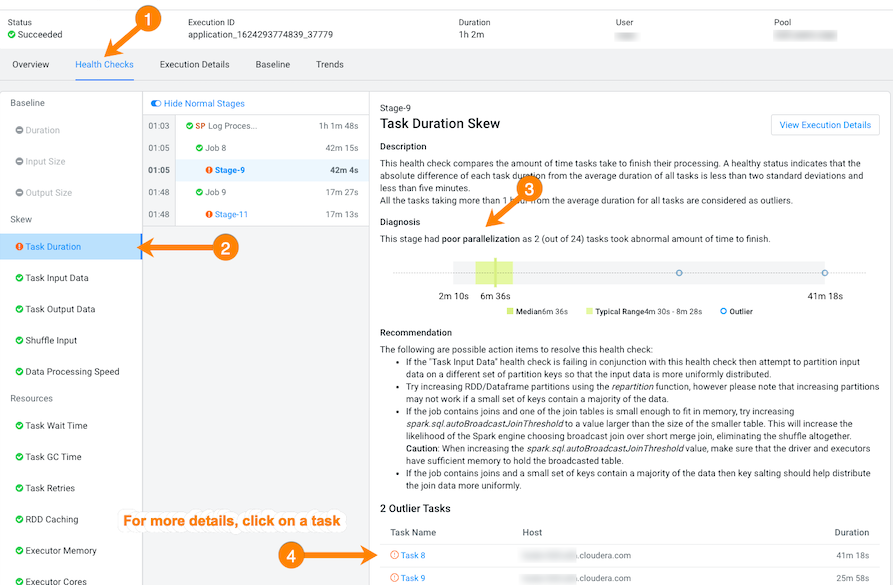
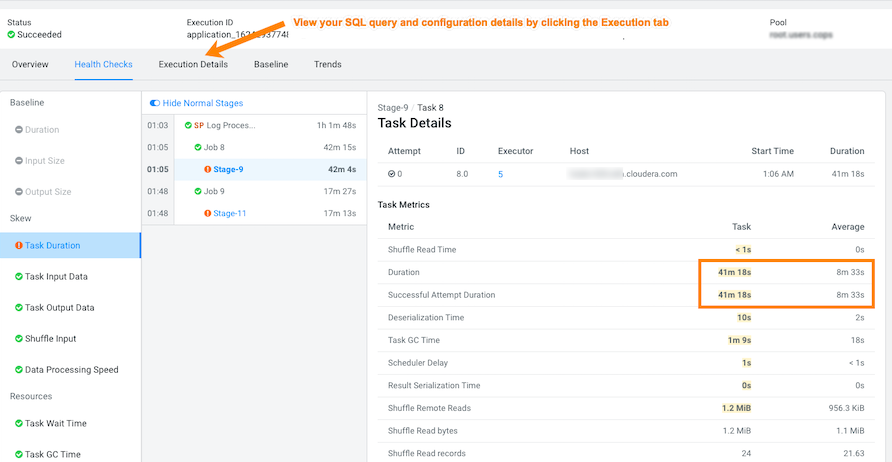
- To display more details about an outlier, click the outlier task, which
opens the Task Details panel. In the following example, the Task Details show that the outlier task took significantly more time to complete compared to previous runs. In this case, 41 minutes as compared to 8 minutes:
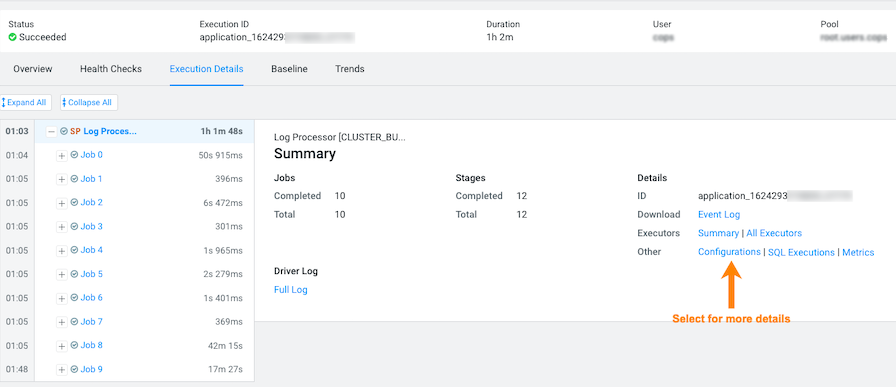
- To gain more insights about the task's duration, such as checking memory
allocation, click the Execution Details tab and then
in the Summary panel, click Configurations:
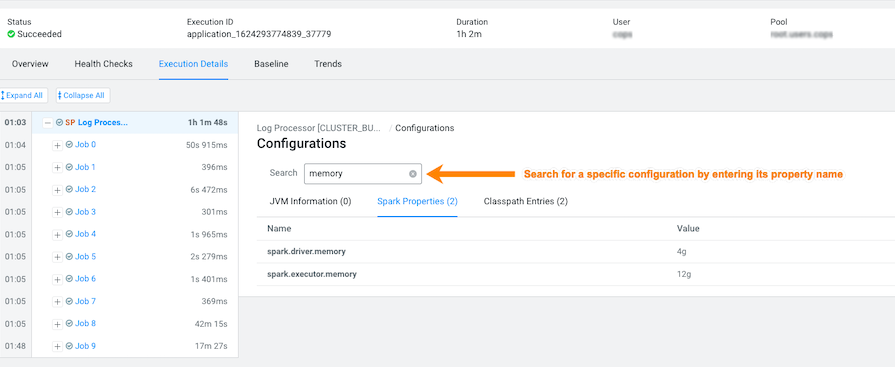
- In the Configurations panel, click the Spark
Properties tab and search for the memory configuration
settings and their values. If memory is less than the recommended value,
increasing its value will improve cluster performance:
- To display more information about the length of time the processing
tasks took within a job, select Task Duration, which
opens a panel that describes the health check, displays information about
the possible causes, and lists recommended solutions.
