Secure in-bound communication
The CDP Control Plane reaches out to workload environments for various command and control purposes. These connections currently go over the Internet to the workload environment hosts. As a consequence, CDP currently deploys workloads into public (Internet routable) subnets.
To operate in public subnets, CDP secures in-bound communication to the listening ports using TLS encryption. Connections are authenticated using environment- or cluster-specific credentials that CDP manages internally. As appropriate, administrators can further secure listening ports by authenticating IP addresses and/or ports:
- Identifying authentic connections: Use security group rules to ensure in-bound connections originate from the set of stable IP addresses that belong to your organization.
- Identifying authentic ports: In-bound connections take place on an identifiable set of ports, which can be used to additionally narrow the allowlist.
In addition to the CDP management traffic, your organization's use cases may specify connecting to the workload hosts over the Internet. These communications may involve different endpoints, protocols, ports, and credentials than CDP management traffic.
Endpoints fall into four categories today, associated with our shared Environment services on the Data Lake and on Data Hub, Data Warehouse, and Machine Learning workloads. The following sections enumerate the communications for each of those categories.
Data Lake communication endpoints
In-bound communication for shared services support CDP management of FreeIPA and Data Lake services.
Each Environment contains a deployment of FreeIPA and a Data Lake cluster that support the following security and governance activities:
- Free IPA identity and security services
-
- LDAP: User Directory
- Kerberos KDC: Manages a Kerberos Realm for the Environment
- DNS: Provides internal resolution of workload hostnames
- Certificate Authority: Issues TLS certificates for internal use, and for the in-bound CDP control connections
- Data Lake cluster services
-
- Hive Metastore: Tabular metadata storage
- Ranger: Security policies and audit trail
- Atlas: Data lineage, tagging, analytics
- ID Broker: Mapping of CDP identities to cloud provider identities
- Knox: A proxy gateway for access to cluster services
- Cloudera Manager: Local management for the data lake services
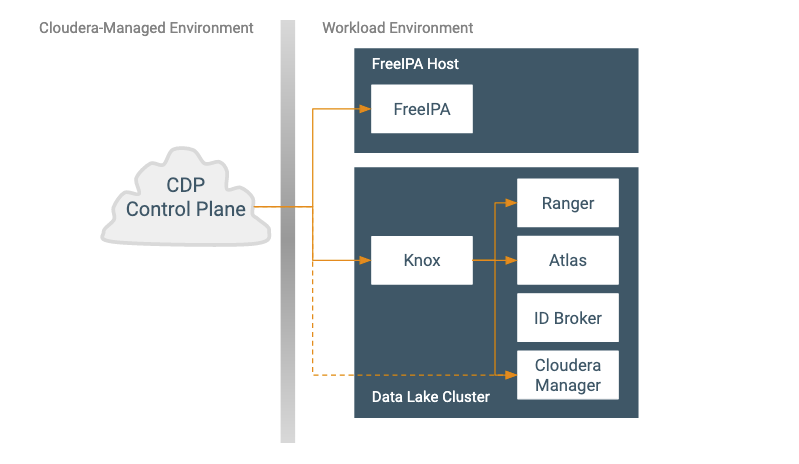
Communication to the CDP Control Plane includes the following:
- Free IPA identity and security services
-
-
User and Group synchronization
-
Service Principal management
-
Retrieving the CA root certificate
-
- Data Lake cluster services
-
- Core lifecycle management operations (sent directly between CDP and Cloudera Manager to include the Knox proxy as one of the managed entities; shown as a dashed line in the picture)
- Communication (via Knox proxy)
- General Cloudera Manager operations
- Ranger operations to manage repositories for workloads
- ID Broker mappings (updated via Cloudera Manager)
- Data Catalog communicates with Atlas and Ranger to surface information
Data Hub communication endpoints
Data Hub clusters are built on the same underlying technology as the Data Lake cluster and so present a similar connectivity profile.
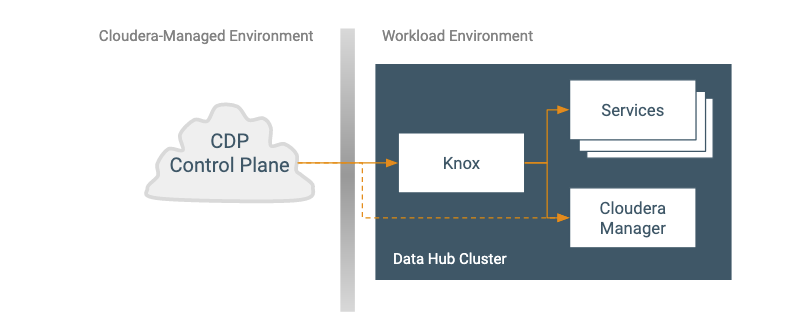
Communication to the CDP Control Plane includes the following:
- Free IPA identity and security services
-
-
User and Group synchronization
-
Service Principal management
-
Retrieving the CA root certificate
-
- Data Lake cluster services
-
- Core lifecycle management operations (sent directly between CDP and Cloudera Manager because the Knox proxy is one of the managed entities; shown as a dashed line in the previous picture)
- Communication (via Knox proxy)
- General Cloudera Manager operations
- Service-specific communication depending on the specific DataHub cluster in question
Data Warehouse communication endpoints
The Data Warehouse service operates significantly differently from Data Hub, as it runs on top of a Kubernetes cluster and does not include a Cloudera Manager instance.
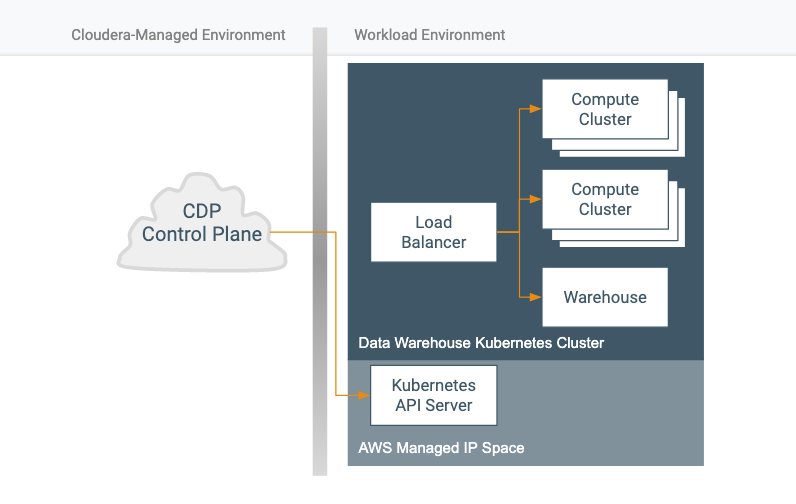
Primary command and control communication goes to the Kubernetes API server. This endpoint is specific to a particular Kubernetes cluster, but it is provisioned by the cloud provider outside of the customer VPC. Whether or not it is Internet-facing is independent of the VPC configuration. The Data Warehouse service doesn’t make connections to endpoints in the cluster.
Machine Learning communication endpoints
In terms of communication, a Machine Learning Workspace looks very similar to a Data Warehouse workspace in that it is also a Kubernetes cluster, although the contents differ.
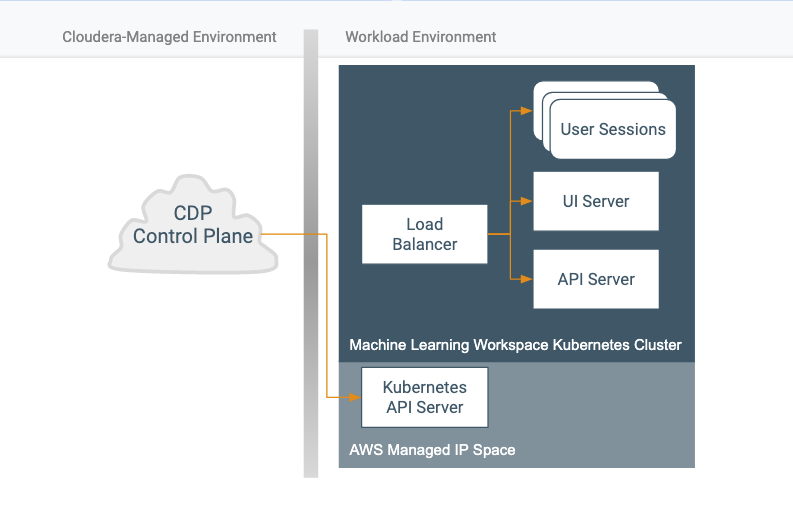
Primary command and control communication goes to the Kubernetes API server. This endpoint is specific to a particular Kubernetes cluster, but it is provisioned by the cloud provider outside of the customer VPC. Whether or not it is Internet-facing is independent of the VPC configuration. The Machine Learning service doesn’t make connections to endpoints in the cluster.
