Spark entities created in Apache Atlas
Each Spark entity in Atlas includes detailed metadata collected from Spark.
The following diagrams show a summary of the entities created in Atlas for Spark operations. The data assets that Spark operations act upon are collected through HMS. The supertypes that contribute attributes to the entity types are shaded.
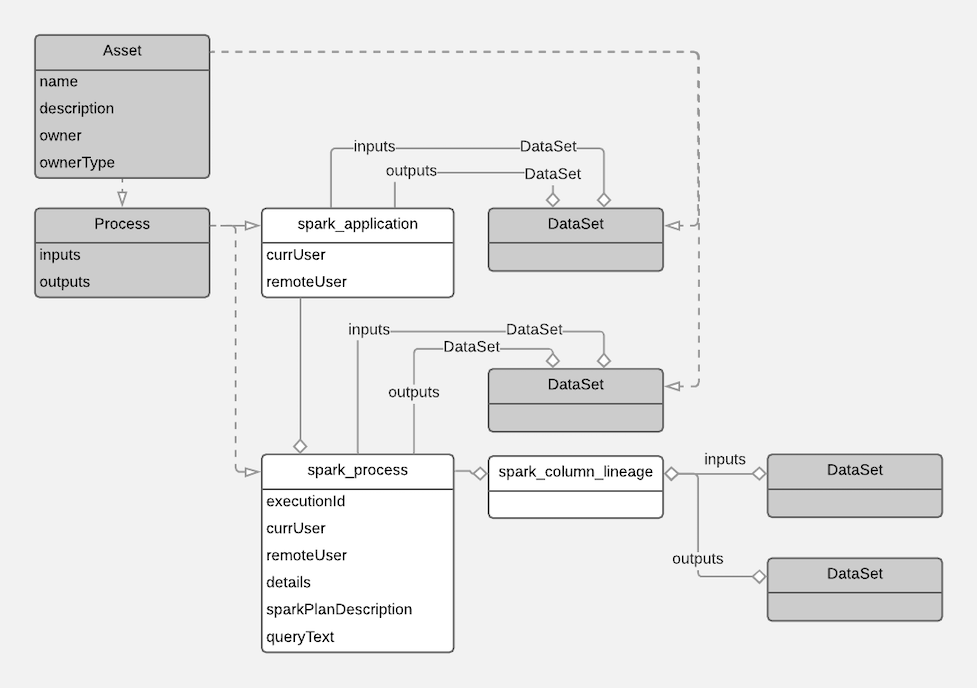
The metadata collected for each entity type is as follows:
Spark Application
| Identifier | Example content |
|---|---|
| typeName | spark_application |
| guid | System generated ID. This value is used to identify the entity in the Atlas Dashboard URL. |
| qualifiedName |
|
| name | Spark Job + <Spark application
ID> |
| description | Metadata from Spark. Reserved for future use. |
| displayName | Reserved for future use. |
| owner | Metadata from Spark. Reserved for future use. |
| currentUser | Metadata from Spark. In a Kerberized environment, this value contains the principal name. |
| remoteUser | Metadata from Spark. In a Kerberized environment, this value contains the principal name. |
| userDescription | Metadata from Spark. Reserved for future use. |
| replicatedFrom | Reserved for future use. |
| replicatedTo | Reserved for future use. |
| Relationship: inputs | Reserved for future use. |
| Relationship: outputs | Reserved for future use. |
| Relationship: processes | List of Spark process entities created as part of the processing accomplished in this Spark job. |
Spark Process
| Identifier | Example content |
|---|---|
| typeName | spark_process |
| guid | System generated ID. This value is used to identify the entity in the Atlas Dashboard URL. |
| qualifiedName |
where n is a sequential integer assigned by the Spark engine and the application ID is for the parent Spark job. |
| name |
where n is a sequential integer assigned by the Spark engine. The number is unique only for the job, so it is possible to have Spark processes with duplicate names in Atlas. |
| description | Metadata from Spark. Reserved for future use. |
| owner | Metadata from Spark. Reserved for future use. |
| details | Metadata from Spark describing the logical plan. |
| displayName | Reserved for future use. |
| executionId | Metadata from Spark. |
| inputs | List of the input tables or views, including each entity’s type name and the qualified name. |
| outputs | List of the output objects, including each entity’s type name and the qualified name. |
| queryText | Metadata from Spark. Reserved for future use. |
| currUser | Metadata from Spark. In a Kerberized environment, this value contains the principal name. |
| remoteUser | Metadata from Spark. In a Kerberized environment, this value contains the principal name. |
| executionTime | Metadata from Spark. |
| details | Query plan text, including parsed logical plan, analyzed logical plan, optimized logical plan, and physical plan. |
| sparkPlanDescription | Physical plan text. |
| replicatedFrom | Reserved for future use. |
| replicatedTo | Reserved for future use. |
| userDescription | Metadata from Spark. Reserved for future use. |
| Relationship: inputs | List of the input tables or views, including each entity’s type name and the qualified name. |
| Relationship: outputs | List of the output objects, including each entity’s type name and the qualified name. |
| Relationship: application | The Spark application entity that describes the Spark job in which this process was created. |
Spark Column Lineage
| Identifier | Example Content |
|---|---|
| typeName | spark_column_lineage |
| guid | System generated ID. This value is used to identify the entity in the Atlas Dashboard URL. |
| qualifiedName | <output_table_name>-<timestamp>-<output_column_name> |
| name | Same as qualifiedName. |
| Relationship: Process | Name of the spark_process entity that
produced this lineage.
spark_process_column_lineages |
| Relationship: inputs | List of the input columns, including each entity’s type name and the qualified name. |
| Relationship: outputs | Output column, including each entity type name and the qualified name. |
