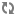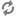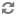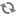If your environment is using Active Directory, you must enable remote scripting and configure domain policies for Windows Remote Management, complete the following instructions on a domain controller machine.
Open the Group Policy Management Editor by clicking Default Domain Policy from
Group Policy Management > Domains > <domain name> > Default Domain Policy, and then click Edit.Set the WinRM service to
autostart.From the Group Policy Management Editor, go to
Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Remote Management (WS-Management).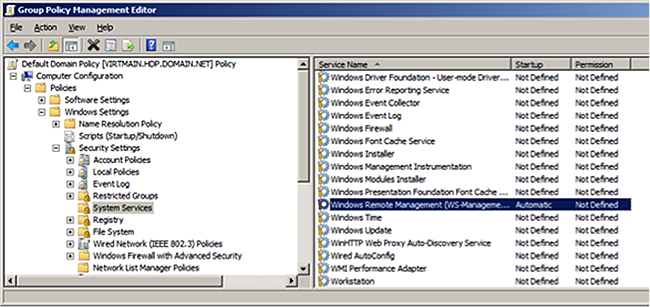
Set
Startup ModetoAutomatic.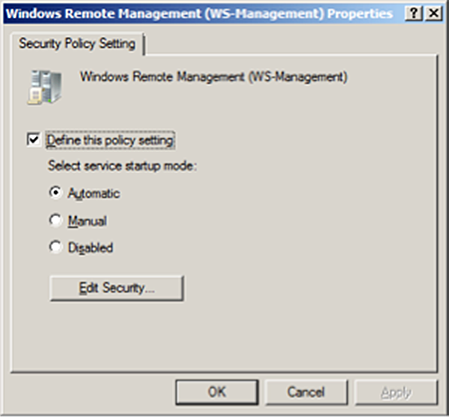
Add firewall exceptions to allow the service to communicate.
Go to
Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.To create a new Inbound Rule, right-click
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
Specify the rule type as
Predefined, Windows Remote Management.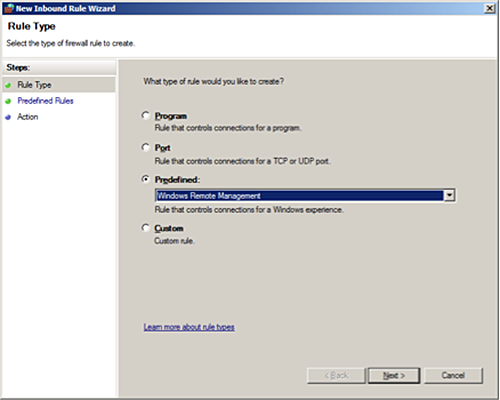
The Predefined rule automatically creates two rules:
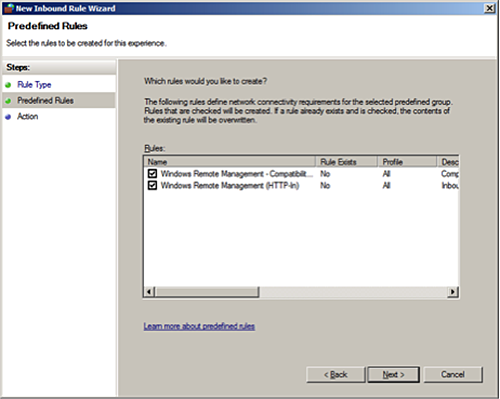
Configure
ActionasAllow the connection.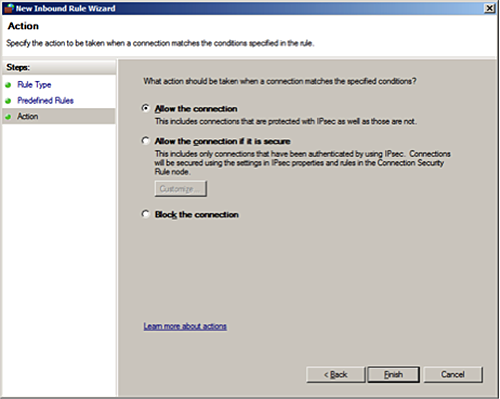
Click
Finish.
Set script execution policy.
Go to
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows PowerShell.At
Setting, selectTurn on Script Execution.Set
Execution PolicytoAllow all scripts.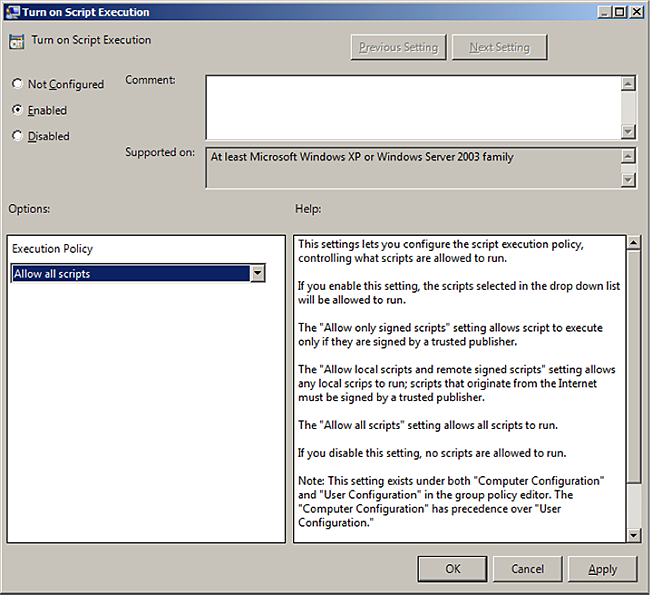
Set up the WinRM service.
Go to
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Remote Management (WinRM) > WinRM Service.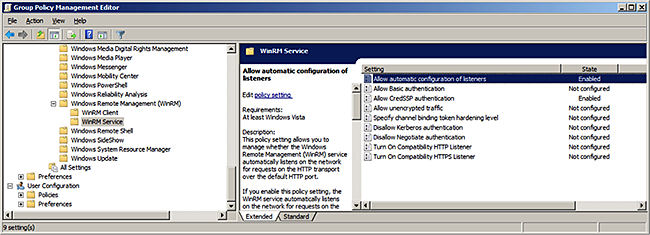
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
Note In Windows Server 2012, the "
Allow automatic configuration of listeners" option has changed to "Allow remote server management through WinRM".Create a WinRM listener.
To allow automatic configuration of listeners, select
Enabled, and then setIPv4 filterto*(all addresses) or specify a range: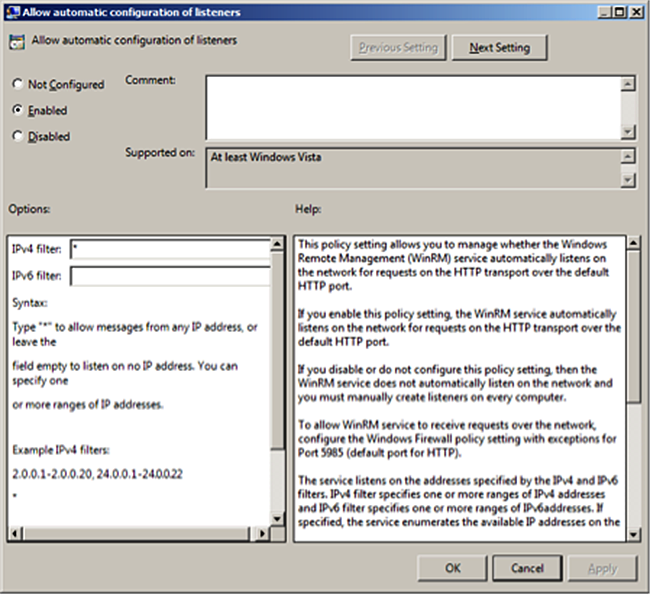
Allow
CredSSPauthentication and clickOK.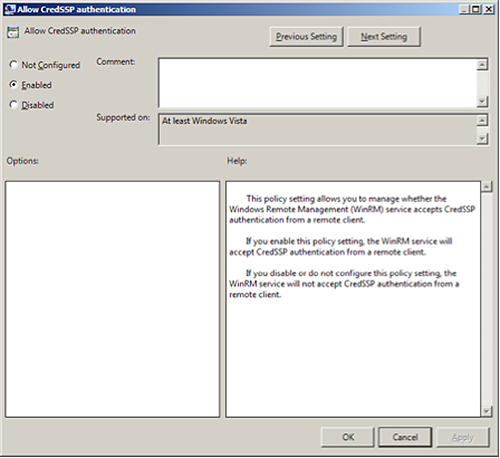
Set up the WinRM client.
Go to
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Remote Management (WinRM) > WinRM Client.Configure the trusted host list (the IP addresses of the computers that can initiate connections to the WinRM service).
Set
TrustedHostsListto*(all addresses) or specify a range.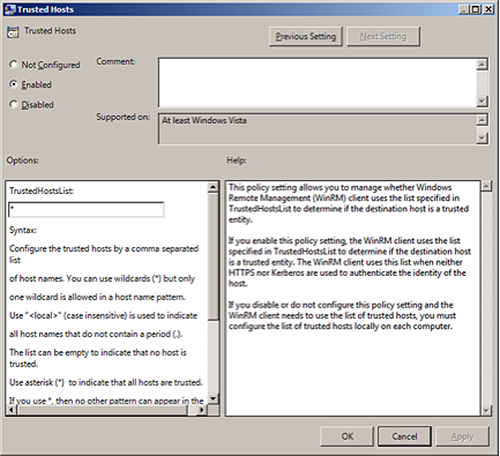
Set
Allow CredSSP authenticationtoEnabled, and clickOK.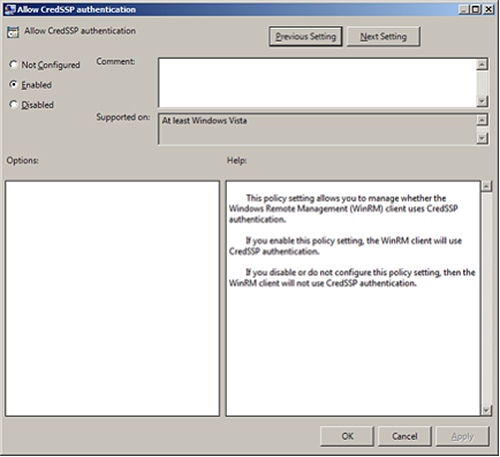
Enable credentials delegation.
Go to
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > System > Credentials Delegation.To allow delegation of fresh credentials, select
Enabled.Under
Options, selectShow. SetWSMANto*(all addresses) or specify a range. ClickNext Setting.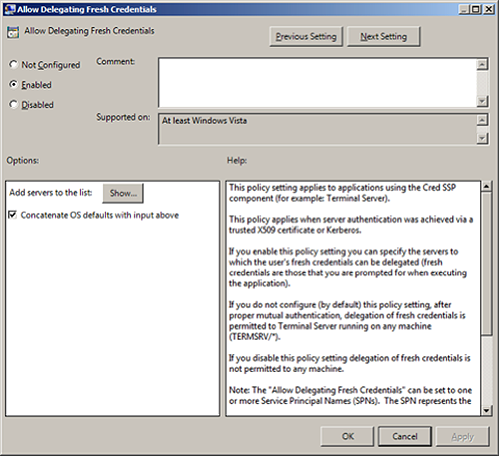
Select
Enabledto allow delegation of fresh credentials with NTLM-only server authentication.Under
OptionsclickShow. SetWSMANto*(all addresses), or specify a range. ClickFinish.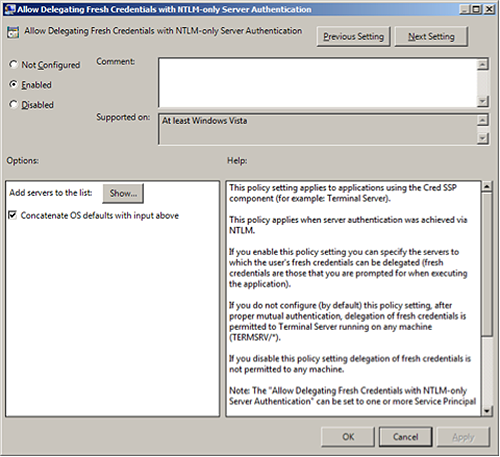
Enable the creation of WSMAN SPN.
Go to
Start > Run. In the dialog box, enterADSIEdit.msc. ClickEnter.Expand the
OU=Domain Controllersmenu item and selectCN=domain controller hostname.Go to
Properties > Security > Advanced > Add.Enter
NETWORK SERVICE, clickCheck Names, then clickOK.In the
Permissionfield, selectValidated write to service principal name.Click
Allow.To save your changes, click OK.
Restart the WinRM service and update policies.
At the domain controller machine, open a PowerShell window and enter:
Restart-Service WinRM
At each of the other hosts in domain, enter:
gpupdate /force
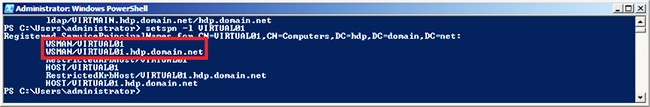
Ensure that SPN-s WSMAN is created for your environment.
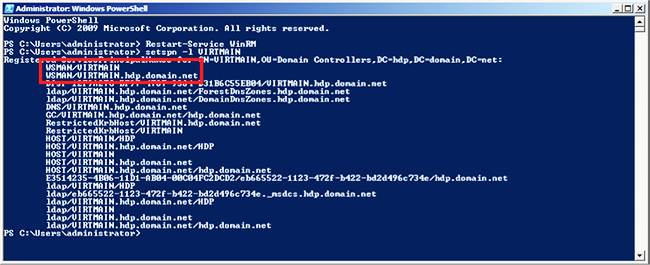
At your domain controller machine, enter:
setspn -l Domain_Controller_Hostname
You should see output similar to the following:
Check the WSMAN SPN on other hosts in the domain. Run the following command on any one of your host machines:
setspn -l Domain_Controller_Hostname
You should see output similar to the following: