How NFS Gateway authenticates and maps users
The manner in which NFS Gateway authenticates and maps users determines how NFS client users access HDFS through the NFS Gateway.
NFS Gateway uses AUTH_UNIX-style authentication, which means that
the user logged on the client is the same that NFS passes to HDFS.
For example, suppose that the NFS client has current user as admin.
When the user accesses the mounted HDFS directory, NFS gateway accesses HDFS as the
user admin. To access HDFS as hdfs user, you must
first switch the current user to hdfs on the client system before
accessing the mounted directory.
For the NFS client users accessing HDFS, the Gateway converts the User Identifier (UID) to a username, which is used by HDFS to check permissions. Therefore, you must ensure that the user on the NFS client host has the same name and UID as that on the NFS Gateway host.
 | Note |
|---|---|
If you use the same user management system such as LDAP/NIS to create and deploy
users to the HDP nodes and to the client host, then the user names and UIDs are
usually identical on both the client and the Gateway. |
If the user is created manually on different hosts, you might need to modify the UID, as specified in the following example, on either the client or the NFS Gateway to make them the same:
usermod -u 123 $myusername
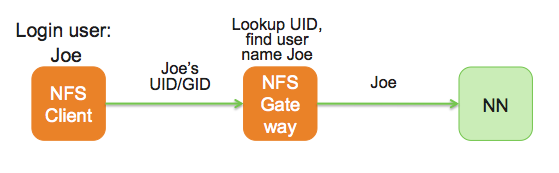
The following diagram illustrates how the UID and name are communicated between the NFS client, NFS gateway, and NameNode.