Securing KRaft
Learn about KRaft security and security configuration in CDP.
When you deploy Kafka in KRaft mode a set of specialized broker roles, KRaft Controller roles, are deployed on your cluster. KRaft Controllers communicate with brokers to serve their requests and to manage Kafka’s metadata. The connection between controllers and brokers can be secured using TLS/SSL encryption, TLS/SSL authentication, and/or Kerberos authentication.
By default KRaft Controllers inherit the security configuration of the parent Kafka service. For example, if TLS/SSL is enabled for Kafka, then Cloudera Manager automatically enables TLS/SSL for the KRaft Controllers in the cluster. As a result, if you configure security for the Kafka service, no additional configuration is required to secure KRaft Controllers.
However, if required, some security properties related to encryption and authentication can be configured separately for KRaft Controllers.
- TLS/SSL encryption and authentication
TLS/SSL configuration can be configured separately as the KRaft Controller role has its own set of TLS/SSL properties. You can enable or disable TLS/SSL as well as configure the key and truststore that the KRaft Controller roles use. For more information see, Configuring TLS/SSL for KRaft Controllers.
- Kerberos authentication
Kerberos cannot be enabled or disabled separately for KRaft Controllers. The default Kerberos principal for KRaft controllers, the
kraftuser, can be changed using the Role-Specific Kerberos Principal Kafka service property.
Ranger authorization
In addition to encryption and authentication, the default principal that KRaft Controllers run as is integrated with Ranger. For more information on the default policies set up for the user, see KRaft Ranger authorization.
Configuring TLS/SSL for KRaft Controllers
Learn how to configure TLS/SSL for KRaft Controllers.
KRaft Ranger authorization
Learn how KRaft integrates with Ranger as well as the default policies and permissions set up for KRaft.
KRaft in CDP uses the KafkaRangerAuthorizer to authorize requests coming from other entities. In KRaft mode, Kafka brokers forward requests to the controllers and the controllers authorize these requests.
Kraft Controllers run as the kraft user. By default, the Kafka resource-based
service in Ranger includes a kraft internal - topic policy. This policy grants
all permission on the __cluster_metadata topic for the kraft
user as well as Describe, Describe Configs, and Consume permissions for the
kafka user (default user for brokers). By default, other users do not have
access to the __cluster_metadata topic.
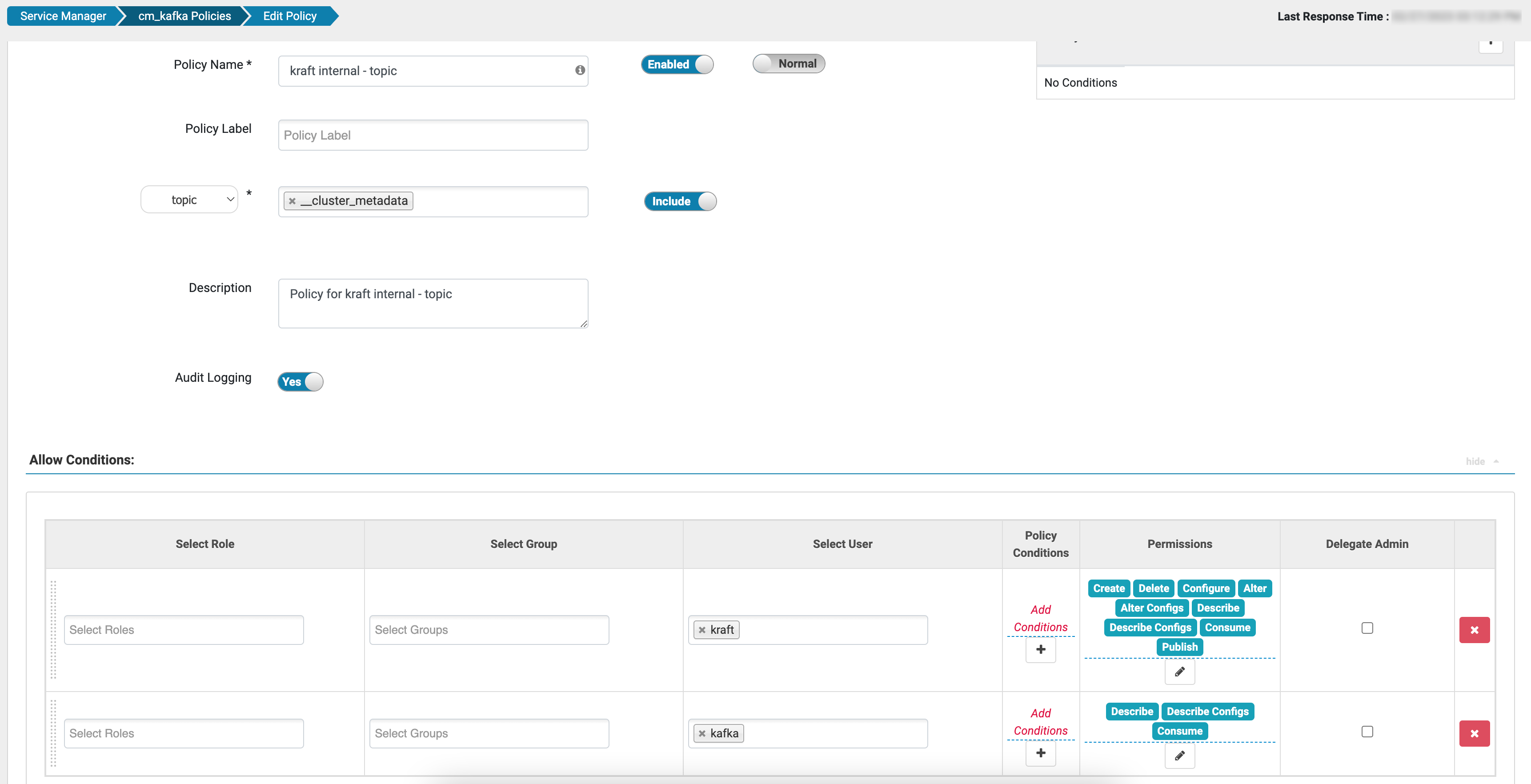
In addition, the kraft user is added to all default Kafka policies that grant
all permissions on Kafka resources.