November 3, 2020
This release of the Cloudera Data Warehouse (CDW) service on CDP Public Cloud introduces the new features and improvements that are described in this topic.
Impala Virtual Warehouse improvements
The following improvements to Impala Virtual Warehouses have been added in this release:
- High availability improvements, including fault-tolerance and multi-threading improvements.
- Full support for reading tables based on the ORC file format. This improves collaboration across the data lifecycle. Now Hive and Impala Virtual Warehouses can use the same data format and the SQL engine can be selected to optimize the workload without restrictions tied to the file format.
-
Ability to stop, start, and suspend Impala Virtual Warehouses:
Figure 1. Starting an Impala Virtual Warehouse 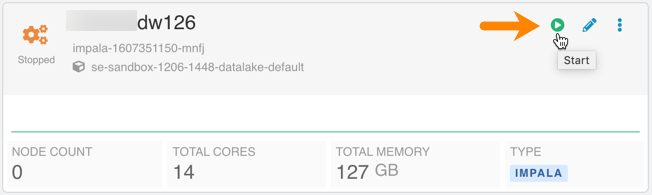
Figure 2. Stopping an Impala Virtual Warehouse 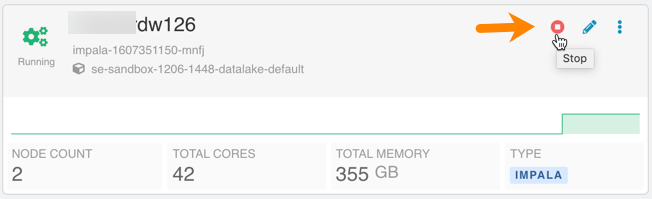
Figure 3. Suspending an Impala Virtual Warehouse 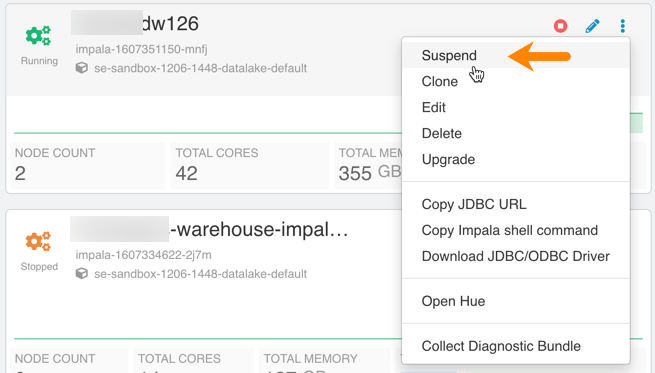
Hive Virtual Warehouse improvements
- Increased stability for Hive ACID and Compaction.
- Performance improvements:
- For short-running ad-hoc queries by decreasing task startup latency.
- For late projections by delay joins.
- For increased optimization of 'shared work.'
Improved security with machine user implementation
When you activate a new environment in Cloudera Data Warehouse (CDW), a machine user is created in the CDP User Management System (UMS) and is synchronized with the FreeIPA Management System (FMS). The FreeIPA machine user is used by most of the services such as Hue, Impala, VizApp, etc. instead of the FreeIPA LDAP admin user to communicate with the services within the Data Lake (for example, Ranger) that is associated with the CDP environment. As a security measure, Cloudera recommends upgrading the CDW environment, Database Catalogs, and the Virtual Warehouses to the latest CDW release.
To upgrade the CDW environment, contact Cloudera Support.
To upgrade the Database Catalog and the Virtual Warehouse, see Upgrading Database Catalogs and Virtual Warehouses in Cloudera Data Warehouse Public Cloud.
When you delete a CDW environment, the machine user is deleted from the UMS and the FMS.
Azure environments
- Executor nodes for Virtual Warehouses can now be scaled down to zero nodes, thereby using zero Azure resources for idle workloads, saving costs.
