Authenticating Cloudera AI Inference service
Cloudera AI Inference service uses Cloudera Workload Authentication JSON Web Token (JWT) to authenticate users and clients that interact with all HTTP endpoints exposed by the service workload.
Authenticating using JWT: All client applications must present a valid JWT as an HTTP Authorization Bearer token, as shown in the following example:
$ export CDP_TOKEN=${JWT}
$ curl -H "Authorization: Bearer ${CDP_TOKEN}" <URL>Supported JWT Issuers
Cloudera AI Inference service supports JWTs issued by the following identity providers:
- Knox Gateway Server (running in the Data Lake environment)
- User Management Service (UMS) (part of the Cloudera Control Plane)
Using Data Lake Knox JWT
You can use the Data Lake Knox JWT for most authentication scenarios. For more information about Apache Knox configuration, see Knox documentation.
- Open the Data Lake tab in the CDP environment UI.
- Click the Token Integration link.
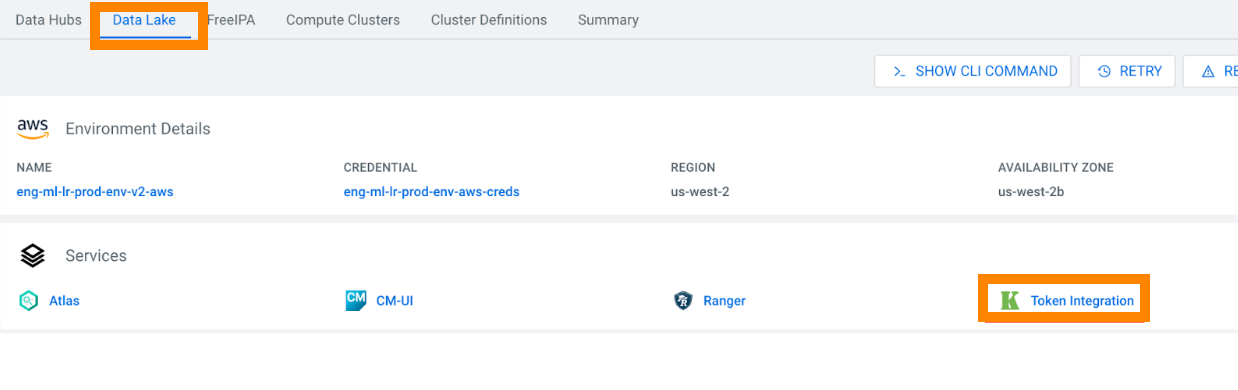
- In the newly opened window, click Token Generation.
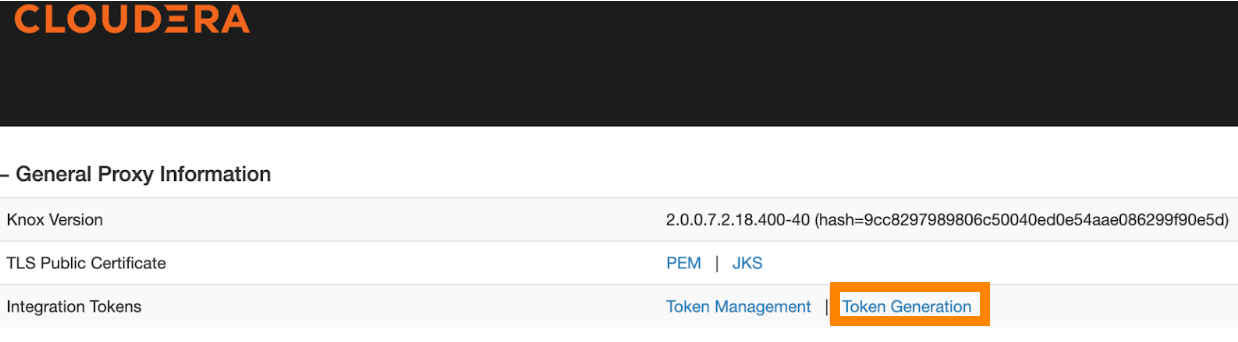
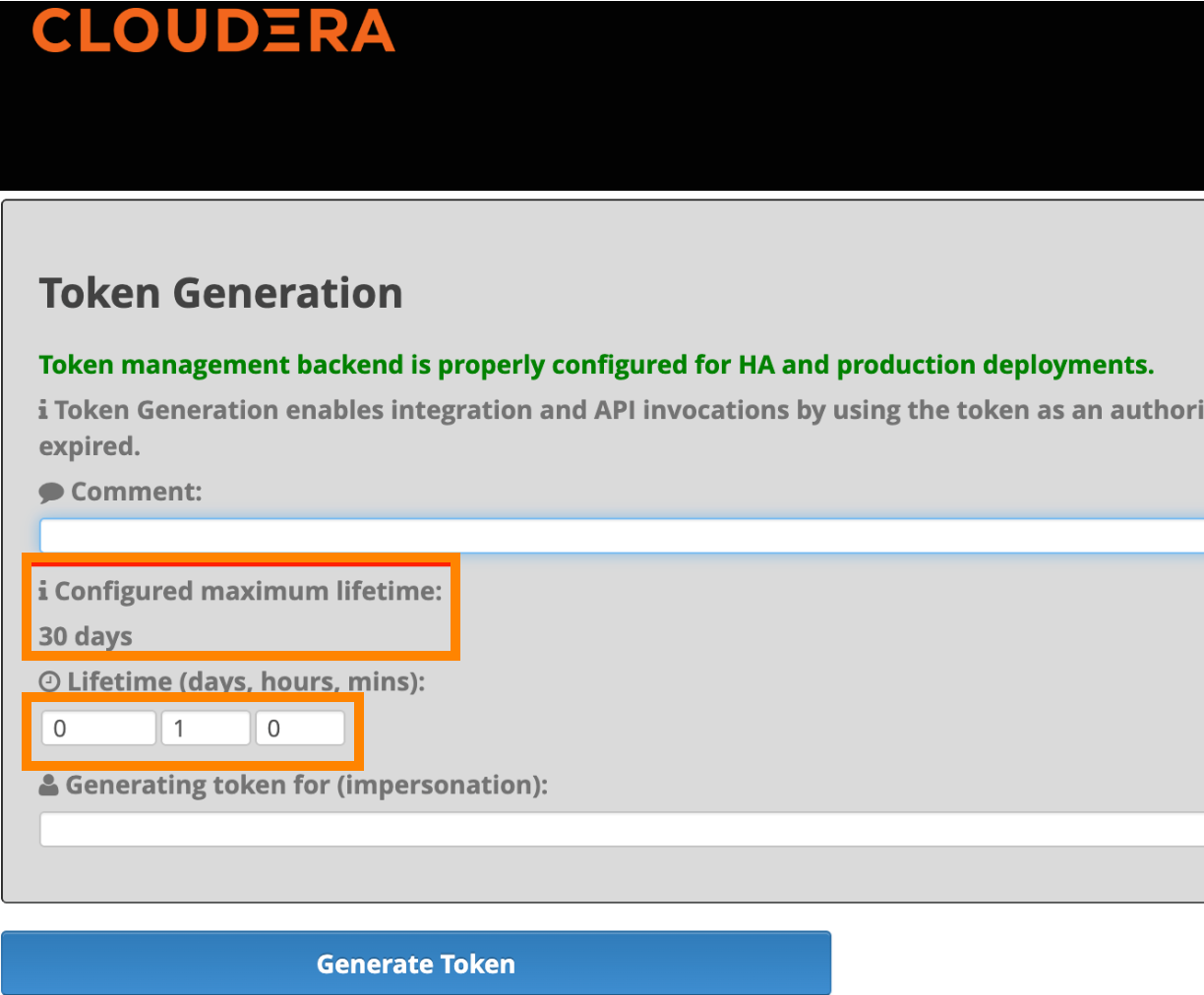
- Use the new window, set the desired token lifetime and generate a JWT.
- Copy the generated JWT from the Knox UI and use it in your application as an Authorization Bearer Token.
Using Auto-generated Kerberos JWTs
Some applications, such as Cloudera AI Workbench, automatically generates JWTs using the user's Kerberos credentials. These JWTs are automatically injected into all user workload pods , such as, workbench session pod, or an application pod and are stored at /tmp/jwt.
import json
JWT = json.load(open('/tmp/jwt', 'r'))['access_token']Use this token to authenticate your app to the AI Inference service.
Using a UMS JWT
- Option 1: Using the CDP
CLI:
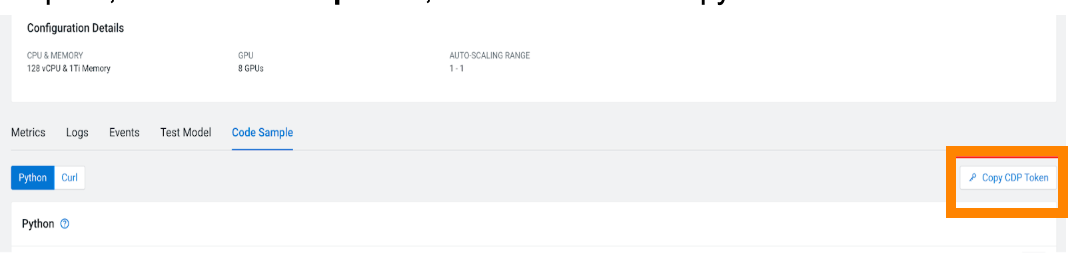
$ CDP_TOKEN=$(cdp iam generate-workload-auth-token --workload-name DE | jq -r '.token') - Option 2: Using Cloudera AI Inference service UI:
- Open the model's Endpoint details page.
- click Code Sample tab.
- Click Copy CDP Token.
UMS Token Expiration
- UMS tokens expire after one hour by default.
- If a token is expired, the service returns an HTTP 401 Unauthorized response.
- To extend the token lifetime, use the following
command:
$ cdp iam set-authentication-policy --workload-auth-token-expiration-sec <expiration-time-in-seconds>
Selecting the appropriate JWT token for Cloudera AI Inference service
Model Endpoint Management
Currently, Cloudera AI Registry supports only UMS JWT tokens. Therefore, when creating Model Endpoints in Cloudera AI Inference service, you must use a UMS JWT token. This is because the token is forwarded to the Cloudera AI Registry for the registry-level authentication.
All other use cases
For all other use cases, such as programmatic interactions and or automation workflow, including listing of Model Endpoints or performing inference calls, you should use the Data Lake Knox JWT instead of the UMS JWT. The Data Lake Knox JWT offers several advantages::
-
Faster Authentication : Authentication latency of the Data Lake Knox token is lower compared to the UMS token because the issuer operates within the same environment as Cloudera AI Inference service.
-
Environment Scope: Data Lake Knox JWT is scoped to a single Cloudera environment, unlike the tenant-wide scope of the UMS JWT.
-
Simplified Expiration Management: Configuring the expiration policy for the Data Lake Knox JWT is simpler.
-
Better Machine User Support: Creating and managing JWTs for machine users (or service accounts) is more easy when using the Data Lake Knox server.
Recomended best practices for authenticating long-running AI applications
AI applications, such as LLM-based chatbots, are often developed using SDKs that expect long-lived authentication tokens, such as API keys, which either do not expire, or have extended expiration periods. For such scenarios, Cloudera recommends creating a machine user and configuring the AI application to use the machine user’s credentials, that is, a JWT token, to interact with Model Endpoints hosted on Cloudera AI Inference service. Generating a long-lived JWT for a machine user is more secure than doing so for a human user.
- Create a Machine User in Cloudera.
- In the environment hosting the Cloudera AI Inference service, assign the EnvironmentUser and MLUser resource roles to the machine user. For more information, see Assign an environment resource role to a user.
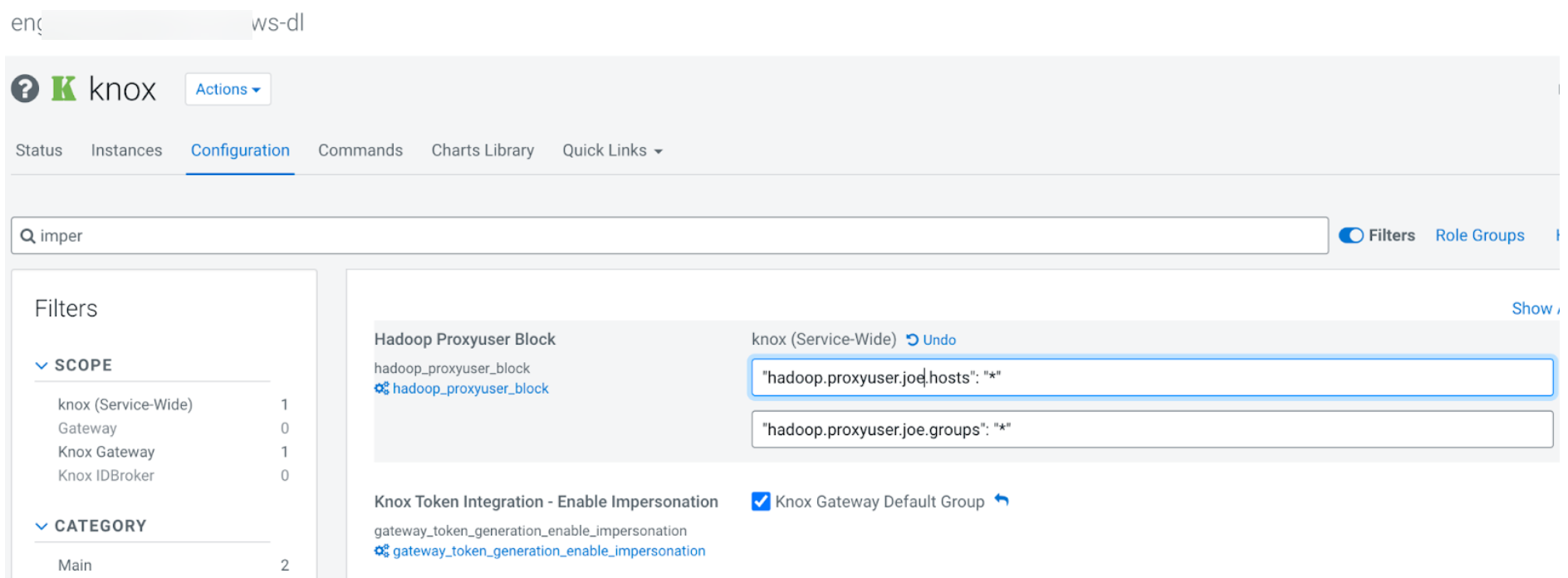
- Ensure that Impersonation is enabled in the Knox configuration for the
environment administrator. This can be done in the Data Lake's Cloudera Manager UI. The
following example screenshot illustrates Knox impersonation enabled for an environment
administrator with the username joe, allowing joe
to impersonate all environment users.
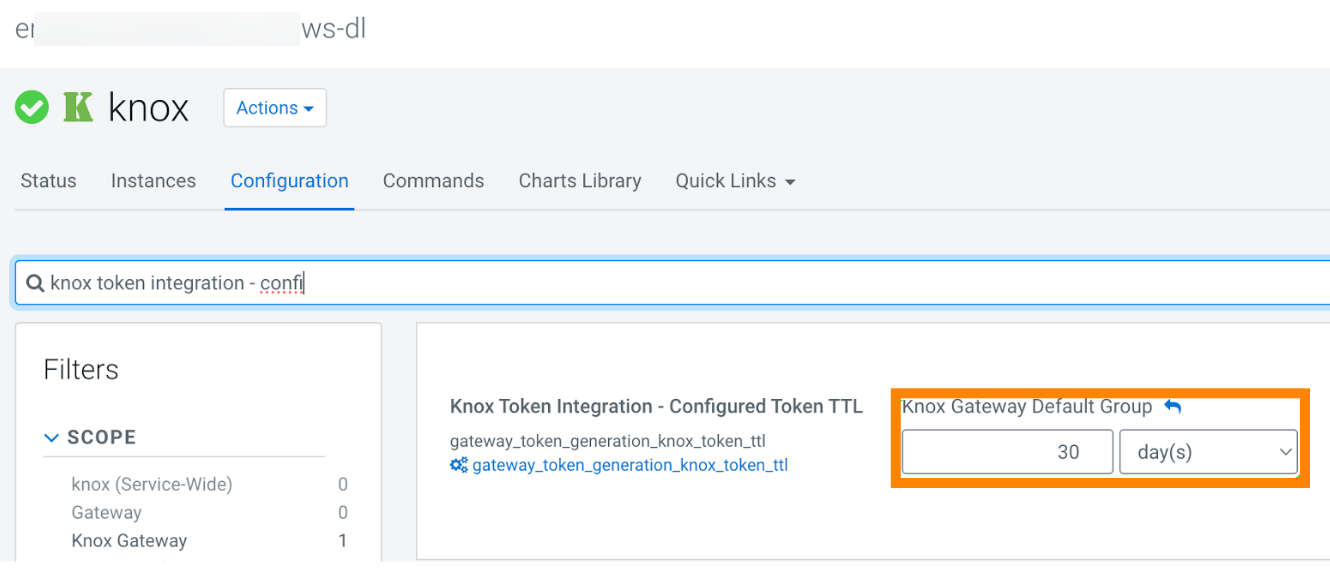
- Modify the maximum Time-to-Live (TTL) of Knox JWT token as needed. You have to restart
the Knox service if you make configuration changes. The following screenshot illustrates
an example where the maximum TTL is set to 30 days for this environment.
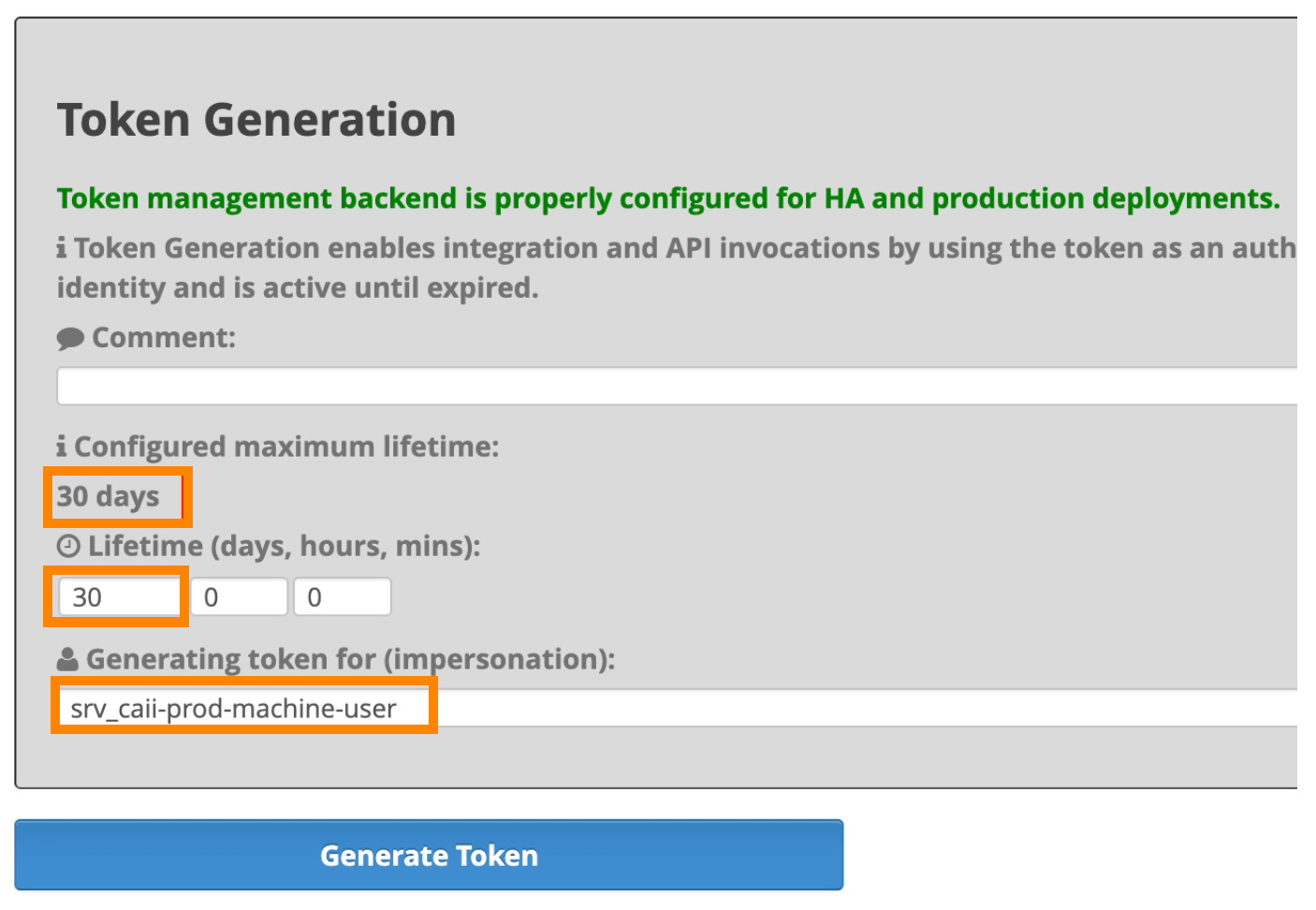
- Generate Knox JWT for the machine user. Refer to the Knox documentation for additional options
and detailed instructions. The following screenshot demonstrates the generation of a
token for a machine user.
- Copy the generated Knox JWT and configure your AI application to use it as a bearer token to authenticate with Cloudera AI Inference service.
- After generating the required token, you can optionally revert the maximum TTL of the Knox JWT token to its original value to prevent human users generating long-lived tokens
