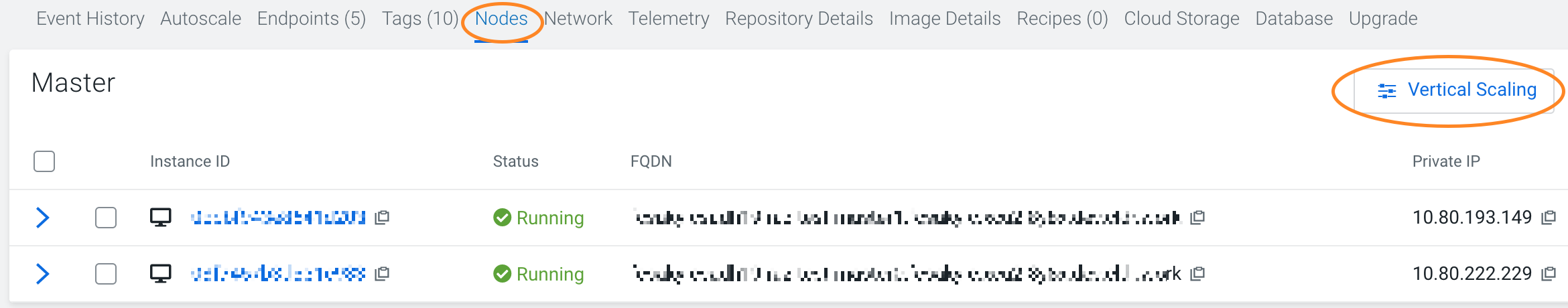
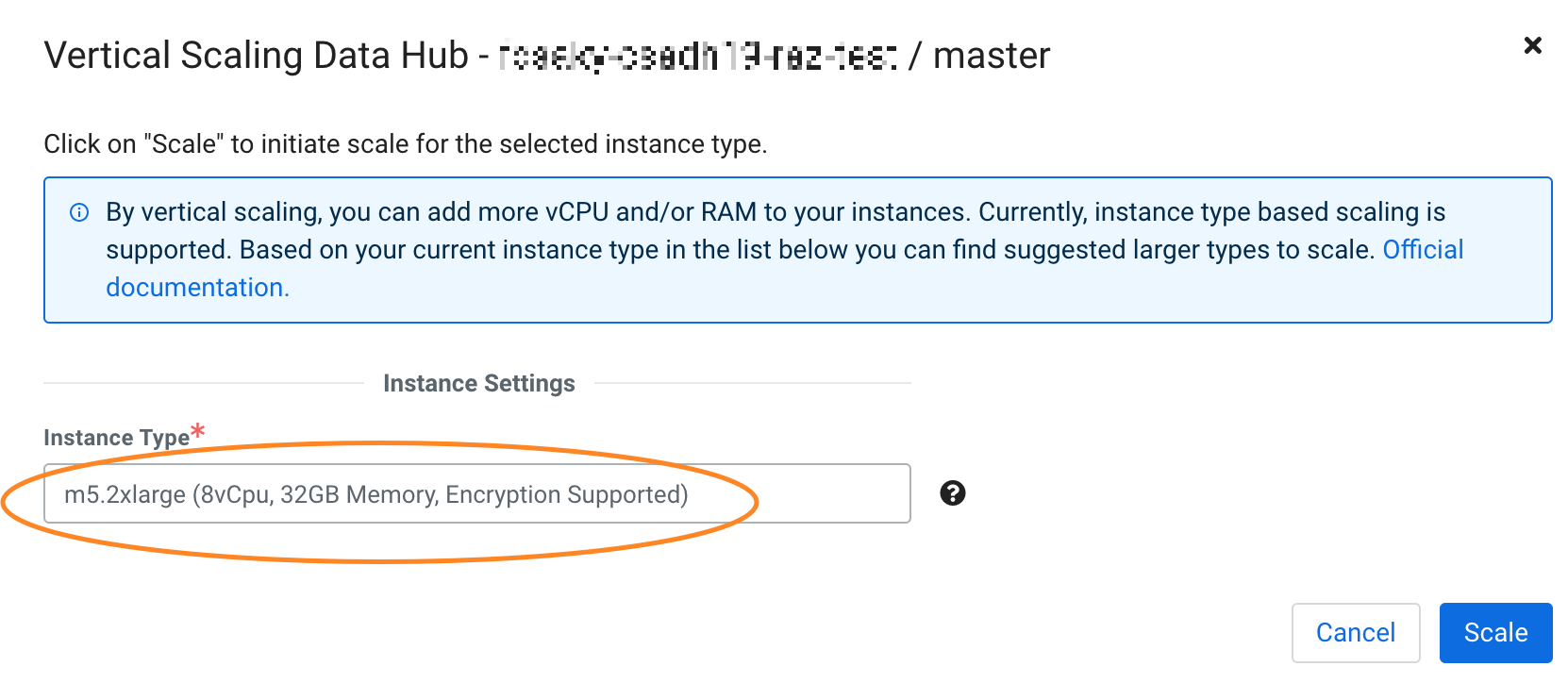
Vertically scaling instance types
If necessary, you can select a larger or smaller instance type for a Cloudera Data Hub or Data Lake cluster after it has been deployed in AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Limitations:
- You cannot scale down to a target instance type that has fewer ephemeral volumes than the current instance type.
- Vertical scaling to Azure v5 instances is not supported and results in the following
error:
Unable to resize since changing from resource disk to non-resource disk VM size and vice-versa is not allowed. - Vertical scaling is supported on AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- If you are using an instance without ephemeral disks, you can scale up or down to a new instance with ephemeral disks; however, the reverse is not supported. You cannot start with an instance with ephemeral disks and move to an instance without ephemeral disks.
For information on vertically scaling FreeIPA, see Vertically scale FreeIPA instances.