Adding a customer managed encryption key to a Cloudera environment running on Azure
By default, local Data Lake, FreeIPA, and Cloudera Data Hub disks attached to Azure VMs and the PostgreSQL server instance used by the Data Lake and Cloudera Data Hub clusters are encrypted with server-side encryption (SSE) using Platform Managed Keys (PMK), but you can optionally configure SSE with Customer Managed Keys (CMK).
The CMK can be specified during environment registration and, if present, is used for encrypting Data Lake, FreeIPA, and Cloudera Data Hub disks and PostgreSQL server instances. Alternatively, it is possible to specify it once the environment is running, in which case the CMK will only be used for Cloudera Data Hub clusters created after the CMK was added.
The disks that are attached to the VMs of the Data Lake, FreeIPA, and Cloudera Data Hub clusters will be associated with a Disk Encryption Set (DES) that is created with the key URL as the underlying encryption key version. The DES dedicated to the Cloudera environment will be created in the resource group of the environment before the FreeIPA launch at the beginning of the environment creation process.
- Azure prerequisites for using a CMK
- Registering a new Azure environment and specifying a CMK
- Creating a Cloudera Data Hub with the same CMK
- Checking whether a CMK exists for an Azure environment
- Adding a CMK to an existing Azure environment
Azure prerequisites for using a CMK
You can use your existing Azure vault and vault key or create a new Azure vault and vault key.
For detailed requirements, refer to Azure Prerequisites: Customer managed encryption keys.
Register an Azure environment with a CMK
You can specify an existing customer managed key (CMK) during Azure environment registration and the encryption key will be used to encrypt the VMs and databases running in the environment.
Steps
- Under Customer-Managed Keys, click Enable Customer-Managed Keys.
- In the same section, under Select Resource group select the resource group where the CMK is located.
- Provide the URL of the key value where the CMK resides. This is the same as the key identifier that you can copy directly from Azure Portal.
Use the following CDP CLI command to create an environment with the encryption key
created earlier. Replace the placeholders with actual values. For example
<ENVIRONMENT-NAME> should be replaced with an actual name.
cdp environments create-azure-environment \
--environment-name <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> \
--credential-name <CREDENTIAL_NAME> \
--region <REGION> \
--security-access cidr=<YOUR-ORGANIZATION’S_CIDR> \
--public-key '<SSH_PUBLIC_KEY>' \
--log-storage <STORAGE_LOCATION> \
--description '<DESCRIPTION>' \
--resource-group-name <ENV_RESOUCE_GROUP_NAME> \
--encryption-key-resouce-group-name <CMK_RESOUCE_GROUP_NAME> \
--encryption-key-url <KEY_RESOUCE_ID>
cdp environments set-id-broker-mappings \
--environment-name <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> \
--data-access-role <DATA_ACCESS_IDENTITY>\
--ranger-audit-role <RANGER_AUDIT_IDENTITY> \
--set-empty-mappings
cdp datalake create-azure-datalake \
--datalake-name <DATALAKE_NAME> \
--environment-name <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> \
--cloud-provider-configuration <STORAGE_LOCATION_BASE_CONFIGURATION>The encryption key can be present in a separate resource group than in which the
environment is being created. The resource group in which encryption key is present can be
provided using --encryption-key-resouce-group-name. Either
--encryption-key-resouce-group-name or --resource-group-name
must be present. Depending on the resource group where you environment and encryption key
reside, there are three possible use cases:
-
If your encryption key is in the same resource group as you wish to create the environment in, you can provide a common resource group with
--resource-group-nameparameter. In this case, you do not need to provide the--encryption-key-resouce-group-nameparameter. -
If your encryption key is in a different resource group than you wish to create the environment in and you wish to use some other existing resource group for the environment, you can provide encryption key’s resource group with
--encryption-key-resouce-group-nameand the environment’s resource group with--resource-group-name.
--encryption-key-resouce-group-name and the environment’s resource groups will
be created by Cloudera. You can obtain more complete commands using the instructions in Obtain CLI commands for registering an environment.
If you are using Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server in Cloudera, you can also specify a managed identity and thus use the same CMK for encrypting the Azure Flexible Server database instance used by Cloudera. For more information, see Configuring a CMK for data encryption in Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server .
Create a Cloudera Data Hub on Azure with a CMK
Use Cloudera web interface or CDP CLI to create a Cloudera Data Hub cluster. Note that this doesn’t require any extra steps, so you can refer to the Cloudera Data Hub documentation.
The disks that are attached to the VMs of the Cloudera Data Hub cluster will be associated with a Disk Encryption Set (DES) that is created with the key URL as the underlying encryption key version. The DES dedicated to the Cloudera environment will be created in the resource group of the environment at the beginning of the environment creation process (before the FreeIPA launch, specifically).
Check Azure environment’s CMK
You can check in an Azure environment’s summary whether a CMK is used to encrypt a given environment.
Steps
- In the Cloudera Management Console, navigate to Environments and click on the environment for which you would like to set a CMK.
- Click on the Summary tab.
- Scroll down to the Customer Managed Encryption Key section. If a CMK exists, the entry will look similar to:

- You can also find the CMK information by clicking on the Data Lake tab and then navigating to the Hardware tab.
- Click on >> on the right side of the screen next to any of the nodes to expand the node related information.
- Under Storage Details, the following information is included about the
CMK:
- Whether the node has been encrypted with a CMK
- CMK encryption key URL
- Disk Encryption Set ID
For example: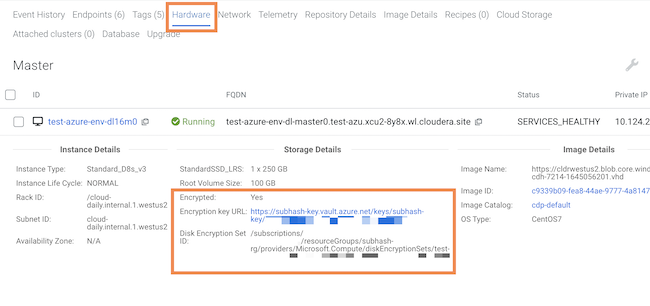
You can use the cdp environments
update-azure-encryption-resources command to check environment’s CMK encryption
status.
cdp environments
update-azure-encryption-resources command will return the disk encryption set,
encryption key, and encryption key's resource group details.Check Cloudera Data Hub's CMK
You can check in a Cloudera Data Hub’s hardware tab whether a CMK is used to encrypt it.
Steps
-
Navigate to the Cloudera Data Hub details > Hardware tab.
-
Click on >> on the right side of the screen next to any of the nodes to expand the node related information.
-
Under Storage Details, Under Storage Details, the following information is included about the CMK:
- Whether the node has been encrypted with a CMK
- CMK encryption key URL
- Disk Encryption Set ID
Set a CMK for an existing Azure environment
You can set a CMK for an existing environment. The CMK will be only used for encrypting disks of Cloudera Data Hub clusters created after the CMK was added.
Steps
-
In the Cloudera Management Console, navigate to Environments and click on the environment for which you would like to set a CMK.
-
Click on the Summary tab.
-
Scroll down to the Encryption section.
-
If no CMK has been set, you will see a message stating that there is no customer-managed key enabled.
-
Click on the edit button in the top right corner of the tab.
-
Click on the toggle button next to Enable Customer-Managed Keys to enable adding a CMK.
- Provide the following:
-
Provide the encryption key URL. This is the same as the key identifier that you can copy directly from Azure Portal.
-
If your encryption key resource group is different from the environment’s resource group, provide the name of the resource group.
-
Click Save.
-
You can add an encryption key for an existing environment that does not yet have encryption enabled.
cdp environments update-azure-encryption-resources \
--environment-name <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> \
--encryption-key-url <CMK_URL> \cdp environments update-azure-encryption-resources \
--environment-name <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> \
--encryption-key-url <CMK_URL> \
--encryption-key-resource-group-name <CMK_RESOURCE_GROUP>If you are using Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server in Cloudera, you can also specify a managed identity and thus use the same CMK for encrypting the Azure Flexible Server database instance used by Cloudera. For more information, see Configuring a CMK for data encryption in Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server .
