Encrypting Azure resources with customer managed keys
By default, local Data Lake, FreeIPA, AKS Volumes, AKS Secrets, and Cloudera Data Hub disks attached to Azure VMs and the PostgreSQL server instance used by the Data Lake and Cloudera Data Hub clusters are encrypted with server-side encryption (SSE) using Platform Managed Keys (PMK), but you can optionally configure SSE with Customer Managed Keys (CMK).
The CMK can be specified during environment registration and, if present, is used for encrypting Data Lake, FreeIPA, AKS Volumes, AKS Secrets, and Cloudera Data Hub disks and PostgreSQL server instances.
The disks that are attached to the VMs of the Data Lake, FreeIPA, and Cloudera Data Hub clusters will be associated with a Disk Encryption Set (DES) that is created with the key URL as the underlying encryption key version. This disk encryption set is also used for volume encryption for AKS clusters. The DES dedicated to the Cloudera environment will be created in the resource group of the environment before the FreeIPA launch at the beginning of the environment creation process.
When meeting Azure requirements for Cloudera, you should do the following:
- Add additional permissions for Cloudera provisioning credential
-
Create a key vault and a vault key
- If you are using Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server with Cloudera, you can optionally use the CMK used for encrypting VM disks for encrypting the Azure Flexible Server database instance used by Cloudera. In this case, you should create a managed identity.
Add additional permissions to your Azure policy
Make sure that the following additional permissions are set up for the Azure credential used in Cloudera environment creation, in addition to what is documented in Azure permissions.
All of them are actions and shall be granted at the scope of the resource group hosting the Cloudera environment:
"Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/read",
"Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/write",
"Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/deploy/action",
"Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/read",
"Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/write",
"Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/delete",
"Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/servers/read",
"Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/servers/keys/write",
"Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/accessPolicies/write"The following table explains why Cloudera needs these permissions:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
|
Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/read and Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/write |
Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/read is required to read the vaults. Without this, vaults in your subscription cannot be detected by Cloudera. Specifically, Cloudera must update the Key Vault access policy to add an entry for the DES SP. For this, Cloudera invokes an "update key vault" operation, which Azure implements as the following series of steps:
|
| Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/write | This is required to update the access policies for the DES created in the vault. |
| Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/deploy/action | This is required to create DES resources. Specifically, it’s required for DES SP creation (performed automatically alongside the DES creation) that will ultimately be used to access the Key Vault from the DES. |
| Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/read | This is required to check for the existence of and fetch the properties and status of DES resources created by Cloudera. |
| Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/write | This is required to create DES resources. |
| Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/delete | This is required to delete the DES during environment termination. |
|
Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/servers/keys/write and Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/accessPolicies/write |
This is required for setting up access policies and keys via an Azure Resource Manager template. |
Create a vault and add a vault key
You can use your existing vault and vault key or create a new vault and vault key.
Regardless of which of the two options you choose, the vault and the vault key must fulfill the following requirements:
-
The key vault must have purge protection enabled and be located in the same subscription and region as the target Cloudera environment.
-
The CMK must be an RSA key with a size of 2048 bits.
-
The number of Disk Encryption Set (DES) resources is limited to 1000 per region per subscription. In the present implementation, a single DES is created for each Cloudera environment, so this permits at most 1000 environments created in that region/subscription. The actual practical limit may be lower due to the limits set for other resource types.
Using an existing vault and vault key
If you have an existing key vault in Key Vaults in your Azure Portal:
-
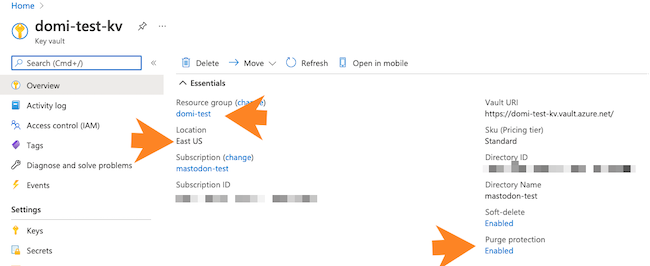
Navigate to the key vault’s Overview page and verify that the following parameters are set to the correct values:
-
The Region matches the target region of the Cloudera environment. Storage accounts can be in different resource groups than the key vault, provided the location/region is the same.
-
The Purge protection is enabled.
-
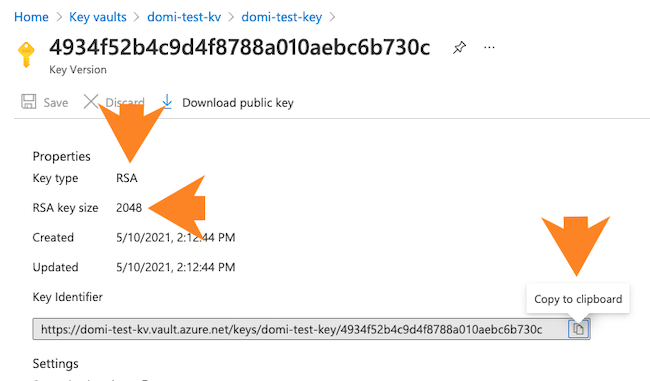
- Next, navigate to the vault key and:
-
Make sure that it is an RSA key with a size of 2048 bits.
-
Copy the key identifier (which is a HTTPS URL) for the key that is created. You will need to provide it during Cloudera environment registration later.
-
Creating a new vault and vault key
To create a vault and vault key, perform the following steps on your Azure portal:
- Create a key vault in the same region and resource group as the one that you would like to
use for registering the Cloudera environment.
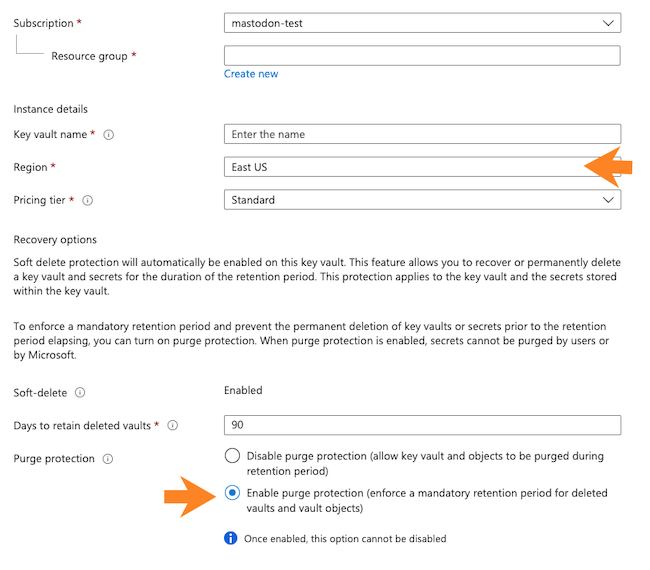
To create a key vault, navigate to Key vaults in Azure Portal and click on +New or on Create key vault. When providing key vault parameters, make sure that:
-
The Region matches the target region of the Cloudera environment. Storage accounts can be in different resource groups than the key vault, provided the location/region is the same.
-
The Purge protection is enabled.
-
Provide other parameters based on your organization's requirements. For instructions, see Create a vault in Azure documentation. Once done, click Create.
The following screenshot points out these three important parameters when creating a new key vault:
-
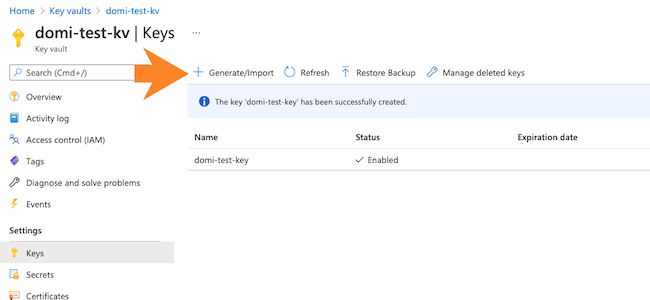
- Generate or import a key in the previously created key vault. Make sure that it is an RSA
key with a size of 2048, 3072 or 4096 bits. To generate a key, on your key vault’s properties pages, select Keys and then click on Generate/Import:
 Next provide key name and key type (make sure to select RSA). For detailed instructions, see Add a key to Key Vault in Azure documentation.
Next provide key name and key type (make sure to select RSA). For detailed instructions, see Add a key to Key Vault in Azure documentation.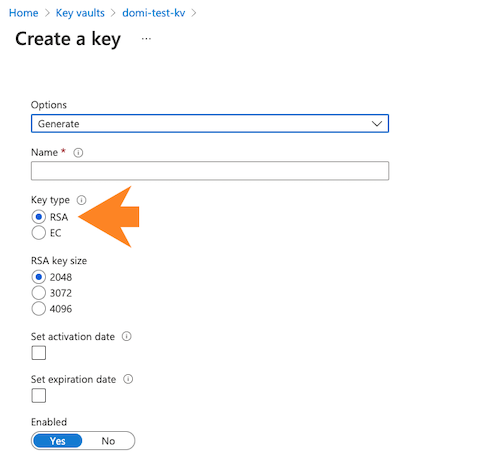
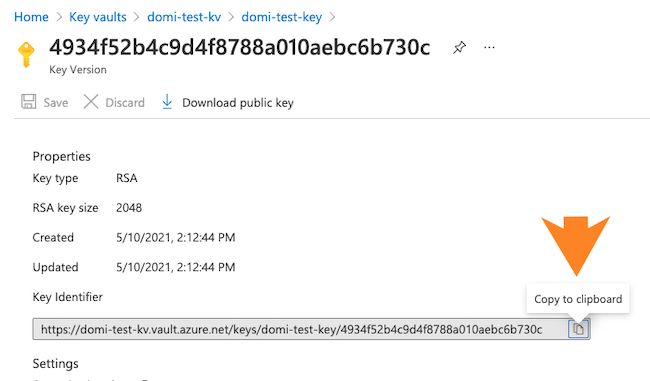
- Once the key has been created, navigate to the vault key details and copy the key identifier
(which is a HTTPS URL) for the key that is created. You will need to provide it during Cloudera environment registration later.
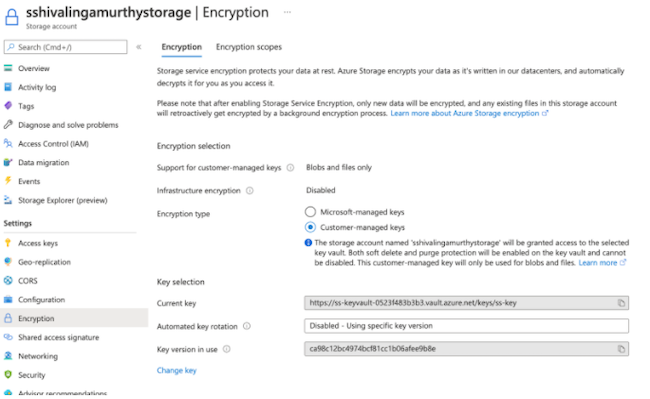
- If you need encryption on the Azure storage account, you can set it up using Azure portal
with the same or different encryption key. You can do this from the Encryption section
of your storage account settings.
Managed identity for encrypting Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server
If you are using Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server with Cloudera, you can optionally use the CMK used for encrypting VM disks for encrypting the Azure Flexible Server database instance used by Cloudera.
"dataActions": [
"Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/read",
"Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/wrap/action",
"Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/unwrap/action"
],There are two options:
Using a built-in role provided by Azure:
Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User contains the bare minimum set of cryptographic permissions, although theMicrosoft.EventGrid/*permissions are actually not needed. Alternatively, Key Vault Crypto User is also satisfactory, although it grants too many extra permissions on top of the ones that are strictly required.
Using a custom role:
We suggest cloning the Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User and possibly removing theMicrosoft.EventGrid/*permissions, which are not needed. Note that all the DataActions forMicrosoft.KeyVault/*specified in this role are needed.
In either of the two cases, the role assignment of the managed identity should be scoped at the target Key Vault of the CMEK.
For information about providing the managed identity in Cloudera, see Configuring a CMK for data encryption in Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server.
