Cloudera reference network architecture on Azure
This topic includes a conceptual overview of the Cloudera on cloud network architecture for Azure, its use cases, and personas who should be using it.
Overview
Cloudera on cloud allows customers to set up cloud Data Lakes and compute workloads in their cloud accounts on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. It maps a cloud account to a concept called the environment into which all Cloudera workloads, including Cloudera Data Hub clusters (compute workload clusters)and data services (such as Cloudera Data Engineering, Cloudera Data Warehouse, Cloudera AI, Cloudera Operational Database, Cloudera DataFlow) are launched. For these Data Lakes, Cloudera Data Hub clusters, and data services to function correctly, several elements of the cloud architecture need to be configured appropriately: access permissions, networking setup, cloud storage and so on. Broadly, these elements can be configured in one of two ways:
- Cloudera can set up these elements for the
customer
Usually, this model helps to set up a working environment quickly and try out Cloudera. However, many enterprise customers prefer or even mandate specific configurations of a cloud environment for Infosec or compliance reasons. Setting up elements such as networking and cloud storage requires prior approvals and they would generally not prefer, or even actively prevent, a third party vendor like Cloudera to set up these elements automatically.
- Cloudera can work with pre-created elements
provided by the customer
In this model, the flow for creating the cloud Data Lakes accepts pre-created configurations of the cloud environment and launches workloads within those boundaries. This model is clearly more aligned with enterprise requirements. However, it brings with it the risk that the configuration might not necessarily play well with Cloudera requirements. As a result, customers might face issues launching Cloudera workloads and the turnaround time to get to a working environment might be much longer and involve many tedious interactions between Cloudera and the customer cloud teams.
From our experience in working with several enterprise customers, the most complicated element of the cloud environment setup is the cloud network configuration. The purpose of this document is to clearly articulate the networking requirements needed for setting up a functional Cloudera environment on cloud into which the Data Lakes and compute workloads of different types can be launched. It attempts to establish the different points of access to these workloads and establishes how the given architecture helps to accomplish this access.
Along with this document, you can use the Terraform Cloudera deployment to automatically set up a model of this reference architecture, which can then be reviewed for security and compliance purposes. For more information, see Deploy Cloudera using Terraform.
Use cases
Cloudera on cloud allows customers to process data in the cloud storage under a secure and governed Data Lake using different types of compute workloads that are provisioned via Cloudera Data Hub or data services. Typically the lifecycle of these workloads is as follows:
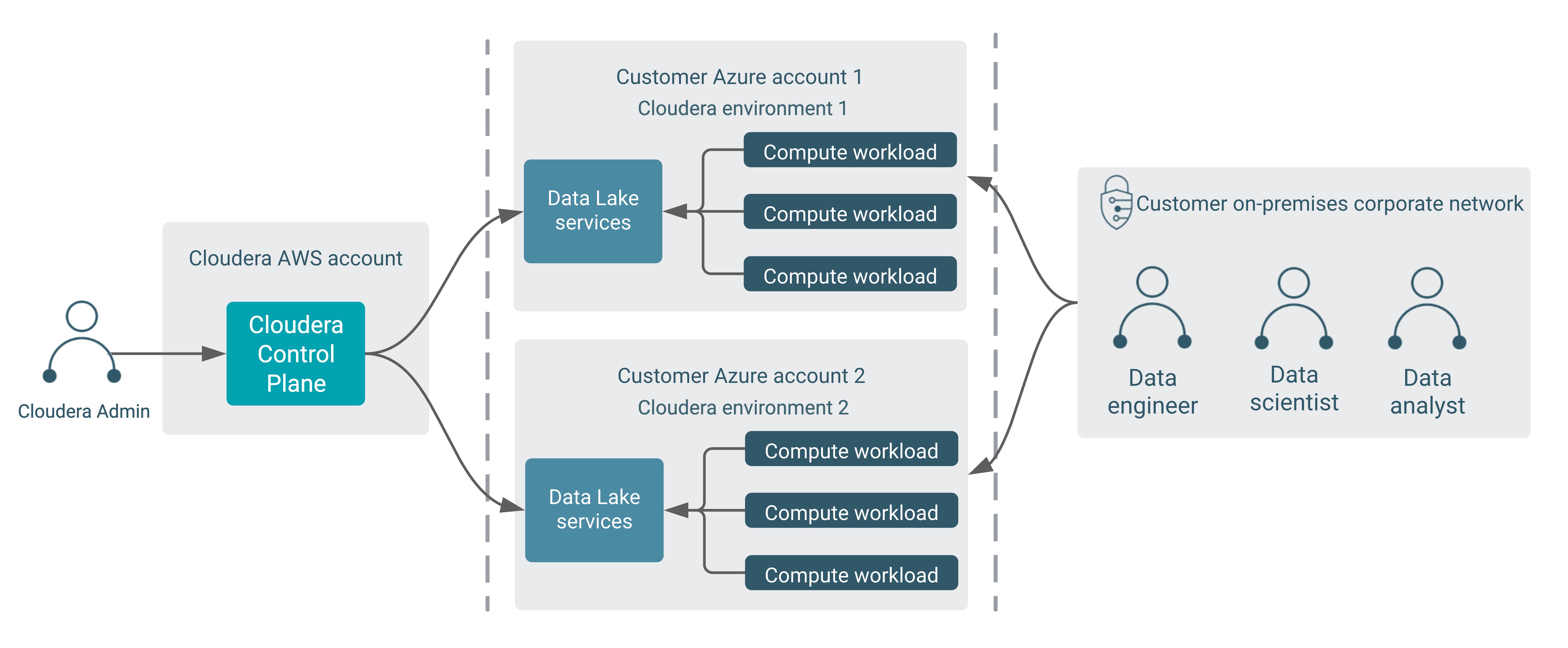
- A Cloudera environment is set up by a Cloudera admin using their cloud account. This sets up a cloud Data Lake cluster and FreeIPA cluster with security and governance services and an identity provider for this environment. The Cloudera admin may need to work with a cloud administrator to create all the cloud provider resources (including networking resources) that are required by Cloudera.
- Then one or more Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services can be launched, linked to the Data Lake. Each of these Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services typically serves a specific purpose such as data ingestion, analytics, machine learning and so on.
- These Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services are accessed by data consumers such as data engineers, analysts or scientists. This is the core purpose of using Cloudera on the public cloud.
- These compute workload clusters and data services can be long-running or ephemeral, depending on the customer needs.
There are two types of Cloudera users who interact with the product for different purposes:
- Cloudera admins - These persons are usually concerned with the launch and maintenance of the cloud environment, and the Data Lake, FreeIPA, Cloudera Data Hub clusters, and data services running inside the environment. They use a Cloudera Management Console running in the Cloudera AWS account to perform these operations of managing the environment.
- Data consumers - These are the data scientists, data analysts, and data engineers who use the Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services to process data. They mostly interact directly with the compute workloads (Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services) running in their cloud account. They could access these either from their corporate networks (typically through a VPN) or other cloud networks their corporate owns.
These two types of users and their interaction with Cloudera are represented in the following diagram: