Identifying Rogue Users from a Workload View
This task identifies rogue users, which are users that consume excessive amounts of resources that can impact your costs.
Describes how to use Workload Manager or Workload XM to identify rogue users.
- In a supported browser, log in to the Workload Manager or the Workload XM web UI.
- In the Clusters page, select the cluster required for analysis.
- From the Usage Analysis chart widget, select the required engine, such as Impala.
- In the engine page, locate the engine Usage Analysis chart widget.
-
From the Top Users by list do the following:
- Select the # Queries option and identify any rogue users who are running more than the average share of jobs or queries.
- Select the Memory option and identify any rogue users whose jobs or queries are consuming the largest amount of memory.
- Select the CPU option and identify any rogue users whose jobs or queries are over exceeding the cluster’s CPU.
-
Record any problems.
For example, when comparing memory consumption with the number of queries assigned to all users in the following Usage Analysis chart widget you will notice that the 3xksle8z user is running only 3% of the queries assigned, yet their queries are consuming more memory (5.9 PiB) than any other user.
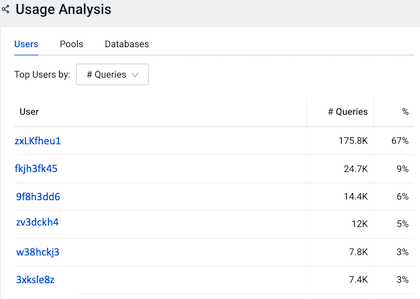
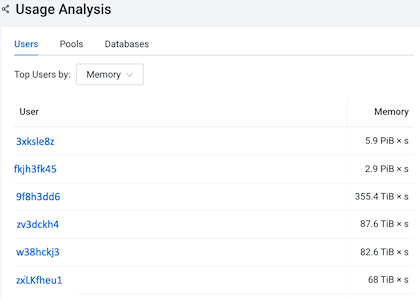
To discover which queries executed by user 3xksle8z are consuming the largest amount of memory, a new workload view was created to track this user’s resource consumption.
The following image shows the metrics of a SQL Statement that was identified as using an excessive amount of CPU from the new workload view, where there was over 200hrs CPU usage during a 34 hour period. Further metrics are displayed that show performance issues, identified as aggregation issues, and that show there are 14 tables missing table statistics.