Taxonomy of network architectures
This topic provides a high-level overview of each type of network architecture that Cloudera supports.
At a high level, there are several types of network architectures that Cloudera supports. As can be expected, each type brings a unique trade-off among various aspects, such as ease of setup, security provided, workloads supported, and so on. This section only provides a high level overview of each type. The characteristics of each type are explained under appropriate sections in the rest of the document. The users must review the advantages and disadvantages of each of these taxonomies in detail before making a choice suitable to their needs.
| Name | Description | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|
| Publicly accessible networks | Deploys customer workloads to hosts with public IP addresses. Security groups must be used to restrict access only to corporate networks as needed. | Easy to set up for POCs. Low security levels. |
| Semi-private networks | Deploys customer workloads to private subnets, but exposes services to which data consumers need access over a load balancer with a public IP address. Security groups or allow-lists (of IP addresses or ranges) on load balancers must be used to restrict access to these public services only to corporate networks as needed. | This option is fairly easy to set up too, but it may not solve all the use cases of access (in semi private networks). The surface of exposure is reduced, and it is reasonably secure. |
| Fully private networks | Deploys customer workloads to private subnets, and the services to which data consumers need access are only on private IPs. Requires connectivity to corporate networks to be provided using solutions like VPN gateways, and so on. | Complex to set up depending on prior experience of establishing such connectivity, primarily due to the way the customer has to solve the corporate network peering problem. But it is very secure. |
| Fully private outbound restricted networks | This is the same as fully private networks; Except, in addition, Cloudera provides a mechanism for users to configure an outbound proxy or firewall to monitor or restrict the communication outside their networks. | Most complex to set up, mainly considering the varied needs that data consumers would have to connect outside the VNet on an evolving basis. It is also the most secure for an enterprise. |
Cloudera Management Console to customer cloud network
This topic explains the possible ways in which the Cloudera Control Plane can communicate with the compute infrastructure in the customer network, in the context of the Cloudera Management Console.
As described previously, the Cloudera admin would typically use the Cloudera Management Console that runs in the Cloudera Control Plane to launch Cloudera environments with Data Lakes, FreeIPA, Cloudera Data Hub clusters, and data services into their cloud accounts. In order to accomplish this, the Cloudera Control Plane and the compute infrastructure in the customer network (such as VMs, AKS clusters) should be able to communicate with each other. Depending on the chosen network architecture, this communication can occur in the ways described below.
Publicly accessible networks
In this model of publicly accessible networks, the compute infrastructure must be reachable over the public internet from the Cloudera Management Console. While this is fairly easy to set up, it is usually not preferred by enterprise customers, as it implies that the VM nodes or AKS nodes are assigned public IP addresses. While the access control rules for these nodes can still be restricted to the IP addresses of the Cloudera Management Console components, it is still considered insecure for each of the network architectures described earlier.
Semi-private networks
Publicly accessible networks are easy to set up for connectivity, both from the Cloudera Control Plane and the customer on-prem network, but have a large surface area of exposure as all compute infrastructure has public IP addresses. In contrast, fully private networks need special configuration to enable connectivity from the customer on-prem network, due to having no surface area of exposure to any of the compute infrastructure. While very secure, it is more complex to establish.
There is a third configuration supported by Cloudera, semi-private networks, that provides some trade-offs between these two options. In this configuration, the user deploys the worker nodes of the compute infrastructure on fully private networks as described above. However, the user chooses to expose UIs or APIs of the services fronting these worker nodes over a public network load balancer. By using this capability, the data consumers can access the UIs or APIs of the compute infrastructure through these load balancers. It is also possible to restrict the IP ranges from which such access is allowed using security groups.
While this option provides a trade-off between ease of setup and exposure levels, it may not satisfy all use cases related to communication between various endpoints. For example, some compute workloads involving Kafka or NiFi would not benefit from having a simple publicly exposed load balancer. It is recommended that customers evaluate their use cases against the trade-off and choose an appropriately convenient and secure model of setup.
Fully private networks
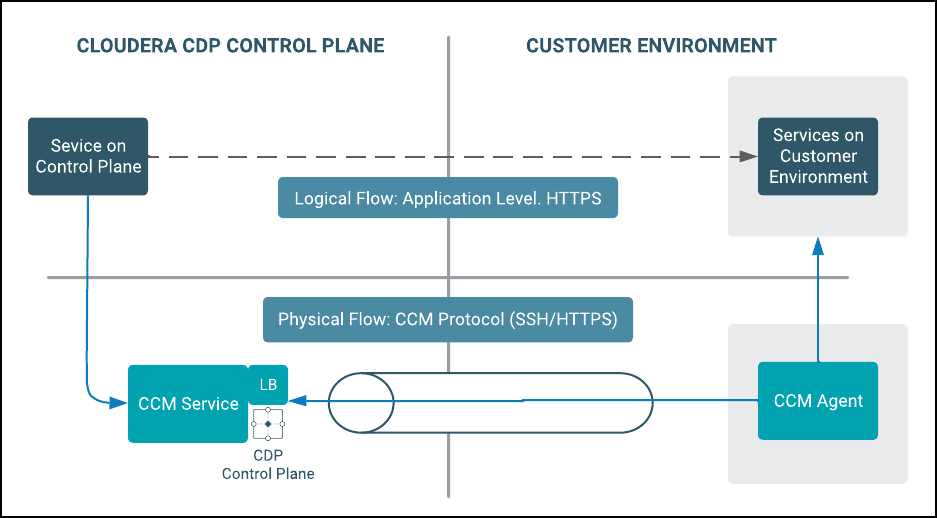
In this model of fully private networks, the compute infrastructure is not assigned any public IP addresses. In this case, communication between the Cloudera Control Plane and compute infrastructure is established using a “tunnel” that originates from the customer network to the Cloudera Control Plane. All communication from the Cloudera Control Plane to the compute nodes is then passed through this tunnel. From experience, Cloudera has determined that this is the preferred model of communication for customers.
To elaborate on the tunneling approach, Cloudera uses a solution called Cluster Connectivity Manager
. At a high level, the solution uses two components, an
agent (Cluster Connectivity Manager agent) that runs on a VM provisioned in the
customer network and a service (CCM service) that runs on the Cloudera Control Plane. The Cluster Connectivity Manager agent, at
start-up time, establishes a connection with the Cluster Connectivity Manager
service. This connection forms the tunnel. This tunnel is secured by asymmetric encryption.
The private key is shared with the agent over cloud specific initialization mechanisms, such as
a user-data script in Azure.
When any service on the Cloudera Control Plane wants to send a request to a service deployed on the customer environment (depicted in the below diagram as the “logical flow”), it physically sends a request to the Cluster Connectivity Manager service running in the Cloudera Control Plane. The Cluster Connectivity Manager agent and Cluster Connectivity Manager service collaborate over the established tunnel to accept the request, forward it to the appropriate service, and send a response over the tunnel to be handed over the calling service on the Cloudera Control Plane.
Currently, all AKS clusters provisioned by various Cloudera data services are enabled with public and private cluster
endpoints. The AKS public endpoint is needed to facilitate the interactions between Cloudera Control Plane and the AKS cluster while worker nodes and Kubernetes control
plane interact over private API endpoints. Cloudera Data Warehouse supports private
AKS endpoints today (see Enabling a private Cloudera Data Warehouse environment
in Azure Kubernetes Service
). There are plans to support private AKS endpoints for other
data services in the future. When this occurs, the documentation will be updated to reflect the
same.
Fully private outbound restricted networks
Fully private outbound restricted networks is a variant of the fully private network where customers would like to pass outbound traffic originating from their cloud account through a proxy or firewall and explicitly allow-list URLs that are allowed to pass through. Cloudera on cloud supports such configuration. If such network architecture is chosen, the customer must ensure the following:
-
Users configure a proxy for the environment via Cloudera, as documented in
Using a non-transparent proxy
. -
Compute resources (such as VMs used by Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services) can connect to the proxy or firewall via appropriate routing rules.
-
The proxy or firewall is set up to allow connections to all hosts, IP ranges, ports, and protocol types that are documented in
Azure outbound network access destinations
.
Customer on-prem network to cloud network
After Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services are launched in the customer’s cloud network, data consumers such as data engineers, data scientists, and data analysts access services running in these Cloudera data services. Sometimes, Cloudera admins who set up and operate these clusters might need this access to diagnose any issues the clusters face.
Examples of these include:
- Web UIs such as:
- Hue: For running SQL queries in Hive tables
- Cloudera AI Workbenches: For accessing Cloudera AI projects, models, notebooks, and so on
- Cloudera Manager: For Cloudera Data Hub clusters and Data Lakes
- Atlas and Ranger: For metadata, governance, and security in the Data Lake
- JDBC endpoints: Customers can connect tools such as Tableau using a JDBC URL pointing to the Hive server.
- SSH access: Data engineers might log in to nodes on the compute workload clusters and data services to run data processing jobs using YARN, Spark, or other data pipeline tools.
- Kube API access: Cloudera data services that run on AKS (such as Cloudera Data Warehouse and Cloudera AI) also provide admin access to Kubernetes for purposes of diagnosing issues.
- API access: Customers can use APIs for accessing many of the services exposed via the web UIs for purposes of automation and integration with other tools, applications, or other workloads they have. For example, Cloudera AI exposes the Cloudera AI API v2 to work with Cloudera AI projects and other entities. See Cloudera AI API v2.
These services are accessed by these consumers from within a corporate network inside a VPN. These services typically have endpoints that have a DNS name, the format of which is described more completely in the DNS section of this reference architecture documentation. These DNS names resolve to IP addresses assigned to the nodes, or load balancers fronting the ingest controllers of Kubernetes clusters. Note that these IP addresses are usually private IPs; Therefore, in order to be able to connect to these IPs from the on-premise network within a VPN, some special connectivity setup would be needed, typically accomplished using technologies like VPN peering, DirectConnect, transit gateways, and so on. While there are many options possible here, this document describes one concrete option of achieving this connectivity.
