Architecture diagrams
This topic includes diagrams illustrating the various elements of the network architecture in the customer’s cloud account into which Cloudera environments with Data Lakes, Cloudera Data Hub clusters, and data services will be launched.
Cloudera recommends that customers configure their cloud networks as described in this chapter and illustrated in the following diagrams. This will help onboarding Data Lakes, Cloudera Data Hub cluster, and data services smoothly. The following diagram illustrates the configuration for a fully private network that can be configured by the customer. This configuration can be provided by the Cloudera admins when they are setting up Cloudera environments and workloads which will get launched into this configuration.
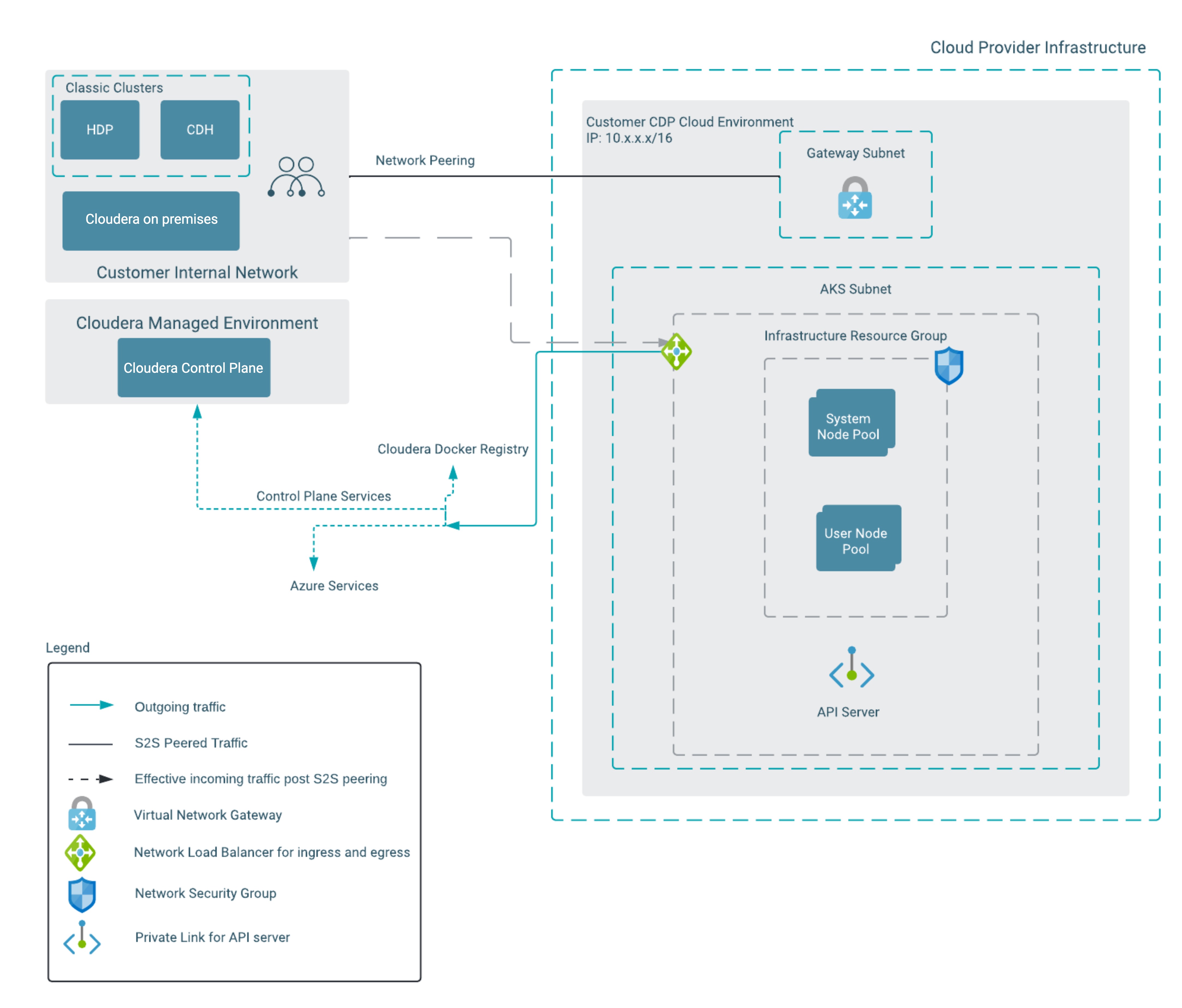
Note the following points about this architecture:
- The configuration is a fully private network configuration - that is, the workloads are launched on nodes that do not have public IP addresses.
- Workloads connect to the Cloudera Control Plane over a fixed IP and port range.
- For users to be able to connect from the customer on-prem network to the Cloudera workloads in the private subnet, some network connectivity setup is required. In this case, a customer's network peered to Azure VNet via Azure VPN gateway is shown.
Some of the Cloudera data services are based on Azure AKS clusters. Azure’s AKS manages the Kubernetes control plane nodes while the worker nodes that make up the Cloudera workload cluster get provisioned in the customer’s VPC. The AKS control plane has an API endpoint for administrative purposes which is commonly referred to as API server address. The data service itself is accessible through a service endpoint ELB.
This is illustrated in the following diagram:
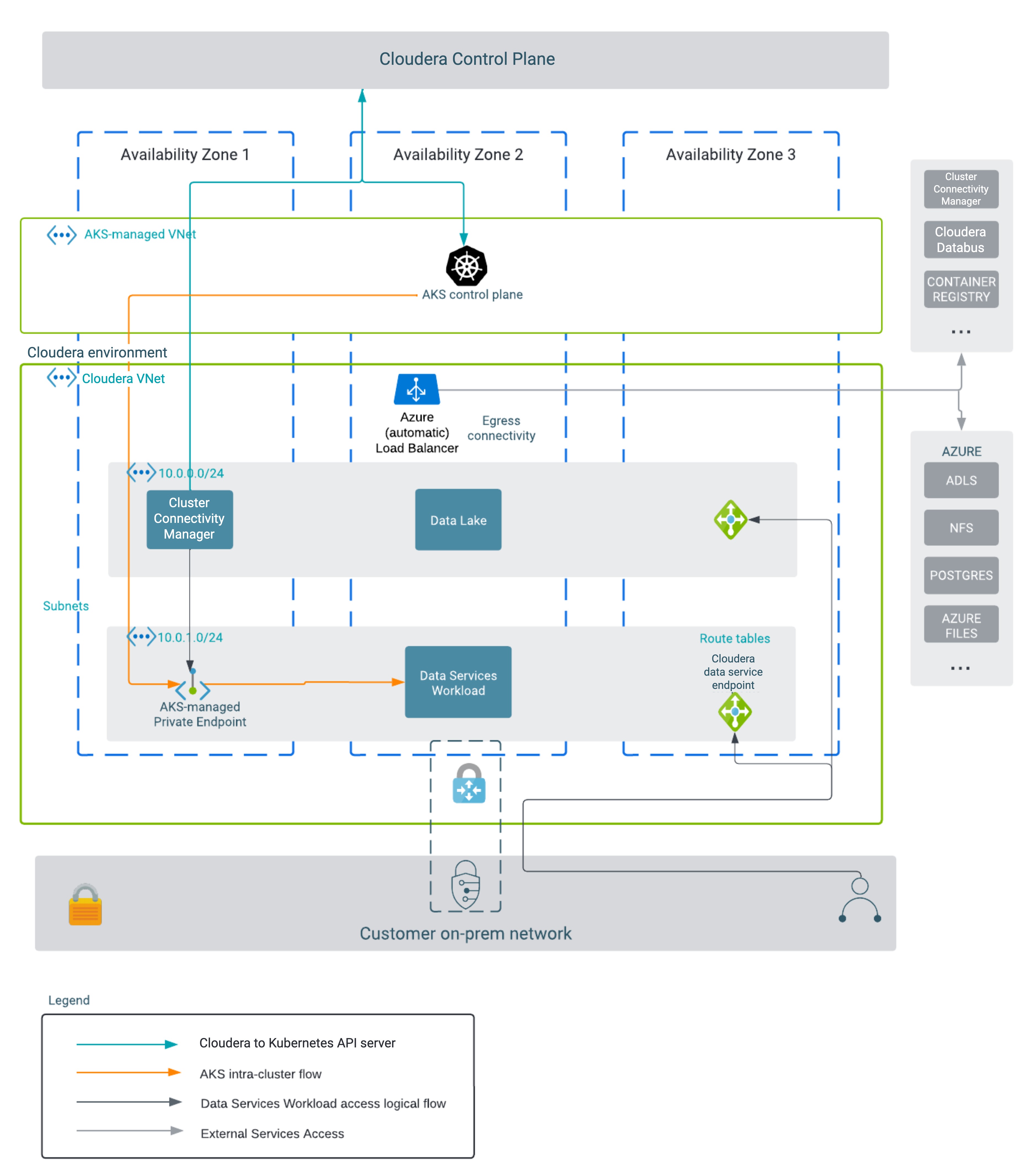
As can be seen in the above diagram, Cloudera
workloads have dependencies on some Azure cloud services such as ADLS, Azure Postgres and so
on. A full list of these services, described in the context of each workload is specified in
Azure outbound network access destinations
.
In this example of a fully private deployment with an existing network of your own configuration, you must configure your own egress connectivity through a NAT gateway setup or user-defined routing. For more information see VNet and subnets and Azure Load Balancers in Data Lakes and Cloudera Data Hub clusters.
In the chapters that follow, we detail the elements of this architecture, including specifying the configuration and options in each of the components.
