Azure Load Balancers in Data Lakes and Cloudera Data Hub clusters
The Azure Load Balancer is used in multiple places in Cloudera Data Lakes and Cloudera Data Hub clusters. It is used as a frontend for Knox in both Data Lakes and Cloudera Data Hub clusters, and for Oozie HA in HA Cloudera Data Hub clusters.
| Cloudera component | Azure Load Balancer use case |
|---|---|
| Data Lake | A load balancer is configured in front of Knox for Data Lakes of all shapes. |
| HA Cloudera Data Hub | A load balancer is configured for all Cloudera Data Hub
clusters created from a default template where Knox and/or Oozie is running in HA
mode. This can be overridden by setting the “enableLoadBalancer” setting in a custom template to “false”. |
| An environment with Public Endpoint Access Gateway enabled | When the Endpoint Gateway is enabled, Load balancers are created in front of Knox for all Data Lakes and Cloudera Data Hub clusters attached to the environment. |
In the event that a Data Lake or Cloudera Data Hub cluster uses private networks (meaning the “Create Public IPs” option is disabled during environment creation and the Public Endpoint Access Gateway is not enabled), an internal load balancer is created for ingress traffic to Knox in all Data Lakes and in Knox HA Cloudera Data Hub clusters running in that environment.
Because Cloudera uses a Standard SKU Azure Load Balancer for new Load Balancers, the private load balancer does not allow for public egress, and a public load balancer is required for public outbound destinations as described in the Azure network reference architecture. If you are creating an environment with an existing network of your own configuration, which is assumed to be fully private (the "Create Public IPs" option and Public Endpoint Access Gateway are disabled), it is your responsibility to create egress connectivity for the required subnets in your VNet. This can be accomplished through a NAT gateway setup or user-defined routing.
If you want Cloudera to create a secondary load
balancer for egress in an existing network of your own configuration, be aware that it
requires certain public IP permissions that are granted as part of the required Azure permissions. However, you can
create this secondary public egress load balancer when you create an Azure environment through
the CLI with the options –no-enable-outbound-load-balancer and
–enable-outbound-load balancer. The secondary public egress load balancer
created by Cloudera has only outbound rules defined, and does
not handle ingress traffic.
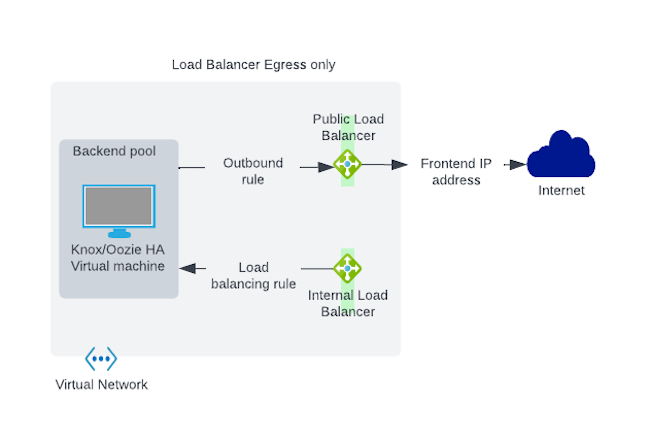
If you are creating a new network during environment registration, Cloudera ensures that egress connectivity is available. If the "Create Public IPs" option and Public Endpoint Access Gateway are disabled in your network, a separate load balancer is created for egress, though this load balancer requires certain public IP permissions that are granted as part of the required Azure permissions. If either "Create Public IPs" or Public Endpoint Access Gateway is enabled, then a public load balancer is created to handle both public ingress to port 443 and public egress.
