Data Lake scale
The scale of a Data Lake affects how many workload clusters can access your data using the security and governance services configured in the Data Lake, as well as resiliency of the Data Lake.
Cloudera supports both light duty Data Lakes and enterprise Data Lakes for AWS, Azure, and GCP. Medium duty and enterprise Data Lakes incur additional cost over light duty Data Lakes, but are required for production scenarios that require resiliency and scale. Medium duty and enterprise Data Lakes also have the ability to service a larger number of clients concurrently. See the sections below to understand the differences between light duty, medium duty and enterprise Data Lakes.
At this time, the following Data Lake scales are supported in Cloudera:
| Feature | Light Duty Data Lake | Enterprise Data Lake | Medium Duty Data Lake (Discontinued as of Cloudera Runtime 7.2.18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High availability | Not available |  |
 |
| Backups |  |
 |
 |
| Availability Zones | Single availability zone | Multiple availability zones (AWS and Azure only) | Single availability zone |
| Security | Kerberos + LDAP/AD | Kerberos + LDAP/AD | Kerberos + LDAP/AD |
| Scale | About 5 concurrent workload clusters | About 20 concurrent workload clusters | About 20 concurrent workload clusters |
| Node count | 1 master node running SDX Services 1 IDBroker node running networking authentication services |
2 IDBroker nodes running authentication services 2 master nodes running core services 3 core nodes running HDFS, Kafka, Solr, and HBase 2 gateway nodes 1 auxiliary node |
2 IDBroker nodes running authentication services 2 master nodes running core services in HA-enabled mode, with replication for resilience and scale 3 core nodes running HDFS, Kafka, Solr, and HBase 2 gateway nodes running services with API/UI access 1 auxiliary node for services that cannot run in HA mode |
| Fault tolerance | Services unavailable during cluster node repair | Availability of services depends on the node being repaired. With the exception
of the gateway and auxiliary nodes, the remaining groups can typically survive a
single node failure without affecting workloads or UI/API access. In the event of a gateway node failure on a medium duty Data Lake, the load-balancer will seamlessly route to the other gateway node. As Cloudera Manager runs on only one gateway node (either 0 or 1), if the Cloudera Manager server gateway node fails, Cloudera Manager will not be available at all, but UI and API calls that bypass Cloudera Manager will be routed to the healthy gateway node by the load balancer. If the non-Cloudera Manager server gateway node goes down, Cloudera Manager will still be available, and the load balancer will seamlessly route to the healthy gateway node. |
Availability of services depends on the node being repaired. With the exception
of the gateway and auxiliary nodes, the remaining groups can typically survive a
single node failure without affecting workloads or UI/API access. In the event of a gateway node failure on a medium duty Data Lake, the load-balancer will seamlessly route to the other gateway node. As Cloudera Manager runs on only one gateway node (either 0 or 1), if the Cloudera Manager server gateway node fails, Cloudera Manager will not be available at all, but UI and API calls that bypass Cloudera Manager will be routed to the healthy gateway node by the load balancer. If the non-Cloudera Manager server gateway node goes down, Cloudera Manager will still be available, and the load balancer will seamlessly route to the healthy gateway node. |
| Cloud-based load balancer | Network-based load balancer for front UI and API services. | Network-based load balancer for front UI and API services. | Network-based load balancer for front UI and API services. |
| Additional comments | Enterprise Data Lake is available for environments using Runtime 7.2.17 and newer. | Medium duty Data Lake has been discontinued as of Runtime 7.2.18. |
The following section details the architecture of the different Data Lake scales:
-
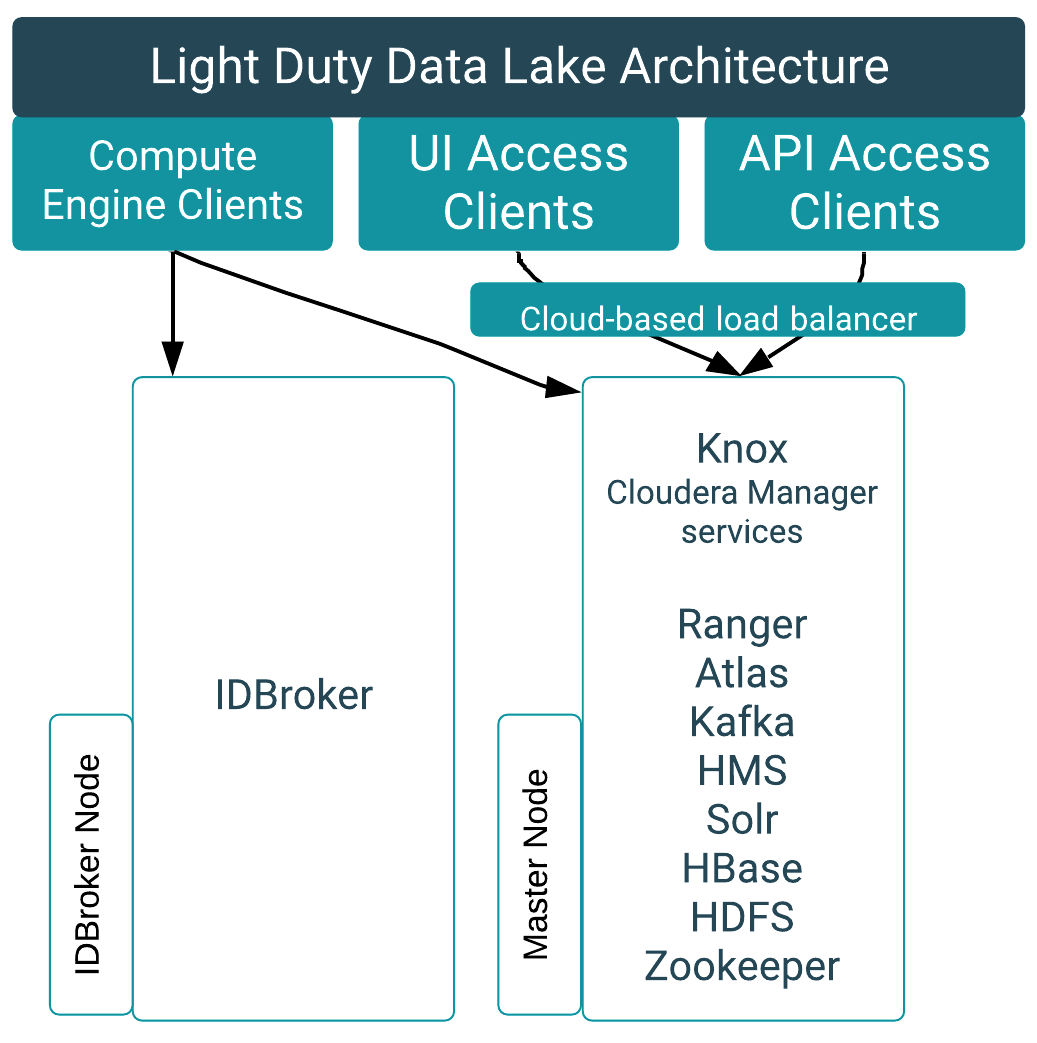
If the master node of a light duty Data Lake fails, compute engine clients such as Hive, Impala, and Spark, are partially resilient due to caching; but new queries cannot run without updated policy information, and audit information can also be affected. Because the Knox gateway also runs on the master node, clients with UI (such as the Ranger Admin UI and Atlas UI) or API access are unavailable in the event of a master node failure. In a light-duty Data Lake, the cloud-based load balancer exists for networking purposes and has no effect on the scale.
If the IDBroker node fails, compute-engine clients are affected because cloud access tokens cannot be verified. Clients with UI/API access remain available.
-
Enterprise Data Lakes, available for Cloudera Runtime 7.2.17 and newer, are a redefined version of medium duty Data Lakes that still offer failure resilience, but utilize resources and allocate memory more efficiently than a medium duty Data Lake at the same cost. Enterprise Data Lakes are configured such that services that do not need to scale are in the master hostgroup; services that need to scale vertically are in the gateway hostgroup; and services that can scale both horizontally and vertically are in the core hostgroup.
Enterprise Data Lakes can handle more intensive workloads than medium duty Data Lakes, support Ranger tag and user sync in HA mode, and when deployed in multi-AZ mode, remain operational during an availability zone outage.
When compared to medium duty Data Lakes, RAZ will perform better and memory allocations for HBase, Solr, and Atlas have been increased. Other memory configurations have also been optimized.
-
Medium duty Data Lakes provide failure resilience for compute engine clients such as Hive, Impala, and Spark; as well as failure resilience for clients with UI and API access, such as the Ranger Admin UI and the Atlas UI.
Note that while Cloudera Manager is shown as running on Gateway Node 0, it can be installed on either gateway node 0 or gateway node 1. You can see which node has Cloudera Manager installed by looking at the Hardware tab of the Data Lake for the gateway node marked "CM Server."
Failures in a medium duty Data Lake impact services as follows:
- Master node failure. Compute engine clients (for example, Hive, Impala, and Spark) are resilient to the failure, due to fallback high availability with smart client failover.
- IDBroker node failure. Both compute engine clients that use standard data connectors (Hive, Impala, Spark) and compute engine clients that use custom data connectors (for example, Hue) are resilient to the failure.
- Gateway node failure. Load-balanced UI and API access are available without interruption.
- Core node failure. Compute engine clients (for example, Hive, Impala, and Spark) are resilient to the failure, due to fallback high availability with smart client failover.
- Auxiliary node failure. Ranger user and tag sync are unavailable.
If you want to scale an existing light or medium duty Data Lake to an enterprise Data Lake, you can perform Data Lake resizing.


