Enabling a private endpoint for Azure Postgres
By default Cloudera uses service endpoints, but you can select to use private endpoints instead. During environment registration you can optionally select the “Create Private Endpoint” option to use private endpoints instead of using a service endpoint. Currently, only one service or private endpoint is used, for Azure Postgres.
The endpoint type - either service or private endpoints - and whether to use your own private DNS zones or have Cloudera create them are decided at environment creation. All services capable of that endpoint type will use the selected endpoint type - this currently means only the Postgres server.
By default service endpoints are used, and in order to use private endpoints the user has to explicitly enable the “Create Private Endpoints“ option from either the Cloudera UI or CDP CLI. There is no option to not use either. Once you have turned on private endpoints then you can specify your own private DNS zone if you wish.
Prerequisites
You should also decide if you would like to use your own Azure private DNS zone or have Cloudera create an Azure private DNS zone for you, and meet the related prerequisites. Review the requirements described in Private endpoint for Azure Postgres.
Enabling private endpoints
You can enable private endpoints and select to use a Cloudera-managed Azure private DNS zone or your own Azure private DNS zone during Azure environment registration in the Cloudera Management Console.
Required role: EnvironmentCreator
Steps
When registering an environment specify the following:
-
In the Resource group section, select to use your pre-created resource group.
-
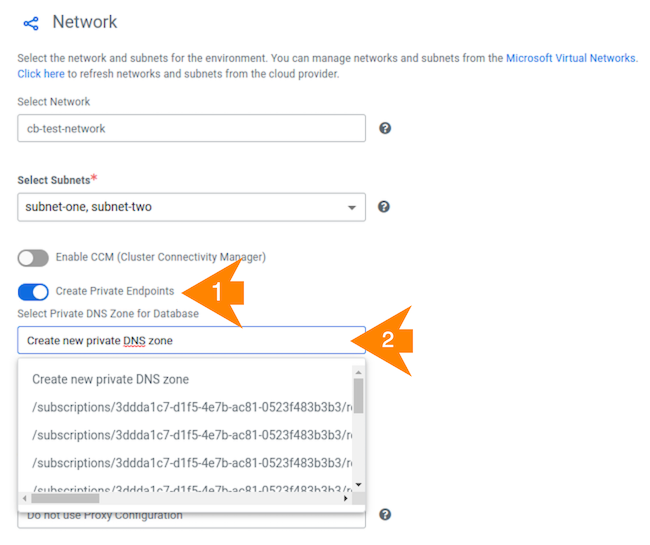
In the Network section of the register environment wizard, enable the "Create Private Endpoints" option.
-
A new drop down option appears. You have two options:
-
Select an existing private DNS zone.
-
If you would like Cloudera to create the private DNS zone, select “Create new private DNS zone”.
-
- Provide other Azure environment parameters as usual and complete environment registration.
The parameter createPrivateEndpoints defines that Azure
Postgres will be configured with a Private Endpoint and a Private DNS Zone. When this
option is disabled, Azure Service Endpoints are created. This option is disabled by
default, so Azure Service Endpoints are used by default.
cdp environments
create-azure-environment
command:--create-private-endpoints
--no-create-private-endpointsdatabasePrivateDnsZoneId as part of
existing-network-params:
--existing-network-params networkId=<NETWORK_ID>,resourceGroupName=<NETWORK_RG_NAME>,subnetIds=<SUBNET_1>,<SUBNET_2>,databasePrivateDnsZoneId=<PRIVATE_DNS_ZONE_RESOURCE_ID>/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME>/providers/Microsoft.Network/privateDnsZones/privatelink.postgres.database.azure.comFor example:
/subscriptions/a9a10f9c-5323-4fd2-8s14-747b2d68784c/resourceGroups/my-resource-group/providers/Microsoft.Network/privateDnsZones/contoso.com