Introduction to Azure environments
In Cloudera, an environment is a logical subset of your cloud provider account including a specific virtual private network. You can register as many environments as you require.
The “environment” concept of Cloudera is closely related to the virtual private network in your cloud provider account. Registering an environment provides Cloudera with access to your cloud provider account and identifies the resources in your cloud provider account that Cloudera services can access or provision. A single environment is contained within a single cloud provider region, so all resources deployed by Cloudera are deployed within that region within one specific virtual network. Once you’ve registered an environment in Cloudera, you can start provisioning Cloudera resources such as clusters, which run on the physical infrastructure in an Azure data center.
The following diagram enumerates the components of an environment:
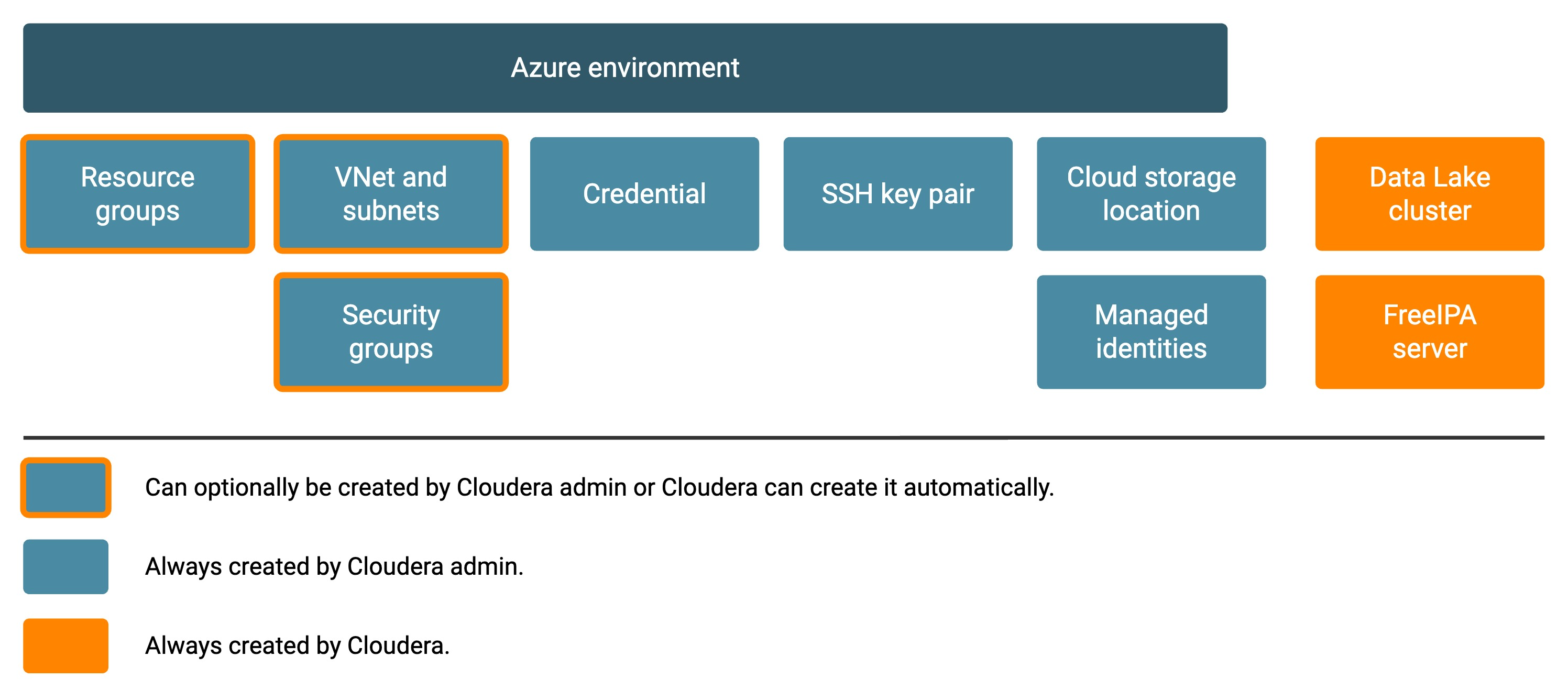
The diagram illustrates all major user-created and Cloudera-created components of an environment:
- The items in dark blue boxes with orange outlines can either be automatically provisioned by Cloudera on your Azure account, or you can optionally pre-create them and specify them when registering an environment.
- The items in dark blue boxes must be pre-created by your Cloudera administrator prior to environment registration and then specified when registering an environment.
- The items in orange boxes are automatically provisioned on Azure by Cloudera as part of environment provisioning.
As shown in the diagram, an environment consists of the following resources:
|
Environment component |
Description |
|---|---|
| Virtual network with subnets | An environment corresponds to one specific virtual network (called VNet on Azure) and subnets in which Cloudera resources are provisioned. |
| Security groups | Security groups (called NSGs on Azure) act as a virtual firewall for your
instances to control inbound and outbound traffic. All VM instances provisioned within an environment use your specified security access settings allowing inbound access to your instances from your organization’s computers. |
| Credential | Cloudera uses the credential for authorization to
provision resources (such as compute instances) within your cloud provider account.
On Azure, credential creation involves creating an application and a service principal within the Azure Active Directory manually (app-based credential). |
| SSH public key | When registering an environment on a public cloud, a Cloudera administrator provides an SSH public key. This way, the administrator has root-level access to the Data Lake instance and Cloudera Data Hub cluster instances. |
| Cloud storage location and managed identities | When registering an environment, you must provide an ADLS Gen2 location for storing:
Furthermore, you must create and assign managed identities so that Cloudera can access the storage location. |
| Data Lake | A data lake is automatically provisioned when an environment is created. It provides a mechanism for storing, accessing, organizing, securing, and managing data. |
| FreeIPA | A FreeIPA server is automatically provisioned when an environment is created. It is responsible for synchronizing your users and making them available to Cloudera services, Kerberos service principal management, and more. |
| Resource groups | Cloudera creates multiple new resource groups for resources that it deploys on your Azure account. |
You may want to register multiple environments corresponding to different regions that your organization would like to use. Once your environment is running, you can provision Cloudera Data Hub clusters, Cloudera Data Warehouses, and other resources in it.
