Launching Cloudbreak on OpenStack
Before launching Cloudbreak on OpenStack, review and meet the prerequisites. Next, import Cloudbreak image, launch a VM, SSH to the VM, and start Cloudbreak. Once Cloudbreak is running, log in to the Cloudbreak UI and create a Cloudbreak credential.
Meet Minimum System Requirements
Before launching Cloudbreak on your OpenStack, make sure that your OpenStack deployment fulfills the following requirements.
Supported Linux Distributions
The following versions of the Red Hat Distribution of OpenStack (RDO) are supported:
- Juno
- Kilo
- Liberty
- Mitaka
Standard Modules
Cloudbreak requires that the following standard modules are installed and configured on OpenStack:
- Keystone V2 or Keystone V3
- Neutron (Self-service and provider networking)
- Nova (KVM or Xen hypervisor)
- Glance
- Cinder (Optional)
- Heat (Optional but highly recommended, since provisioning through native API calls will be deprecated in the future)
Related Links Red Hat Distribution of OpenStack (External)
Meet the Prerequisites
Before launching Cloudbreak on OpenStack, you must meet the following prerequisites.
SSH Key Pair
Generate a new SSH key pair or use an existing SSH key pair to your OpenStack account. You will be required to select it when launching the VM.
Security Group
In order to launch Cloudbreak, you must have an existing security group with the following ports open: 22 (for access via SSH), 80 (for access via HTTP), and 443 (for access via HTTPS).
For information about OpenStack security groups, refer to the OpenStack Administrator Guide.
Related Links OpenStack Administrator Guide (External)
Import Images to OpenStack
An OpenStack administrator must perform these steps to add the Cloudbreak deployer and HDP base and prewarmed images to your OpenStack deployment.
Import Cloudbreak Deployer Image
Import Cloudbreak deployer image using the following steps.
Steps
-
Download the latest Cloudbreak deployer image to your local machine:
curl -O https://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/cloudbreak/266cbdd8-9909-4597-8133-cf3444b8b232.img
-
Set the following environment variables for the OpenStack image import:
export CBD_LATEST_IMAGE=266cbdd8-9909-4597-8133-cf3444b8b232.img export OS_IMAGE_NAME=266cbdd8-9909-4597-8133-cf3444b8b232.img export OS_USERNAME=your_os_user_name export OS_AUTH_URL=your_authentication_url export OS_TENANT_NAME=your_os_tenant_name
-
Import the new image into your OpenStack:
glance image-create --name "$OS_IMAGE_NAME" --file "$CBD_LATEST_IMAGE" --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare --progress
After performing the import, you should be able to see the Cloudbreak deployer image among your other OpenStack images.
Import HDP Base Image
Import HDP base image using the following steps.
Steps
-
Download the latest HDP image to your local machine:
curl -O https://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/cloudbreak/cb-hdp--1801261636.img
-
Set the following environment variables for the OpenStack image import:
export CB_LATEST_IMAGE=cb-hdp--1801261636.img export CB_LATEST_IMAGE_NAME=cb-hdp--1801261636.img export OS_USERNAME=your_os_user_name export OS_AUTH_URL=your_authentication_url export OS_TENANT_NAME=your_os_tenant_name
-
Import the new image into your OpenStack:
glance image-create --name "$CB_LATEST_IMAGE_NAME" --file "$CB_LATEST_IMAGE" --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare --progress
After performing the import, you should be able to see the Cloudbreak image among your OpenStack images.
Import HDP Prewarmed Image
Import HDP prewarmed image using the following steps.
Steps
-
Download the latest HDP image to your local machine:
curl -O https://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/cloudbreak/cb-hdp-26-1802090220.img
-
Set the following environment variables for the OpenStack image import:
export CB_LATEST_IMAGE=cb-hdp-26-1802090220.img export CB_LATEST_IMAGE_NAME=cb-hdp-26-1802090220.img export OS_USERNAME=your_os_user_name export OS_AUTH_URL=your_authentication_url export OS_TENANT_NAME=your_os_tenant_name
-
Import the new image into your OpenStack:
glance image-create --name "$CB_LATEST_IMAGE_NAME" --file "$CB_LATEST_IMAGE" --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare --progress
After performing the import, you should be able to see the Cloudbreak image among your OpenStack images.
Launch the VM
In your OpenStack, launch and instance providing the following parameters:
- Select a VM flavor which meets the following minimum requirements: 4GB RAM, 10GB disk, 2 cores.
- Select the Cloudbreak deployer image that you imported earlier and launch an instance using that image.
- Select your SSH key pair.
- Select the security group which has the following ports open: 22 (SSH) and 443 (HTTPS).
- Select your preconfigured network.
SSH to the VM
Now that your VM is ready, access it via SSH:
- Use a private key matching the public key that you added to your OpenStack project.
- The SSH user is called "cloudbreak".
- You can obtain the VM's IP address from the details of your instance.
On Mac OS X, you can SSH to the VM by running the following from the Terminal app: ssh -i "your-private-key.pem" cloudbreak@instance_IP where "your-private-key.pem" points to the location of your private key and "instance_IP" is the public IP address of the VM.
On Windows, you can use PuTTy.
Initialize Your Profile
After accessing the VM via SSH, you must initialize your Profile.
Steps
-
Navigate to the cloudbreak-deployment directory:
cd /var/lib/cloudbreak-deployment/
This directory contains configuration files and the supporting binaries for Cloudbreak deployer.
-
Initialize your profile by creating a new file called
Profileand adding the following content:export UAA_DEFAULT_SECRET=MY-SECRET export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_PW=MY-PASSWORD export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_EMAIL=MY-EMAIL export PUBLIC_IP=VM-PUBLIC-IP
For example:
export UAA_DEFAULT_SECRET=MySecret123 export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_PW=MySecurePassword123 export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_EMAIL=dbialek@hortonworks.com export PUBLIC_IP=34.212.141.253
You will need to provide the email and password when logging in to the Cloudbreak web UI and when using the Cloudbreak CLI. The secret will be used by Cloudbreak for authentication.
Perform Optional Configurations
These configurations are optional.
Configuring a Self-Signed Certificate
If your OpenStack is secured with a self-signed certificate, you need to import that certificate into Cloudbreak, or else Cloudbreak won't be able to communicate with your OpenStack.
To import the certificate, place the certificate file in the /certs/trusted/ directory, follow these steps.
Steps
- Navigate to the
certsdirectory (automatically generated). - Create the
trusteddirectory. - Copy the certificate to the
trusteddirectory.
Cloudbreak will automatically pick up the certificate and import it into its truststore upon start.
Launch Cloudbreak Deployer
Launch Cloudbreak deployer using the following steps.
Steps
-
Start the Cloudbreak application by using the following command:
cbd start
This will start the Docker containers and initialize the application. The first time you start the Coudbreak app, the process will take longer than usual due to the download of all the necessary docker images.
This will start the Docker containers and initialize the application. The first time you start the Coudbreak app, this also downloads of all the necessary docker images.
Once the
cbd starthas finished, it returns the "Uluwatu (Cloudbreak UI) url" which you can later paste in your browser and log in to Cloudbreak web UI. -
Check Cloudbreak deployer version and health:
cbd doctor
-
Next, check Cloudbreak Application logs:
cbd logs cloudbreak
You should see a message like this in the log:
Started CloudbreakApplication in 36.823 seconds.Cloudbreak takes less than a minute to start. If you try to access the Cloudbreak UI before Cloudbreak started, you will get a "Bad Gateway" error or "Cannot connect to Cloudbreak" error.
Access Cloudbreak UI
Log in to the Cloudbreak UI using the following steps.
Steps
-
You can log into the Cloudbreak application at
https://IP_Addresswhere "IP_Address" if the public IP of your OpenStack VM. For examplehttps://34.212.141.253. -
Confirm the security exception to proceed to the Cloudbreak web UI.
The first time you access Cloudbreak UI, Cloudbreak will automatically generate a self-signed certificate, due to which your browser will warn you about an untrusted connection and will ask you to confirm a security exception.
-
The login page is displayed:
-
Log in to the Cloudbreak web UI using the credential that you configured in your
Profilefile when launching Cloudbreak deployer:- The username is the
UAA_DEFAULT_USER_EMAIL - The password is the
UAA_DEFAULT_USER_PW
- The username is the
-
Upon a successful login, you are redirected to the dashboard:
Create Cloudbreak Credential
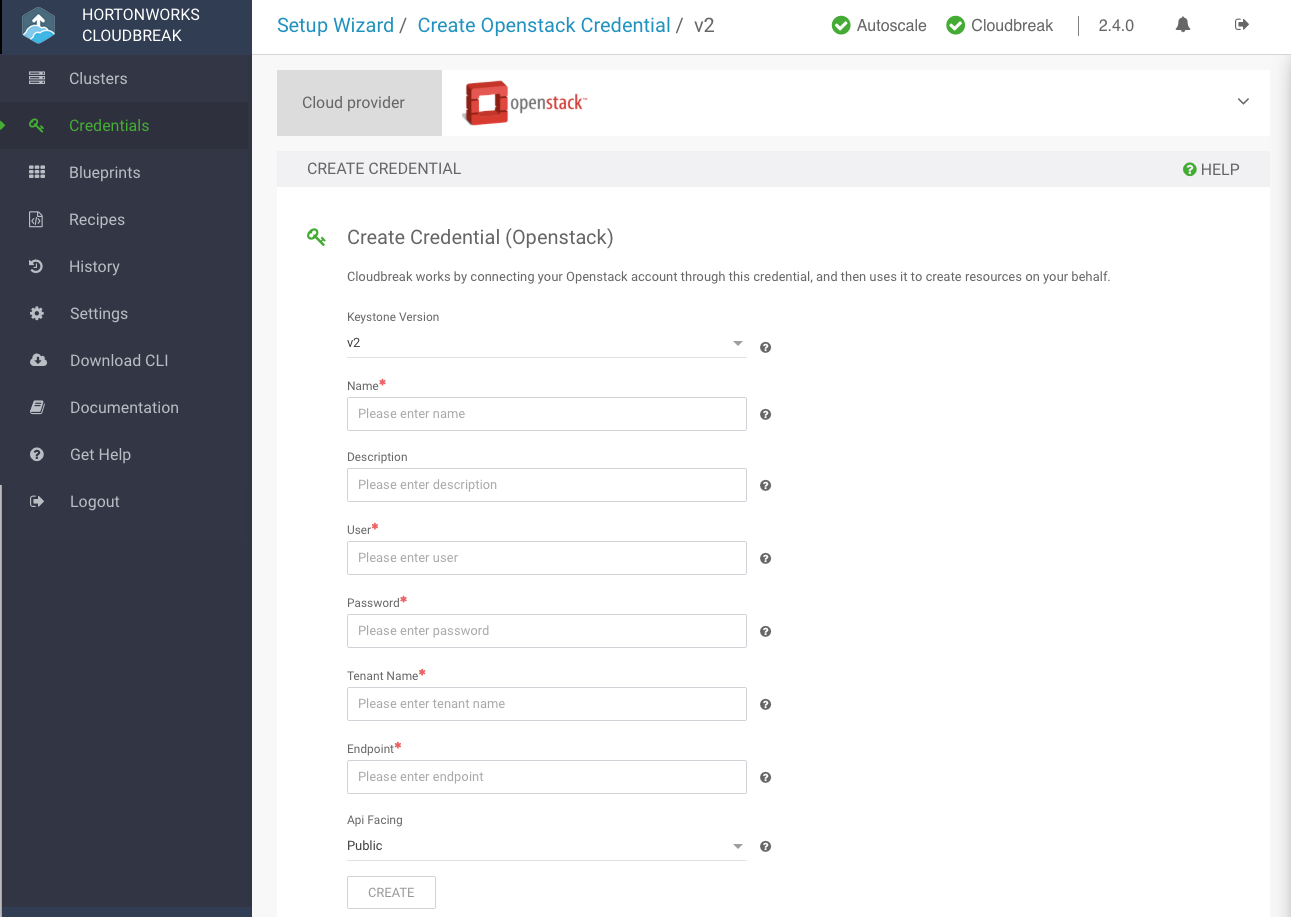
Cloudbreak works by connecting your OpenStack account through this credential, and then uses it to create resources on your behalf. Before you can start provisioning cluster using Cloudbreak, you must create a Cloudbreak credential.
Steps
-
In the Cloudbreak web UI, select Credentials from the navigation pane.
-
Click Create Credential.
-
Under Cloud provider, select "Google Cloud Platform".
-
Select the keystone version.
-
Provide the following information:
For Keystone v2:
Parameter Description Name Enter a name for your credential. Description (Optional) Enter a description. User Enter your OpenStack user name. Password Enter your OpenStack password. Tenant Name Enter the OpenStack tenant name. Endpoint Enter the OpenStack endpoint. API Facing (Optional) Select public, private, or internal. For Keystone v3:
Parameter Description Keystone scope Select the scope: default, domain, or project. Name Enter a name for your credential. Description (Optional) Enter a description. User Enter your OpenStack user name. Password Enter your OpenStack password. User Domain Enter your OpenStack user domain. Endpoint Enter the OpenStack endpoint. API Facing (Optional) Select public, private, or internal. -
Click Create.
-
Your credential should now be displayed in the Credentials pane.
Congratulations! You have successfully launched Cloudbreak and created a Cloudbreak credential. Now you can use Cloudbreak to create clusters.