Example 1: Built-in type Hive
In this scenario, you start up with a standard blueprint, and Cloudbreak injects the JDBC properties into the blueprint.
- Register an existing external database of “Hive” type (built-in type):
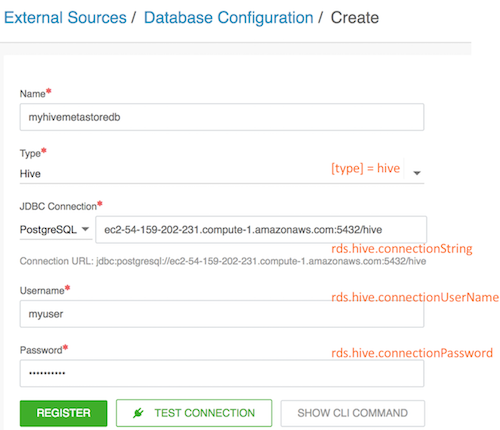
Property variable Example value rds.hive.connectionString jdbc:postgresql://ec2-54-159-202-231.compute-1.amazonaws.com:5432/hive rds.hive.connectionDriver org.postgresql.Driver rds.hive.connectionUserName myuser rds.hive.connectionPassword Hadoop123! rds.hive.fancyName PostgreSQL rds.hive.databaseType postgres - Create a cluster by using a standard blueprint (i.e. one without JDBC related variables) and by attaching the external Hive database configuration.
- Upon cluster create, Hive JDBC properties will be injected into the blueprint according
to the following
template:
... "hive-site": { "properties": { "javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL": "{{{ rds.hive.connectionString }}}", "javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName": "{{{ rds.hive.connectionDriver }}}", "javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName": "{{{ rds.hive.connectionUserName }}}", "javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword": "{{{ rds.hive.connectionPassword }}}" } }, "hive-env" : { "properties" : { "hive_database" : "Existing {{{ rds.hive.fancyName}}} Database", "hive_database_type" : "{{{ rds.hive.databaseType }}}" } } ...

