External database options
Review the following options to find out whether to use a built-in or other external database type.
When using an external database for cluster services and components, Cloudbreak supports selected built-in types and allows for specifying other types. Cloudbreak supports the following external database options:
| Option | Description | Blueprint requirements | Steps | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Built-in types | Cloudbreak includes a few built-in types: Ambari, Beacon, Druid, Hive, Oozie, Ranger, and Superset. | Use a standard blueprint which does not include any JDBC parameters. Cloudbreak automatically injects the JDBC property variables into the blueprint. | Simply register the database in the UI. After that, you can attach the database config to your clusters. | Refer to Example 1 |
| Other types | In addition to the built-in types, Cloudbreak allows you to specify custom types. In the UI, this corresponds to the UI option is called “Other” > “Enter the type”. | You must provide a custom dynamic blueprint which includes RDBMS-specific variables. Refer to Creating a template blueprint. | Prepare your custom blueprint first. Next, register the database in the UI. After that, you can attach the database config to your clusters. | Refer to Example 2 |
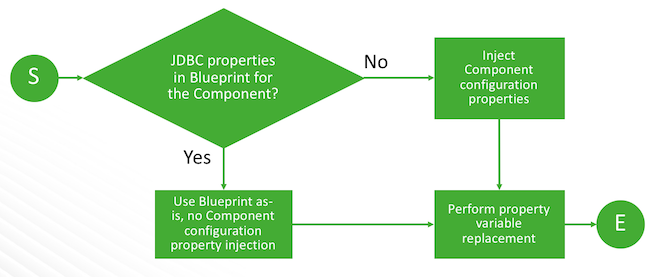
During cluster create, Cloudbreak checks whether the JDBC properties are present in the blueprint: