Before you can use the Cloudera Data Engineering service, you
must add the service to an environment that you want to use Cloudera Data Engineering
on.
Make sure that you have a working environment for which you want to
enable the Cloudera Data Engineering service. For more information about environments, see
Environments.
-
In the Cloudera console, click the
Data Engineering tile. The Cloudera Data Engineering Home page
displays.
-
Click Administration on the left navigation menu, click
 at the top to enable Cloudera Data Engineering service for an
environment.
at the top to enable Cloudera Data Engineering service for an
environment.
If the environment does not have any
Cloudera Data Engineering service, the page displays a
Enable a Service button that launches the same wizard.
-
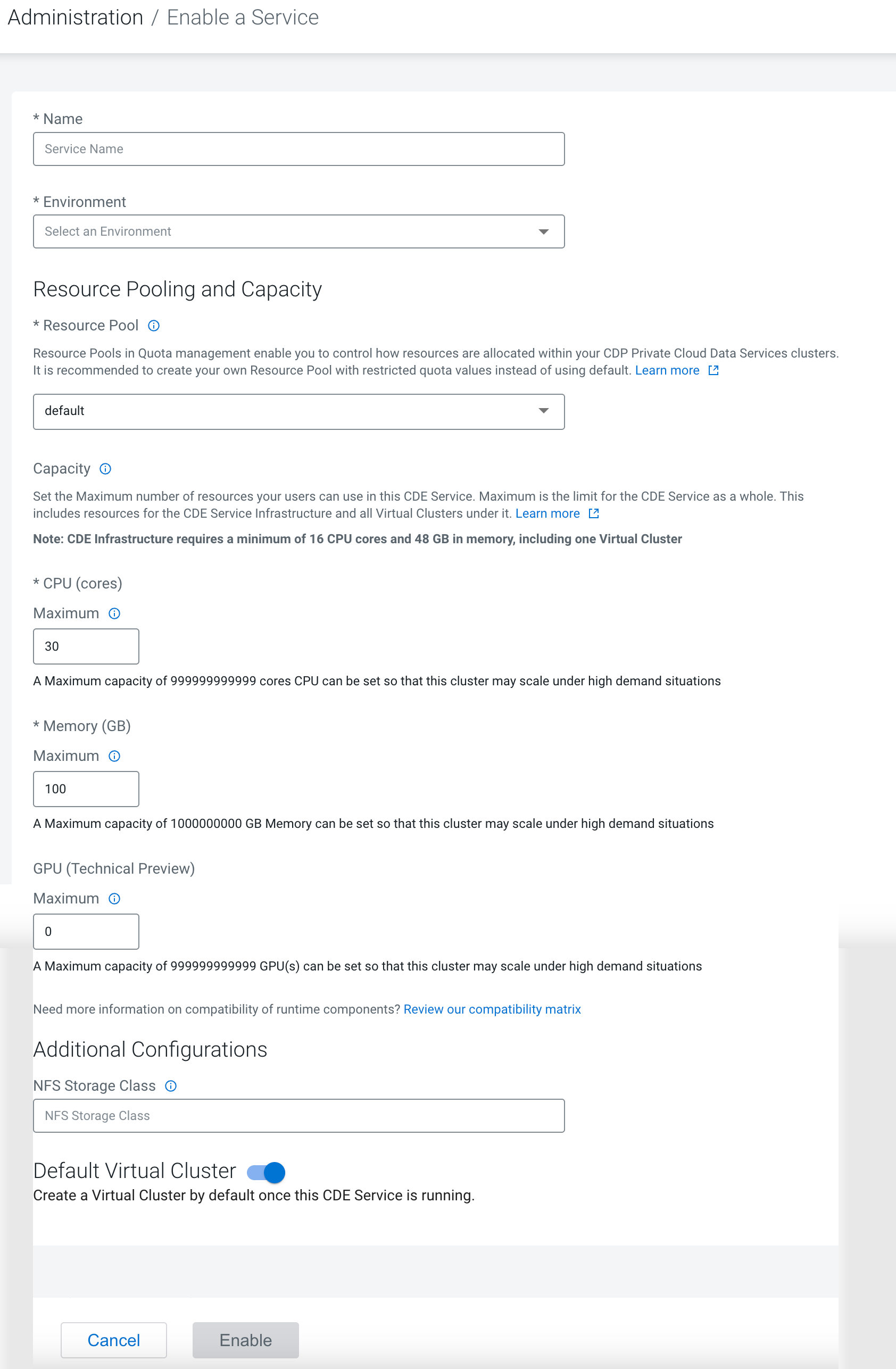
Enter a Name for the Cloudera Data Engineering service you are creating.
-
In the Environment text box, select or type the name of the
environment that you want to enable Cloudera Data Engineering for. The displayed list dynamically updates to
show environment names matching your input. When you see the correct environment, click on
it to select it.
-
In Resource Pool (Technical Preview), select the name of the
resource pool that you want to enable Cloudera Data Engineering service for.
-
In Capacity , use the slider to set the maximum number of CPU
cores and the maximum memory in gigabytes that can be used by this Cloudera Data Engineering service.
- Optional:
GPU (Technical Preview), in Capacity , use the slider
to set the maximum number of GPU cores in gigabytes that can be used by this Cloudera Data Engineering service.
GPU resources are limited in the cluster and all data services like Cloudera AI and Cloudera Data Engineering
could share or dedicatedly set resource quotas for their experience. For information about
configuring resource pool and capacity, see Managing cluster resources using Quota Management
(Technical Preview).
- Optional:
Under Additional Configurations, in NFS Storage
Class, specify the name of the custom NFS storage class. The storage
provisioner must support ReadWriteMany access modes. By default, Cloudera Data Engineering uses CephFS provisioner in the
OpenShift Container Platform and Longhorn provisioner in the Cloudera Embedded Container Service. If it
does not exist, the Cloudera Data Engineering service initialisation
fails.
You can specify the name of the Portworx storage class specified during the
Cloudera Data Services installation to use the Portworx
storage class. The storage provisioner must support ReadWriteMany access mode. You can
obtain the name of the Portworx storage class from your cluster by running the
kubectl get sc command. The
Cloudera Data Engineering
service and virtual clusters will now use the Portworx storage class instead of the
default storage class of the platform.
For more information, see Installing in
internet environment and Storage Classes.
-
Default Virtual Cluster selection is enabled by default to
create a default virtual cluster after enabling a Cloudera Data Engineering service. This helps you to create
your jobs easily, without having to wait to create a Cloudera Data Engineering virtual cluster as mentioned in
Creating virtual clusters, making the onboarding smoother. You can turn this toggle off if
you do not wish to use a default virtual cluster.
- Click Enable.
The Cloudera Data Engineering Home page displays the status of
the Cloudera Data Engineering service initialization. You can view logs for the service by
clicking on the service vertical ellipsis (three dots) menu, and then
clicking View Logs.
 at the top to enable
at the top to enable 
