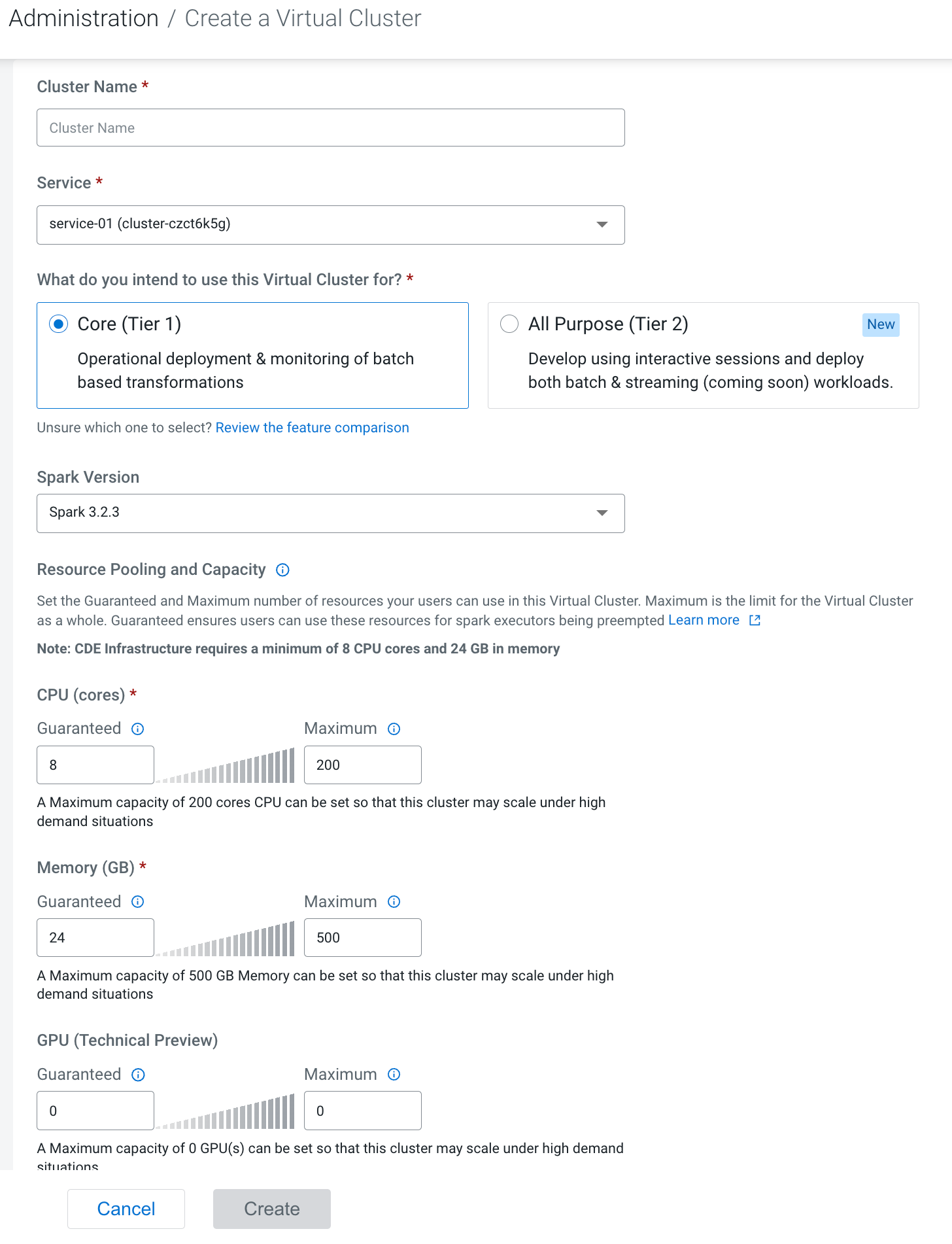
Creating virtual clusters
In Cloudera Data Engineering, a virtual cluster is an individual auto-scaling cluster with defined CPU and memory ranges. Jobs are associated with virtual clusters, and virtual clusters are associated with an environment. You can create as many virtual clusters as you need.
To create a virtual cluster, you must have an environment with Cloudera Data Engineering enabled.
You must initialize each virtual cluster you create and configure users before creating jobs.
Cloudera Data Engineering provides a suite of example jobs with a combination of Spark and Airflow jobs, which include scenarios such as reading and writing from object storage, running an Airflow DAG, and expanding on Python capabilities with custom virtual environments. For information about running example jobs, see Cloudera Data Engineering example jobs and sample data.
 at the top right to create a new virtual
cluster.
at the top right to create a new virtual
cluster.