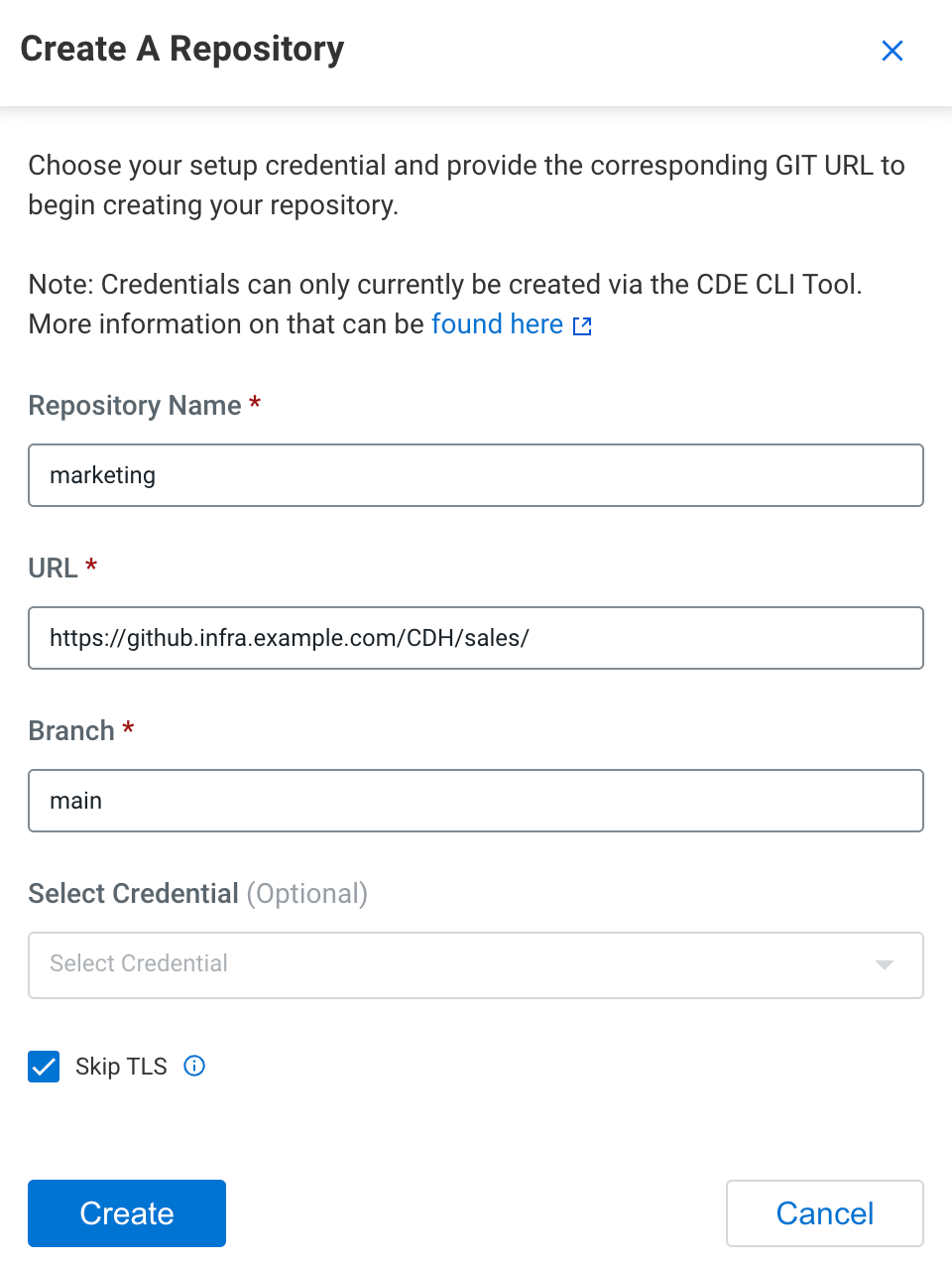
Creating a Git repository in Cloudera Data Engineering (Technical Preview)
Git repositories allow teams to collaborate, manage project artifacts, and promote applications from lower to higher environments. Cloudera currently supports Git providers such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket. Learn how to use Cloudera Data Engineering with version control service.
Supported version control service providers: Cloudera
currently supports the following version control service providers:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
cde credential create --type basic --username myuser --name
my-credential
The command above prompts you for a password where you can either provide your Personal Access
Token (PAT) or provide a password for your Git repository account, for example, Github.