Microsoft Azure prerequisites for Cloudera Data Engineering
Microsoft Azure prerequisites for Cloudera Data Engineering.
Review Azure account prerequisites for Cloudera
Refer to the Azure subscription requirements, and make sure that the Azure account you are using for Cloudera has the required resources, and that you have the permissions required to manage these resources.
Review Cloudera Data Engineering-specific Azure resource requirements
The following Azure services are required to provision a Cloudera Data Engineering Service and virtual clusters:
Azure Services used by Cloudera Data Engineering
- Network – VNet and Subnets(see below for requirements)
- Database – Azure Database for MySQL server
- Compute – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Load Balancing - Azure Load Balancer
- Virtual machine scale set
- Storage account - Cloudera Data Engineering stores workload data and logs in Azure Data Lake Store Gen 2 (ADLS Gen2) environment storage account. The AKS service also generates a separate storage account for use with Azure Files.
- Azure Files - Contain job resources, application code, Apache Airflow DAG files and any other uploaded files. The AKS service generates an ADLS Gen2 storage account for these files.
- Log Analytics workspace
Refer to the Azure resources used by Cloudera to check the Azure resources used by Cloudera.
Vnet and Subnet Requirements
When registering an Azure environment in Cloudera, you will be asked to select a VNet and one or more subnets. Cloudera Data Engineering runs in the VNet registered in Cloudera as part of your Azure environment.
You have two options:
- Use your existing VNet and subnets for provisioning Cloudera resources
- Have Cloudera create a new VNet and subnets
New VNet and subnets
If you would like Cloudera to create a new VNet, you will need to specify a valid CIDR in IPv4 range that will be used to define the range of private IPs for VM instances provisioned into these subnets. This must be a /16 CIDR, but you can customize the IP Range. The default is 10.10.0.0/16.
Cloudera will divide this address range as follows:
- 32 x /24 private subnet for Cloudera AI and Cloudera Data Engineering
- 3 x /19 private subnet for Cloudera Data Warehouse
- 3 x /19 private subnet for Data Lake and Cloudera Data Hub
- 3 x /24 public subnet
Existing VNet and subnets
VNet Requirements
If you would like to use your own VNet, it needs to fulfill the following requirements:
- The VNet has at least one subnet
- VNet should be able to make an outbound connection with the internet or set of CIDRs and ports provided by Cloudera
Subnet Requirements
Each Cloudera Data Engineering service requires its own subnet, and must not share subnets or routing tables with any other Cloudera service or AKS cluster. Cloudera Data Engineering on AKS uses the Kubenet CNI plugin provided by Azure. In order to use Kubenet CNI, you must create multiple smaller subnets when creating an Azure environment. Cloudera recommends partitioning the VNet with subnets that accommodate the maximum number of expected cluster nodes.
If you are not sure what size of subnet to use, Cloudera recommends a 24-bit subnet mask (/24 CIDR prefix), which can accommodate 254 usable IP addresses per subnet. If you want to use a different subnet size, you can calculate the number of IP addresses required per Cloudera Data Engineering service as follows:
- Each Cloudera Data Engineering service can scale up to 100 compute nodes; each node consumes one IP address.
- Each Cloudera Data Engineering service requires 3 IP addresses for the infrastructure nodes
- Each virtual cluster within a Cloudera Data Engineering service requires 2 IP addresses
For more information, see VNet and subnets, VNet and subnet planning
Firewall requirements
HTTPS access to Cloudera Data Engineering endpoints is available over port 443 for the following cases:
- Internal only – Should be accessible from your organization's network, but not the public internet.
- Internet facing (public endpoint) – Should be accessible from the public internet as well as your organization's internal network.
If you are using a firewall or a security group setting to prevent
egress traffic from the service, make sure that the
container.repository.cloudera.com and
docker.repository.cloudera.com URLs on port 443 are
allowed at all times.
If egress traffic is blocked to these URLs, then autoscaling cannot pull images, which can result in broken pods. For more information on required outbound access, see Outbound network access destinations for Azure and Default security group settings on Azure.
Do not remove firewall rules added during provisioning. The rules are also required for regular operation. You must also maintain the minimum firewall requirements set by the cloud provider. For more information, see Use Azure Firewall to protect Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) Deployments in the Microsoft Azure documentation.
Review the default Azure service limits and your current Azure account limits
Azure portal imposes default limits to the resources available to each user subscription, which may vary for different regions. Make sure you review your Azure subscription’s current usage status and resource limits before you start provisioning additional resources for Cloudera and Cloudera Data Engineering.
If you require more resources than the limit set by Azure, you can create a support request on your Azure Portal.
For example, To register an Azure environment in Cloudera, you may need to increase some of these limits for the region(s) that you are planning to use.Cloudera creates resources such as VMs in your Azure subscription. Depending on the number of clusters that Cloudera creates in your Azure subscription, you might need to raise the limits for certain resources such as VMs and vCPUs in your Azure subscription.
Related Azure quotas documentation: Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.
Supported Azure regions
Cloudera supports the following Azure regions: Supported Azure regions.
- A single Azure environment registered in Cloudera corresponds to a single VNet located in a specific region, and all the resources deployed by Cloudera on Azure are deployed into that VNet.
- Deploying clusters into the region containing the ADLS Gen2 containers that you want to access for input and output data, speeds up the data access.Therefore, when selecting the region to use, you should consider where your data is located.
- Cloudera requires that the ADLS Gen2 storage location provided during environment registration is in the same region as the region selected for the environment.
If you need to use multiple regions, you need to register multiple environments, one per region.
Related Azure documentation: Azure geographies.
Set up an Azure Cloud Credential
You must create the Azure provisioning credential for Cloudera prior to registering an environment. The credential allows Cloudera to access and provision a set of resources in your Azure account.
When working with an Azure environment, you can use the app-based credential to authenticate your Azure account and obtain authorization to create resources on your behalf. The app-based credential allows you to manually configure the service principal created within the Azure Active Directory.
Instructions: Azure Credentials
Register an Azure Environment in Cloudera
Once you have met cloud provider requirements and have created the Azure provisioning credential for Cloudera, you may proceed to register an Azure Environment.
Instructions: Register an Azure environment
Cloudera Data Engineering Role Requirements
There are two Cloudera user roles associated with the Cloudera Data Engineering service: DEAdmin and DEUser. Any Cloudera user with the EnvironmentAdmin (or higher) access level must assign these roles to users who require access to the Cloudera Data Engineering console within their environment.
Furthermore, if you want to allow users to log in to provisioned workspaces and run workloads on them, this will need to be configured separately.
Set up to run kubectl
- Go to the three dots on top right side of the Cloudera Data Engineering UI to see a dropdown menu.
- Click on Download the Kube Config option and save it (For example,
~/.kube/cde-env1-kube-config).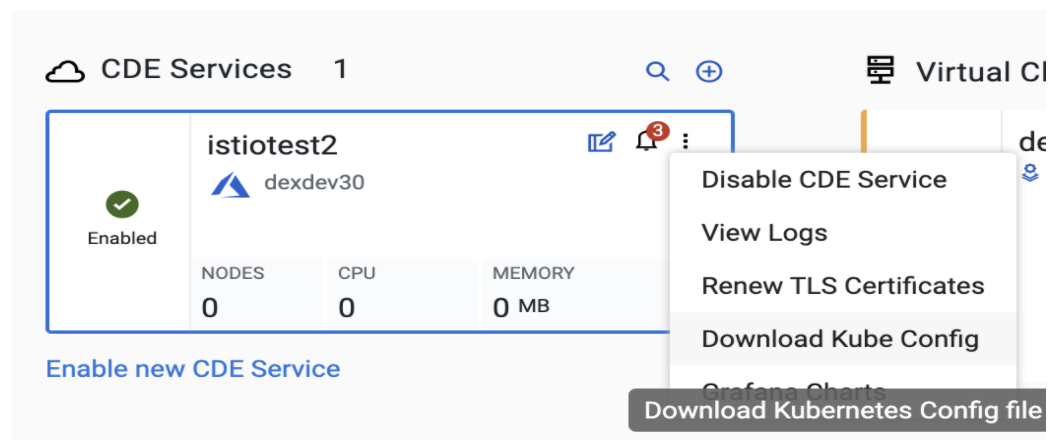
- Run the following shell command.
$ export KUBECONFIG=~/.kube/cde-env1-kube-config - You should now be able to run Kubectl Commands
Browser Requirements
Supported browsers:
- Chrome
- Safari
