Troubleshooting upgrade
Use the information in this section to troubleshoot problems with Cloudera Data Hub cluster upgrades.
Root disk space
Service pack upgrades require a certain amount of root disk space. Cloudera Runtime upgrades require downloading additional parcels, and hence more storage. When you begin an upgrade, Cloudera checks the available root disk space and issues a warning if there is insufficient root disk space for the upgrade:
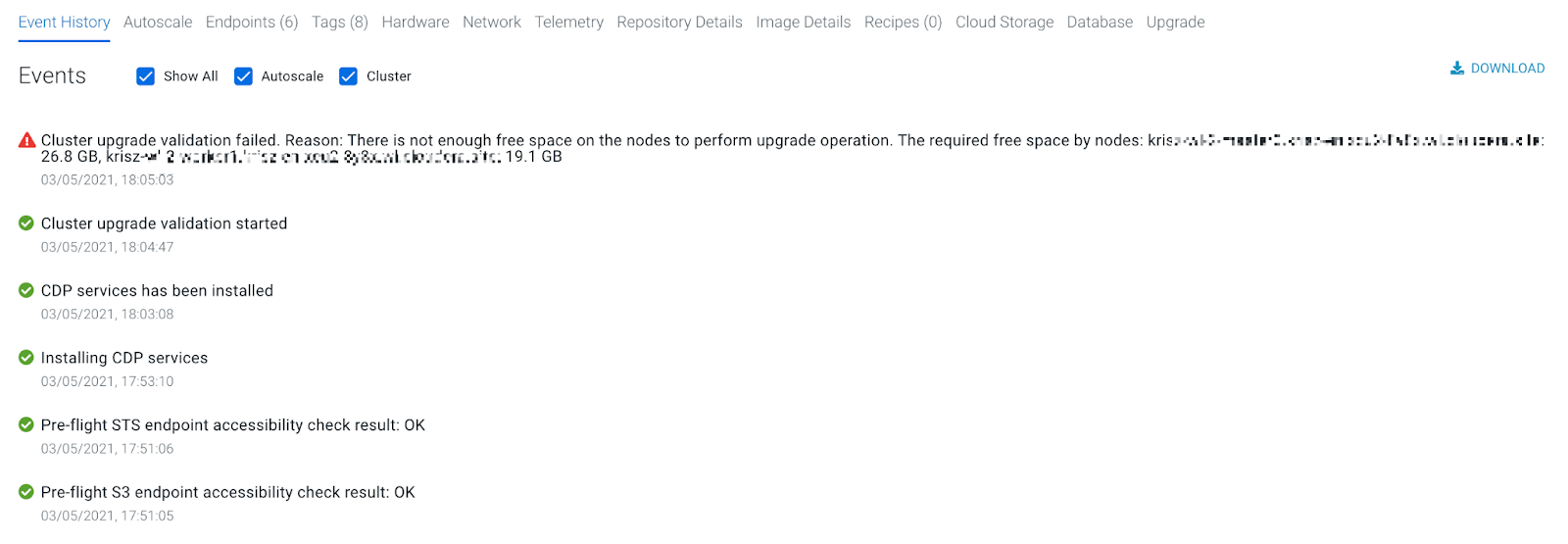
If your instances do not have the free space required for an upgrade (Cloudera Manager: 27 GB, other instances: 20 GB), run the scripts below to increase the root volume of the cluster nodes.
Oozie Shared Library mismatch
If the upgraded cluster contains the Oozie service, it may appear as being in bad health after the upgrade due to an known issue with the Oozie server shared library. On the Oozie Shared Library Check page in Cloudera Manager, you will see an error similar to: “The Oozie Server build version and the Oozie Server shared library version do not match.”
To workaround this issue, follow the steps at the end of the Performing a service pack upgrade section to re-install the Oozie shared libraries and YARN MapReduce Framework JARs.
Upgrade fails due to active Cloudera Manager commands
Upgrade may fail if there are active Cloudera Manager commands running when an upgrade is triggered. If you receive the error message “There are active commands running on Cloudera Manager, upgrade is not possible. Active commands: ApiCommand[..., name: <cm command name>, ]”, then kill the active commands and retry the upgrade.
Cloudera Manager, Cloudera Runtime, or other components are out-of-sync with Cloudera
When an upgrade fails, the versions of Cloudera Manager, Cloudera Runtime, and other components may become out-of-sync with the Cloudera Management Console. Similarly, if you try to fix errors by installing parcels manually, it may not be reflected in the Cloudera Management Console.
To overcome the mismatch between versions reflected in the Cloudera Management Console, run the cdp datahub
sync-component-versions-from-cm CDP CLI command. This command reads the Cloudera Manager, Cloudera Runtime, and other parcel
versions (if applicable) from Cloudera Manager and updates the versions in
the Cloudera Management Console. Using this command forces the Cloudera Management Console back in sync so that it shows the actual versions
installed in Cloudera Manager.
Run the command as follows: cdp datahub sync-component-versions-from-cm
--datahub-name <datahub name or CRN>
Cloudera Manager - memory tuning issue
Cloudera Data Hub and Data Lake services on JDK 17 clusters might fail after upgrading to Cloudera Runtime 7.3.1.500 or lower versions due to a problem in fine memory tuning with JDK17.
Condition
After upgrading to Cloudera Runtime 7.3.1.500 or lower versions,
Cloudera Data Hub and Data Lake services can fail with
Not enough space error if the JDK version of the cluster is
17.
Cause
In certain cases, Cloudera Manager does not fully consider the
memory already assigned to management service roles when calculating memory for
Cloudera Data Hub and Data Lake service roles (such as
Atlas) that are co-located on the same node. As a result, the services might
attempt to acquire more memory than is physically available on the host, causing
the process to fail with the following error:
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Not enough space.
