Deploying Cloudera Manager and CDH on AWS
To deploy Cloudera Manager and CDH on an AWS EC2 instance, begin by creating an environment. The environment defines common settings, like region and key pair, that Cloudera Director uses with AWS. While creating an environment, you are also prompted to deploy its first cluster.
To create an environment:
- Open a web browser and go to the private IP address of the instance you created in Launching an EC2 Instance for Cloudera
Director. Include port 7189 in the address. For example:
http://192.0.2.0:7189
- In the Cloudera Director login screen, enter admin in both the Username and the Password fields.
- In the Cloudera Director Welcome screen, click Let's get started.
This opens a wizard for adding an environment, Cloudera Manager, and a CDH cluster.
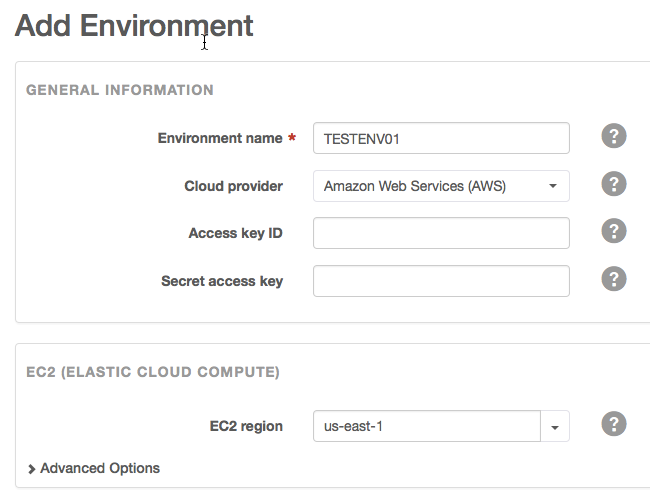
- In the Add Environment screen:
- Enter a name in the Environment Name field.
- Select Amazon Web Services (AWS) from the Cloud provider field.
- Enter your AWS credentials in the Access key ID and Secret access key fields.
- In the EC2 region field, select the same region in which your Cloudera Director instance was created.
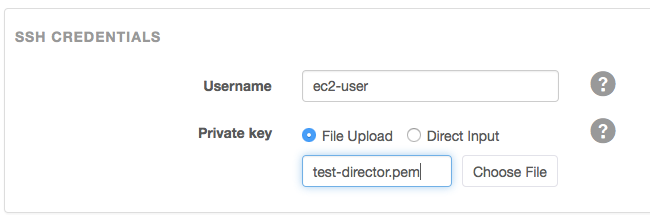
- In the SSH Credentials section:
- For a RHEL AMI, enter ec2-user in the Username field.
- Copy the SSH private key you created in Launching an EC2 Instance for Cloudera Director in the Private key field.
- Click Continue to add Cloudera Manager.
- In the Add Cloudera Manager screen:
- Enter a name for this deployment of Cloudera Manager in the Cloudera Manager name field.
- In the Instance Template field, click Select a Template if you already have one that you want to use, otherwise,
click Create New Instance Template.
The Create New Instance Template modal screen displays.
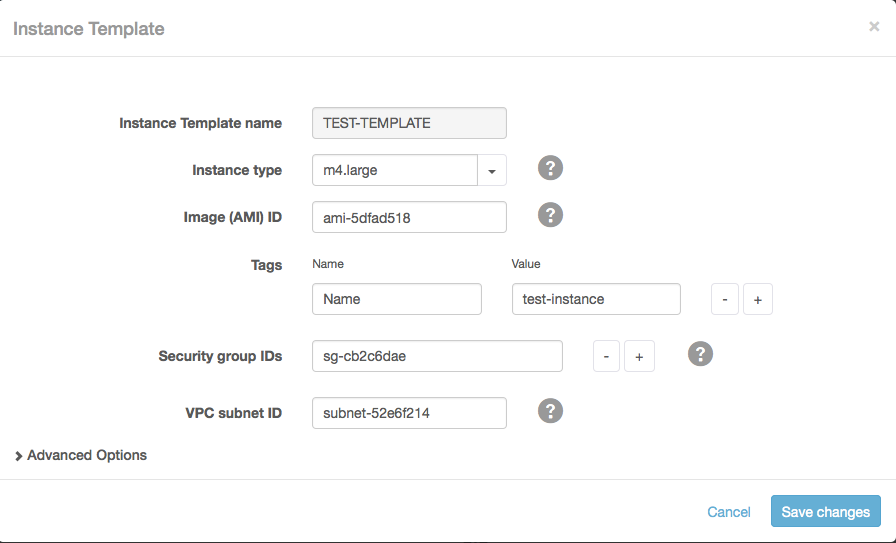
- In the Create New Instance Template modal screen:
- In the Instance Template name field, enter a name for the template.
- In the Instance type field, select m4.large or m4.xlarge.
- In the Image (AMI) ID field, enter the ID for the Amazon machine image (AMI) you chose in Launching an EC2 Instance for Cloudera Director, or find another AMI with a supported operating system.
- In the Tags field, add one or more tags to associate with the instance.
- In the Security group IDs field, enter the security group ID you set up in Creating a New Security Group.
- In the VPC subnet ID field, enter the ID of the VPC subnet that was created during VPC setup.
- Click Advanced Options if you want to specify additional values for optional features, such as EBS, IAM, Spot instances, and AWS user data.
- Click Save changes.
- In the Desired License Type field, select one of the following license types:
- Cloudera Enterprise: includes the core CDH services (HDFS, Hive, Hue, MapReduce, Oozie, Sqoop 1, YARN, and ZooKeeper) and, depending on the license edition, one or more additional services (Accumulo, HBase, Impala, Navigator, Solr, Spark). For more information on Cloudera Enterprise licenses, see Managing Licenses in the Cloudera Manager documentation.
- Cloudera Enterprise Trial: a 60-day trial license that includes all CDH services.
- Cloudera Express: no license required.
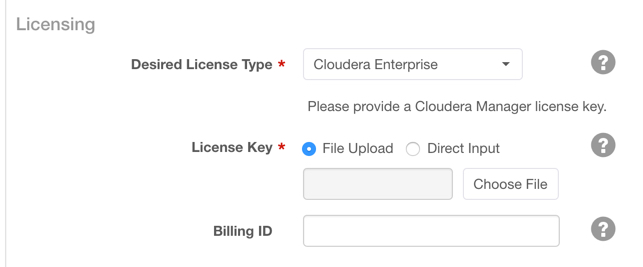
To enable usage-based billing, you must have a Cloudera Enterprise license and a billing ID provided by Cloudera. Perform these steps in the Add Cloudera Manager screen:- In the Desired License Type field, select Cloudera Enterprise.
- In the License Key field, either select a Cloudera Enterprise license file to upload or select Direct Input and input the license file text directly into the text area.
- To enable usage-based billing, enter the billing ID provided to you by Cloudera in the Billing ID field.
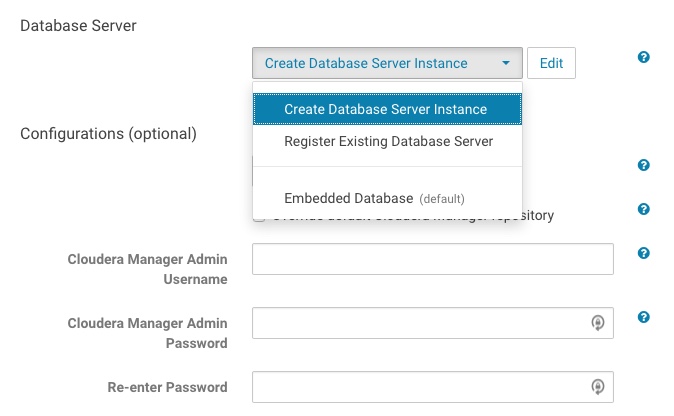
- In the Database Server section, the default selection is Embedded Database. This installs an embedded PostgreSQL database
for Cloudera Manager. The embedded PostgreSQL database should be used only when creating a demonstration or proof-of-concept deployment. It is not recommended for production. If
desired, select Create Database Server Instance or Register Existing Database Server from the dropdown list, instead of Embedded Database:
For information about using an external database for Cloudera Director server, see the following pages: - In the Add Cloudera Manager screen, click Cloudera Manager Configurations.
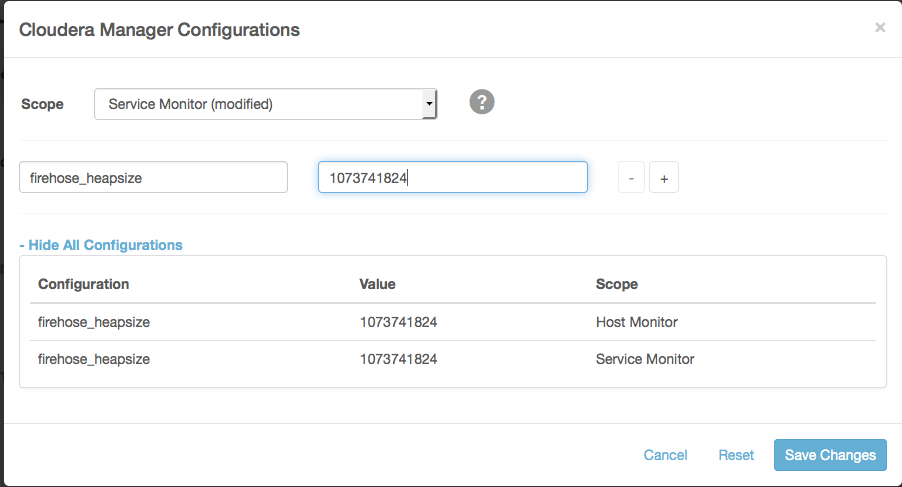
- In the Cloudera Manager Configurations modal screen, set the heap size:
- In the Scope field, select Host Monitor and add firehose_heapsize and 1073741824 in the respective Name and Value fields.
- Click +.
- In the Scope field, select Service Monitor and add firehose_heapsize and 1073741824 in the respective Name and Value fields.
- Click Save Changes.
- By default, the version of Cloudera Manager installed depends on the version of Cloudera Director you are using:
To install a version of Cloudera Manager higher or lower than the default version, perform the following steps:
Cloudera Director version Cloudera Manager version installed Cloudera Director 2.0 Latest released version of Cloudera Manager 5.5 Cloudera Director 2.1 Latest released version of Cloudera Manager 5.7 Cloudera Director 2.2 Latest released version of Cloudera Manager 5.8 Cloudera Director 2.3 Latest released version of Cloudera Manager 5.10 Cloudera Director 2.4 Latest released version of Cloudera Manager 5.11 Cloudera Director 2.5 Latest released version of Cloudera Manager 5.12 Cloudera Director 2.6 Latest released version of Cloudera Manager 5.13 - In the Configurations section, check Override default Cloudera Manager repository.
- In the Repository URL field, enter the repository URL for the version of Cloudera Manager to install. Repository URLs for versions of Cloudera Manager 5 have the form https://archive.cloudera.com/cm5/ followed by the operating system, operating system major version, processor architecture, cm (for Cloudera Manager), and the Cloudera Manager major, minor, and (if applicable) maintenance release number. For example, the repository URL for Cloudera Manager 5.5.4 on any supported version of RHEL 7 is https://archive.cloudera.com/cm5/redhat/7/x86_64/cm/5.5.4/.
- In the Repository Key URL field, enter the URL for the repository key. Repository key URLs have the same form as repository URLs except they end with the name of the key file instead of the Cloudera Manager version. For example, the repository key URL for any version of Cloudera Manager 5 on any supported version of RHEL 7 is https://archive.cloudera.com/cm5/redhat/7/x86_64/cm/RPM-GPG-KEY-cloudera.
- In the Add Cloudera Manager screen, click Continue.
- At the Confirmation prompt, click OK to begin adding a cluster.
- On the Add Cluster screen:
- Enter a name for the cluster in the Cluster name field.
- Enter the version of CDH to deploy in the Version field or leave the default value. By default, the version of CDH installed depends on the version of
Cloudera Director you are using:
To install a version of CDH higher or lower than the default version, perform the following steps:
Cloudera Director version CDH version installed Cloudera Director 2.0 Latest released version of CDH 5.5 Cloudera Director 2.1 Latest released version of CDH 5.7 Cloudera Director 2.2 Latest released version of CDH 5.9 Cloudera Director 2.3 Latest released version of CDH 5.10 Cloudera Director 2.4 Latest released version of CDH 5.11 Cloudera Director 2.5 Latest released version of CDH 5.12 Cloudera Director 2.6 Latest released version of CDH 5.13 - Enter the desired CDH version in the Version field of the Products section. For example, for CDH 5.4.8 enter 5.4.8.
- Scroll down to Configurations (optional) and expand the section.
- Click Override default parcel repositories.
- Enter the repository parcel URL for the version of CDH you want to install. Parcel URLs for versions of CDH 5 have the form https://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/parcels/, followed by the major, minor, and (if applicable) maintenance release number. For example, the URL for CDH 5.4.8 is https://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/parcels/5.4.8.
- In the Services section, select the services you want to install.
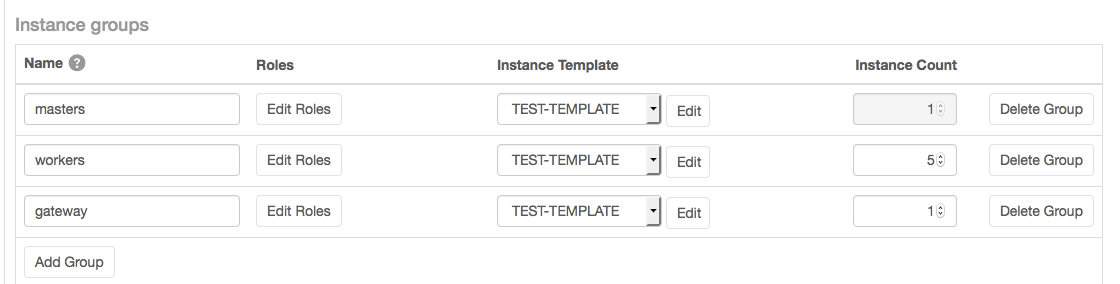
- In the Instance groups area, choose an existing instance template or create a new one, either for the all instance groups in the cluster, or for each
group. For each instance group, indicate the number of instances you want.
If you want to use Spot instances for your workers group:
- In the Create New Instance Template modal screen, click Advanced Options.
- In the Spot bid (USD/hr) field, enter your Spot bid price.
- Click the Use Spot instances checkbox.
- Click Save Changes.
For more information about using Spot instances with Cloudera Director, see Using Spot Instances.
- Click Continue.
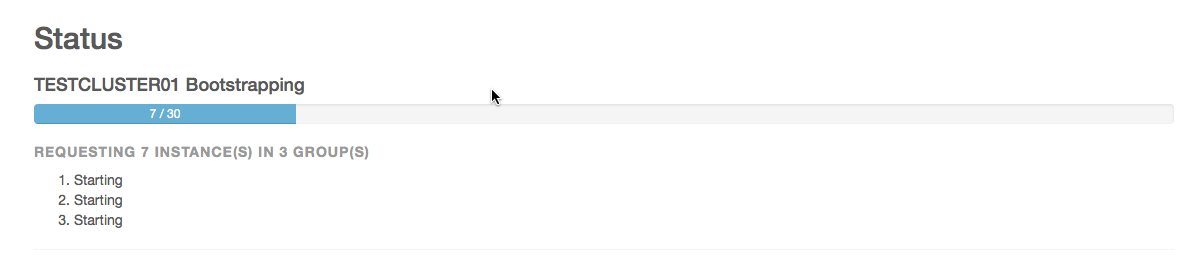
- At the Confirmation prompt, click OK to deploy the cluster. Cloudera Director displays a status screen.
- When the cluster is ready, click Continue.
You are finished with the deployment tasks.