Installing Cloudbreak CLI
The Cloudbreak Command Line Interface (CLI) is a tool to help you manage your Cloudbreak cluster instances. This tool can be used to interact with Cloudbreak for automating cluster creation, management, monitoring, and termination.
The CLI is available for Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows.
Install the CLI
After you have launched Cloudbreak, the CLI is available for download from that Cloudbreak instance.
Steps
- Browse to your Cloudbreak instance and log in to the Cloudbreak web UI.
- Select Download CLI from the navigation pane.
- Select your operating system. The CLI is available for Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows:
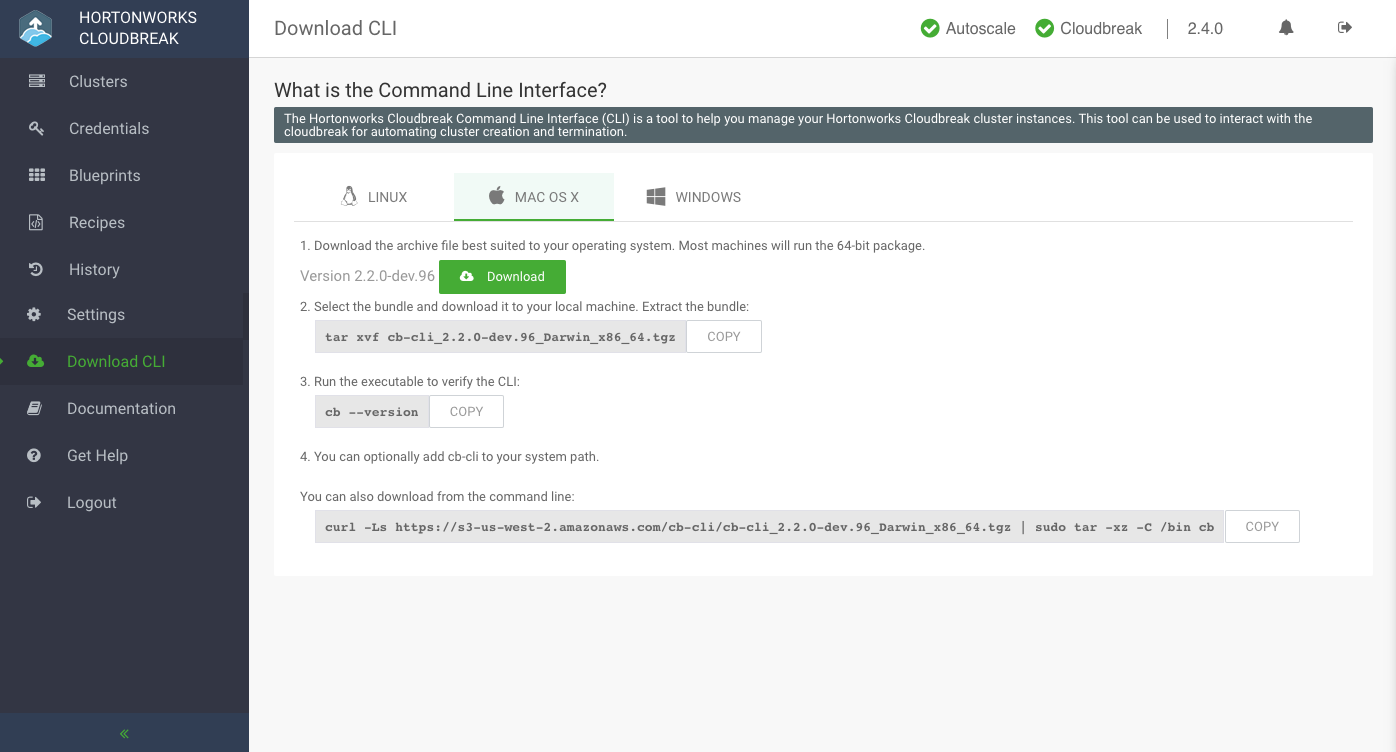
- Download the selected bundle to your local machine.
- Extract the bundle.
- You can optionally add
cbto your system path. -
Run the executable to verify the CLI:
cb --version
Configure the CLI
Once you have installed the CLI, you need to configure the CLI to work with Cloudbreak.
Steps
-
Use the
cb configurecommand to set up the CLI configuration file. The configuration options are:- --server server address [$CB_SERVER_ADDRESS]
- --username user name (e-mail address) [$CB_USER_NAME]
- --password password [$CB_PASSWORD]
The password configuration is optional. If you do not provide the password, no password is stored in the CLI configuration file. Therefore, you will need to provide the password with each command you execute or via an environment variable.
For example:
cb configure --server https://ec2-11-111-111-11.compute-1.amazonaws.com --username admin@hortonworks.com
-
The CLI configuration file will be saved at
~/.cb/config. The content will look similar to the following:default: username: admin@hortonworks.com server: https://ec2-11-111-111-11.compute-1.amazonaws.com
-
Run any command to verify that you can connect to the Cloudbreak instance via CLI. For example:
cb list-clusters
Configuration Precedence
The CLI can look for configuration options from different locations. You can optionally pass the configuration options on each command or from environment variables. The following order is used for the CLI to look for configuration options: Command Line, Environment Variables and the Configuration File.
Add Multiple Configurations
If you are using multiple profiles for multiple environments, you can configure them using the cb configure command and passing the name of your environment-specific profile file using the --profile parameter. After running the command, the configuration will be added as a new entry to the config file. For example, running the following command cb configure --server https://192.167.65.4 --username test@hortonworks.com --profile staging will add the "staging" entry:
default: username: admin@hortonworks.com server: https://192.167.65.4 staging: username: test@hortonworks.com server: https://192.167.65.4
For example:
#cb configure --server https://192.167.65.4 --username test@hortonworks.com --profile staging INFO: [writeConfigToFile] dir already exists: /Users/rkovacs/.cb INFO: [writeConfigToFile] writing credentials to file: /Users/rkovacs/.cb/config # cat /Users/rkovacs/.cb/config default: username: admin@example.com server: https://192.167.65.4 output: table staging: username: test@hortonworks.com server: https://192.167.65.4
Configure Default Output
By default, JSON format is used in command output. For example, if you run cb list-clusters without specifying output type, the output will be JSON. If you would like to change default output, add it to the config file. For example:
default: username: admin@hortonworks.com server: https://192.167.65.4 output: table