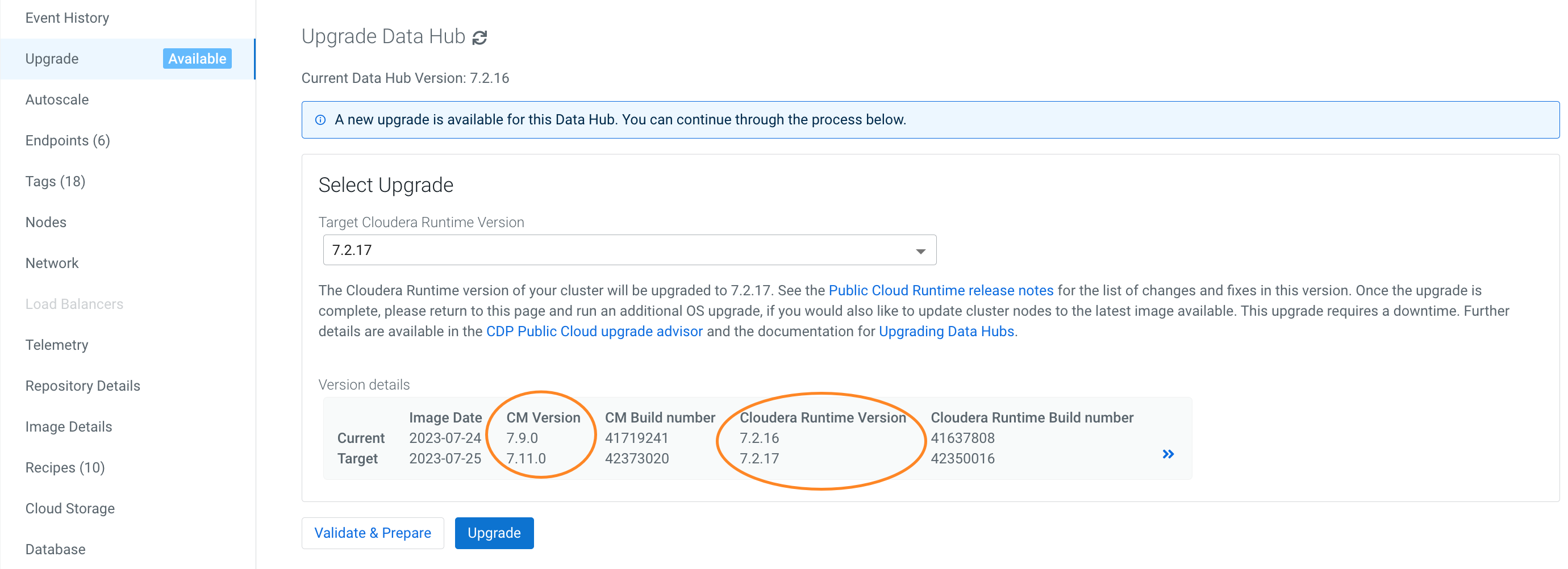
Performing a Cloudera Data Hub major/minor version cluster upgrade
A major/minor version upgrade initiates an upgrade of the major/minor Cloudera Manager and Cloudera Runtime versions, as well as the required additional parcels (Spark3, Flink, Profiler, and Cloudera Flow Management). After you perform a major/minor upgrade on a Data Lake, you should in most cases perform a major/minor version upgrade on each Cloudera Data Hub cluster attached to the Data Lake. The Cloudera Data Hub clusters must run the same major/minor Cloudera Runtime version as the Data Lake--with the exception of Cloudera Data Hub clusters on Cloudera Runtime 7.2.16+, which are compatible with Data Lake versions 7.2.17+.
Complete the steps for each Cloudera Data Hub cluster that you are upgrading.
Required role: DatahubAdmin or Owner over the Cloudera Data Hub cluster
Post-upgrade tasks
After a successful major/minor version upgrade, complete the following tasks if they apply to the cluster you upgraded.
Flow Management clusters
If doing a software-only upgrade for your Flow Management Cloudera Data Hub clusters and later repairing one of the NiFi nodes after the upgrade, you may be in a situation where the JDK used by NiFi is not the same across the nodes. This may cause issues in the NiFi UI and you may get an "Unexpected error" message.
After you upgrade a Flow Management cluster and repair a node, ensure that the same JDK is used across the NiFi nodes and if there is a JDK version mismatch, manually upgrade the JDK to match the JDK version being installed on the node that has been repaired.
Data Engineering upgrades to 7.2.11
Upgrading a cluster with the Spark service from Cloudera Runtime version
7.2.6 or 7.2.7 to version 7.2.11 may cause Spark cluster mode to fail. To workaround this
issue, add the following configuration to the
/etc/spark/conf/atlas-application.properties file:
atlas.kafka.sasl.kerberos.service.name=kafka
Data Engineering HA/Hue HA
If you upgrade a template (such as Data Engineering HA) that contains Hue in an HA configuration, add the Hue load balancer hostnames to Cloudera Manager configurations: Cloudera Manager > Hue > Configuration > knox_proxyhosts. If you do not, you will experience errors preventing users from logging in.
Streams Messaging clusters
Clusters that contain the Streams Replication Manager service require a configuration change following a successful upgrade from Cloudera Runtime 7.2.11 or lower to 7.2.12 or higher. You must configure SRM to use its latest internal changelog data format and intra cluster hostname format. If this configuration is not completed, the SRM Service will not be able to target multiple clusters.
This post upgrade step is required because during an upgrade, SRM is configured to use a legacy version of its changelog data format and intra cluster hostname format. This is done to ensure backward compatibility so that if necessary, a rollback is possible.
Complete the following steps:
- Verify that the SRM Service is up and running. This can be done by testing the REST API endpoints using the Swagger UI. If there are any issues, and a rollback is necessary, complete the rollback. No backward incompatible changes occurred up until this point.
- In Cloudera Manager, select the Streams Replication Manager service.
- Go to Configuration.
- Find and disable the following properties:
- Use Legacy Internal Changelog Data Format
- Use Legacy Intra Cluster Host Name Format
- Restart Streams Replication Manager.
Reset Kafka Connect secret password
After a Data Hub upgarde, you need to manually reset the Kafka Connect password and salt values to the values used before the upgrade was started. This step is required because these values are changed during the upgrade process but unless they are again set to the same values as before, Kafka Connect will go into bad health.
- Restart Kafka Connect after the Data Hub has been recreated.
- Set the following password and salt values to the ones that you have saved before
starting the Data Hub upgrade process:
- kafka.connect.secret.global.password
- kafka.connect.secret.pbe.salt
- Restart Kafka Connect again.
Configure Schema Registry to use V2 of its fingerprinting mechanism after upgrade to 7.2.18:
Following an upgrade to Cloudera Runtime 7.2.18 or later, Cloudera recommends that you configure Schema Registry to use fingerprinting V2. Fingerprinting V2 resolves an issue in V1 where schemas were not created under certain circumstances. For more information on the original issues as well as Schema Registry fingerprinting, see TSB-713. Note that even if you switch to V2, some issues might still persist, see TSB-718 for more information.
- Access the Cloudera Manager instance managing your Cloudera Data Hub cluster.
- Select the Schema Registry service and go to Configuration.
- Set the Fingerprint Version property to VERSION_2.
- Select Actions>Regenerate Fingerprints.
- Click Regenerate Fingerprints to start the action.
- Restart Schema Registry.
Adding configs manually
The major/minor Runtime upgrade does not install additional configs available in the newer versions of the Data Engineering cluster templates. This topic contains a list of configs added over different template versions. Use the Cloudera Manager UI to add them manually, if the config doesn’t already exist.
- Clusters -> HDFS ->
Configuration:
hdfs_verify_ec_with_topology_enabled=false erasure_coding_default_policy=” “ - Clusters -> HDFS -> Configuration -> Cluster-wide Advanced Configuration Snippet
(Safety Valve) for
core-site.xml:
fs.s3a.buffer.dir=${env.LOCAL_DIRS:-${hadoop.tmp.dir}}/s3a HADOOP_OPTS="-Dorg.wildfly.openssl.path=/usr/lib64 ${HADOOP_OPTS}" - Clusters -> Yarn ->
Configuration:
yarn_admin_acl=yarn,hive,hdfs,mapred - Clusters -> Yarn ->
Configuration -> YARN Service MapReduce Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety
Valve):
mapreduce.fileoutputcommitter.algorithm.version=1 mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.list-status.num-threads=100 - Clusters -> Tez ->
Configuration:
tez.grouping.split-waves=1.4 tez.grouping.min-size=268435456 tez.grouping.max-size=268435456 - Clusters -> Tez ->
Configuration -> Tez Client Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for
tez-conf/tez-site.xml:
tez.runtime.pipelined.sorter.lazy-allocate.memory=true - Clusters -> Hive ->
Configuration -> Hive Service Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for
hive-site.xml:
fs.s3a.ssl.channel.mode=openssl hive.txn.acid.dir.cache.duration=0 hive.server2.tez.session.lifetime=30m hive.blobstore.supported.schemes=s3,s3a,s3n,abfs,gs hive.orc.splits.include.fileid=false hive.hook.proto.events.clean.freq=1h hive.metastore.try.direct.sql.ddl=true hive.privilege.synchronizer=false - Clusters -> Hive ->
Configuration:
hiveserver2_idle_session_timeout=14400000 - spark_on_yarn ->
Configuration -> Spark Client Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for
spark-conf/spark-defaults.conf:
spark.hadoop.mapreduce.fileoutputcommitter.algorithm.version=1 spark.hadoop.fs.s3a.ssl.channel.mode=openssl - Clusters -> Hive
Metastore -> Configuration -> Hive Metastore Server Advanced Configuration Snippet
(Safety Valve) for
hive-site.xml
hive.metastore.try.direct.sql.ddl=true - Clusters -> <your
cluster name> -> Configuration -> Suppressed Health and Configuration
Issues:
role_config_suppression_namenode_java_heapsize_minimum_validator=true