Configuring Cloudera Data Science Workbench Engines
This topic describes how to configure and manage engines in Cloudera Data Science Workbench. Cloudera Data Science Workbench currently supports R, Python, and Scala engines. You can use these engines to run data science projects either in isolation, as you would on your laptop, or connect to your CDH cluster using Cloudera Distribution of Apache Spark 2 and other libraries.
Concepts and Terminology
Review basic concepts and terminology related to engines at Cloudera Data Science Workbench Engines.
Managing Engines
Required Role: Site Administrator
Site administrators and project administrators are responsible for making sure that all projects on the deployment have access to the engines they need. Site admins can create engine profiles, determine the default engine version to be used across the deployment, and white-list any custom engines that teams require. As a site administrator, you can also customize engine environments by setting global environmental variables and configuring any files/folders that need to be mounted into project environments on run time.
Managing Engine Profiles
Engine profiles define how many vCPUs and how much memory Cloudera Data Science Workbench will reserve for a particular session/job. As a site administrator you can create several different vCPU, GPU, and memory configurations which will be available when launching a session/job. When launching a new session, users will be able to select one of the available engine profiles depending on their project's requirements.
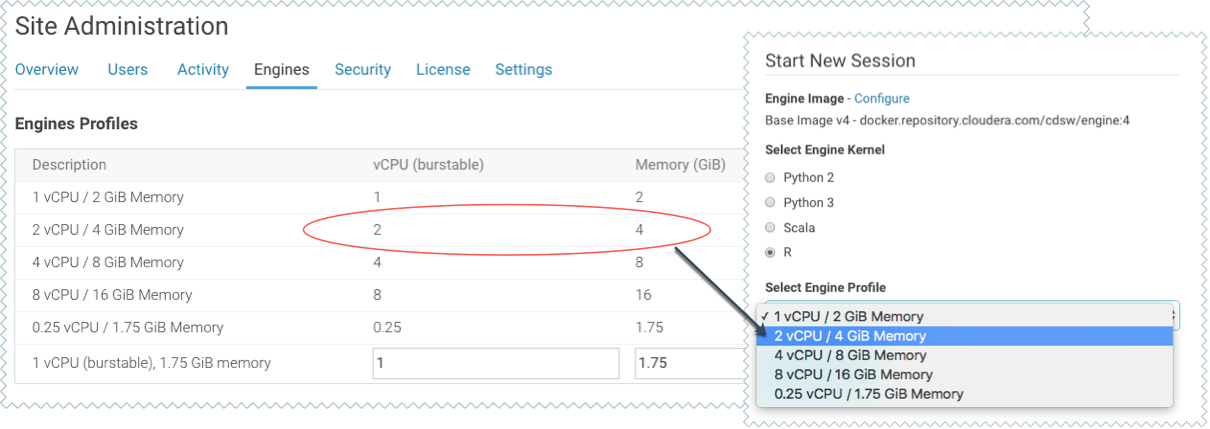
To create engine profiles, go to the page, under Engines Profiles. Cloudera recommends that all profiles include at least 2 GB of RAM to avoid out of memory errors for common user operations.
You will see the option to add GPUs to the engine profiles only if your Cloudera Data Science Workbench nodes are equipped with GPUs, and you have enabled them for use by setting the relevant properties either in Cloudera Manager (for CSD) or in cdsw.conf (for RPM).
Managing Engine Images
By default, Cloudera Data Science Workbench ships a base engine image that includes kernels for Python, R, and Scala, along with some additional libraries that can be used to run common data analytics operations. Occasionally, new engine versions are released and shipped with Cloudera Data Science Workbench releases.
Engine images are available in the Site Administrator panel at , under the Engine Images section. As a site administrator, you can select which engine version is used by default for new projects. Furthermore, project administrators can explicitly select which engine image should be used as the default image for a project. To do so, go to the project's Overview page and click Settings on the left navigation bar.
If a user publishes a new custom Docker image, site administrators are responsible for white-listing such images for use across the deployment. For more information on creating and managing custom Docker images, see Customized Engine Images.
Configuring the Engine Environment
This section describes some of the ways you can configure engine environments to meet the requirements of your projects.
Environmental Variables
For information on how environmental variables can be used to configure engine environments in Cloudera Data Science Workbench, see Engine Environment Variables.
CDH Parcel Directory
By default, Cloudera Data Science Workbench looks for the CDH parcel at /opt/cloudera/parcels. If your CDH parcel is at another location, go to and add that path to the Parcel directory section.
Configuring Host Mounts
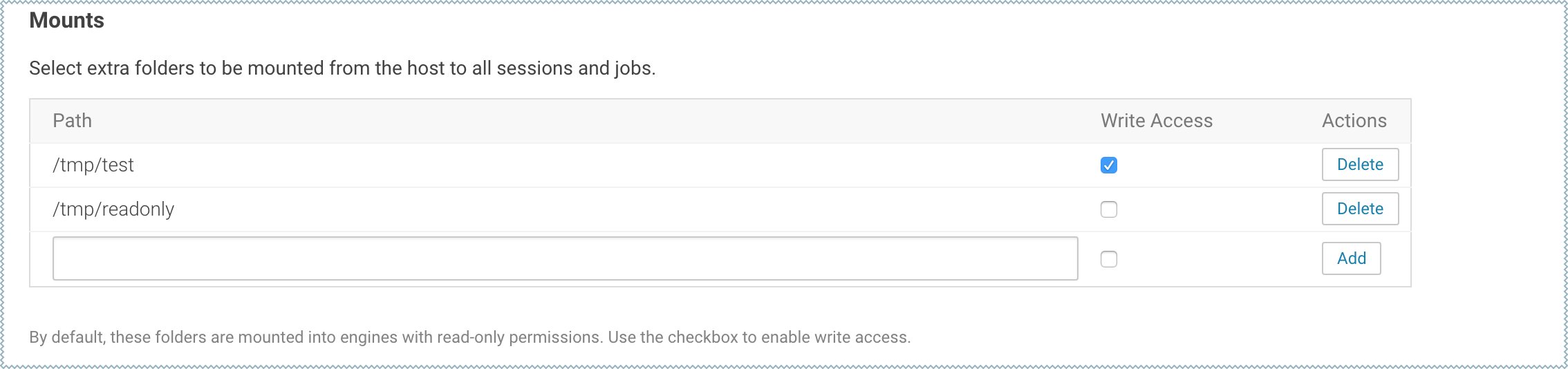
By default, Cloudera Data Science Workbench will automatically mount the CDH parcel directory and client configuration for required services such as HDFS, Spark, and YARN into each project's engine. However, if users want to reference any additional files/folders on the host, site administrators will need to configure them here so that they are loaded into engine containers at runtime. Note that the directories specified here will be available to all projects across the deployment.
To configure additional mounts, go to and add the paths to be mounted from the host to the Mounts section.
| CDSW Version | Mount Point Permissions in Engines |
|---|---|
| 1.4.2 (and higher) |
By default, mount points are loaded into engine containers with read-only permissions. CDSW 1.4.2 (and higher) also include a Write Access checkbox (see image) that you can use to enable read-write access for individual mounted directories. Note that these permissions will apply to all projects across the deployment. |
| 1.4.0 |
Mount points are loaded into engine containers with read-only permissions. |
| 1.3.x (and lower) |
Mount points are loaded into engine containers with read-write permissions. |
-
When adding host mounts, try to be as generic as possible without mounting common system files. For example, if you want to add several files under /etc/spark2-conf, you can simplify and mount the /etc/spark2-conf directory; but adding the parent /etc might prevent the engine from running.
As a general rule, do not mount full system directories that are already in use; such as /var, /tmp, or /etc. This also serves to avoid accidentally exposing confidential information in running sessions.
-
Do not add duplicate mount points. This will lead to sessions crashing in the workbench.
Setting Time Zones for Sessions and Jobs
The default time zone for Cloudera Data Science Workbench sessions is UTC. This is the default regardless of the time zone setting on the Master node.
To change to your preferred time zone, for example, Pacific Standard Time (PST), navigate to . Under the Environmental Variables section, add a new variable with the name set to TZ and value set to America/Los_Angeles, and click Add.